Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Yamada, Yoshihide*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.536 - 546, 2023/05
The distribution coefficient ( ) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The
) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The  values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the
values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the  values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The
values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The  values were determined in the range 8
values were determined in the range 8  pH
pH  12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the
12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the  values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the
values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the  values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
Sugiura, Yuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Doi, Reisuke; Francisco, P. C. M.; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Matsumura, Daiju; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 324(2), p.615 - 622, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Chemistry, Analytical)Iijima, Kazuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*
Radiochimica Acta, 98(9-11), p.729 - 736, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.46(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Distribution behavior of Cs and Am in the synthetic groundwater-bentonite colloids-granite ternary system was investigated. Radionuclide sorbed onto the bentonite colloids is desorbed by addition of granite, indicating that the sorption of Cs and Am onto the bentonite colloids are reversible. The sorption model based on cation exchange and surface complexation reaction considering high edge site density for bentonite colloids is applicable to explain the sorption behavior of Am and Cs in the ternary system.
Iijima, Kazuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Shoji, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Clay Science, 49(3), p.262 - 268, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:71.76(Chemistry, Physical)Sorption and desorption behavior of Cs onto montmorillonite colloids was investigated. The ion exchange and surface complexation model can successfully reproduce the sorption and desorption behavior of Cs. Conditioning montmorillonite in higher Cs concentration than 0.005M causes decrease of interlayer distance which may lead to fixation of Cs in the interlayer. Sorption reversibility of Cs on montmorillonite colloids can be expected in this study due to lower Cs concentration than 0.0001M.
Kitamura, Akira; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Sato, Haruo; Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Research 2008-004, 39 Pages, 2008/03
Distribution coefficient of cesium onto bentonite and sedimentary rocks was determined in saline groundwaters. Distribution coefficient of cesium onto the solid phases was also determined in sodium chloride and potassium chloride solutions in order to elucidate sorption behavior of cesium. It was expected that the sorption behavior of cesium was regarded as ion exchange reactions with sorption sites of the solid phases from the results of dependencies of distribution coefficient on pH and ionic strength. It was found that only potassium ion was competed with cesium for the sorption onto sedimentary rocks, while both sodium and potassium ions was competed with cesium for the sorption onto bentonite. It was also found that sorption behavior of cesium onto sedimentary rocks was well described using a model on the sorption of cesium onto illite. The present study was performed in Tokai Works, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (one of the predecessors of JAEA) in FY 2002-2003.
Iijima, Kazuki; Shoji, Yoshiyuki*; Tomura, Tsutomu*
Radiochimica Acta, 96(9-11), p.721 - 730, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:52.81(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Distribution coefficients of Am onto bentonite colloid were evaluated under weak basic and low ionic strength conditions, in taking the influence of Am colloid into account. The obtained values are larger than those obtained for larger montmorillonite particles in literatures. It is attributed to one order of magnitude higher reactive site density of the bentonite colloid. Applicability of a relatively simple and generalized mechanistic sorption model to the bentonite colloid is also discussed.
Iijima, Kazuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Tsuguya*
Proceedings of 2nd International Meeting on Clays in Natural and Engineered barriers for Radioactive Waste Confinement (TOURS 2005) (CD-ROM), p.607 - 608, 2005/00
The batch sorption and desorption experiments of Cs onto bentonite colloid were carried. The sorption data was fitted to Freundlich isotherm and distribution coefficient was obtained as about 20 m /kg, which is larger than that of powdered bentonite. It might be caused by the difference of the shape of bentonite. In the desorption experiment, almost same distribution coefficient was obtained so that, at least, 30% of Cs was sorbed reversibly.
/kg, which is larger than that of powdered bentonite. It might be caused by the difference of the shape of bentonite. In the desorption experiment, almost same distribution coefficient was obtained so that, at least, 30% of Cs was sorbed reversibly.
Iijima, Kazuki; Masuda, Tsugaya; Tomura, Tsutomu*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (23), p.51 - 61, 2004/06
Sorption and desorption experiments of Cs onto bentonite collid were carried out in order to obtain its distribution coefficient (Kd) and information on the reversibility of its sorption. In addition, sorption behavior was discussed based on its sorption behavior, particle size distribution and shape of colloid.
Kitamura, Akira; Nakata, Kotaro*; Tanaka, Satoru*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Kamei, Gento
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (22), p.59 - 66, 2004/03
Redox reactions between neptunium(V) (Np(V)) and magnetite (Fe(II)1Fe(III)2O4) surface were investigated in N gas atmosphere. A batch method was applied to the experiment. High-pure magnetite and a 0.1 M NaCl were mixed in a polypropylene tube, and pH, redox potential and concentration of dissolved neptunium were measured as a function of shaking time (from 1 hour to 7 days), temperature (298 K and 318 K) and liquid/solid ratio (20, 50 and 100 ml.g
gas atmosphere. A batch method was applied to the experiment. High-pure magnetite and a 0.1 M NaCl were mixed in a polypropylene tube, and pH, redox potential and concentration of dissolved neptunium were measured as a function of shaking time (from 1 hour to 7 days), temperature (298 K and 318 K) and liquid/solid ratio (20, 50 and 100 ml.g ). It was observed that the concentration of dissolved neptunium was reduced rapidly within a day, due to the reducing of Np(V) to Np(IV) and the precipitation of Np(IV). This result was shown typically when the magnetite/solution ratio and the temperature were high. The rate constant of the redox reaction and the activation energy for the rate constant were preliminarily obtained. It was suggested that the redox reaction was promoted by not only Fe(II) on magnetite surface but also Fe(II) inside the magnetite.
). It was observed that the concentration of dissolved neptunium was reduced rapidly within a day, due to the reducing of Np(V) to Np(IV) and the precipitation of Np(IV). This result was shown typically when the magnetite/solution ratio and the temperature were high. The rate constant of the redox reaction and the activation energy for the rate constant were preliminarily obtained. It was suggested that the redox reaction was promoted by not only Fe(II) on magnetite surface but also Fe(II) inside the magnetite.
Kitamura, Akira; Tomura, Tsutomu*
JNC TN8400 2003-025, 67 Pages, 2003/03
The obtained distribution coefficient under reducing conditions was much larger than that under non-reducing conditions at low carbonate concentration. The distribution coefficient decreased with increasing the total carbonate concentration. The experimentally obtained distribution coefficient was analyzed by a least-squares fitting with free parameters of distribution coefficient of neptunium hydrolysis and carbonate complexes. Based on the analytical result, consideration of sorption behavior of neptunium, especially neptunium(IV) hydrolysis species and carbonatohydroxo complexes, was carried out, and a possibility of specific interaction of the neptunium(IV) species with the solid surface was pointed out.
Kitamura, Akira; Tomura, Tsutomu*;
JNC TN8400 2001-015, 30 Pages, 2001/09
Sorption behavior of neptunium onto smectite was investigated upder reducing conditions in carbonate media. Distribution coefficient (K ) of neptunium on smectite was determined by a batch method as a function of total carbonate concentration (C
) of neptunium on smectite was determined by a batch method as a function of total carbonate concentration (C ) in a weak alkaline solution. The C
) in a weak alkaline solution. The C value ranged from 0.09 M (M
value ranged from 0.09 M (M mol
mol dm
dm ) to 1.0 M. The obtained K
) to 1.0 M. The obtained K value decreased with increase the total carbonate concentration. It was found that both Np(IV) and Np(V) coexisted in the solution by a TTA-extraction method. In the present experimental conditions, contribution of neptunyl ion, NpO
value decreased with increase the total carbonate concentration. It was found that both Np(IV) and Np(V) coexisted in the solution by a TTA-extraction method. In the present experimental conditions, contribution of neptunyl ion, NpO
 , carbonate complexes of Np(V), NpO
, carbonate complexes of Np(V), NpO (CO
(CO )
)
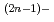 (n=1, 2 and 3), and a carbonatohydroxo complex of Np(IV), Np(CO
(n=1, 2 and 3), and a carbonatohydroxo complex of Np(IV), Np(CO )
) (OH)
(OH)
 , to the sorption onto smectite was expected. The K
, to the sorption onto smectite was expected. The K values of respective species of neptunium were estimated by a least-squares fit to the experimental data. From the obtained K
values of respective species of neptunium were estimated by a least-squares fit to the experimental data. From the obtained K values of respective species, sorption behavior of neptunium onto smectite was discussed.
values of respective species, sorption behavior of neptunium onto smectite was discussed.
Iijima, Kazuki; Shoji, Yoshiyuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*
no journal, ,
Sorption behavior of Am onto bentonite colloid was investigated. The obtained distribution coefficients were larger than those evaluated by the calculation in which ion exchange and surface complexation reactions were assumed. It seems to be due to the higher site density of bentonite colloid for surface complexation compared with bulk bentonite.
Iijima, Kazuki; Shoji, Yoshiyuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*
no journal, ,
Sorption site density of bentonite was investigated by acid titration. As a result, bentonite colloid is considered to have higher sorption site density than that of larger bentonite particle. Thus the high sorption site density, which has been supposed to lead to the large distribution coefficient of Am onto the bentonite colloid in the previous presentation, is experimentally proved.
Iijima, Kazuki; Shoji, Yoshiyuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*
no journal, ,
Sorption behavior of Am onto bentonite colloid was investigated. Distribution coefficient of Am was evaluated taking account for the existence of Am colloid. Obtained values were larger than those obtained with larger bentonite particles included in the JNC-SDB. In the acid-base titration, bentonite colloid shows larger edge site density than larger bentonite particles. In the calculation by sorption model assuming ion exchange and surface complexation, similar distribution coefficient was obtained at pH 8 with this edge site density. Based on these results, it is considered that larger distribution coefficient of bentonite colloid is due to the higher edge site density, which is dominant for the Am sorption.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*; Tits, J.*; Curti, E.*
no journal, ,
Ra-226 is a safety-relevant radionuclide in performance assessments of high-level waste repositories and has thus been deserved special attention. The aim of the proposed study is to provide new key data on the interaction of Ra with calcite and witherite. In this study, the interaction of Ca with calcite and Ba with witherite was measured by using Ca-45 and Ba-133.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*; Tits, J.*; Curti, E.*
no journal, ,
The aim of the proposed study is to provide new key data on the interaction of Ra with calcite, witherite and barite in the presence of selected clay materials Kunigel V1 bentonite representing the backfill, respectively host-rock, of the high-level waste repositories planned in Japan.
Nakata, Kotaro*; Iijima, Kazuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*
no journal, ,
In this study, a new experimental system has been developed to obtain the information on distribution of raidonuclide between aqueous, colloid and rock phases. Sorption, desorption and distribution experiments of Cs on smectite colloid and granite were carried out with new developed system. After confirmation of applicability of the developed system, Kd values were obtained in 3 phases coexist system. The results of desorption experiment indicated sorption of Cs on smectite colloid is reversible.
Iijima, Kazuki; Nakata, Kotaro*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*
no journal, ,
Batch type distribution experiments of Cs and Am in the solution-bentonite colloid-granite ternary system were carried out. Considering Na concentration, distribution coefficient of Cs on bentonite colloids obtained in the ternary system is similar to the calculated value using ion selectivity coefficient evaluated in the binary system. It indicates that the method to estimate the distribution behavior in the binary system is applicable to the ternary system in this case.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Tobita, Minoru*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*; Tits, J.*; Curti, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yasuo; Takahashi, Hiroaki; Tachi, Yukio; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Nemoto, Kazuaki*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*
no journal, ,
Am(III) diffusion experiment were performed by reservoir depletion (RD) test method coupled with thin layer ID profile fitting in 0.1 or 0.5M NaCl / 0.05M NaHCO - bentonite (kunipia-F) system. The Kd values were also measured using batch technique in the same experimental conditions. In an ordinary ID profile acquisition cutting the bentonite by scraper, the compacted bentonite sample can be cut into 100
- bentonite (kunipia-F) system. The Kd values were also measured using batch technique in the same experimental conditions. In an ordinary ID profile acquisition cutting the bentonite by scraper, the compacted bentonite sample can be cut into 100  m thick slices. Using this technique, it was possible to divide the ID profile into 10
m thick slices. Using this technique, it was possible to divide the ID profile into 10  m and therefore, to analyze diffusion distance layer larger than 50
m and therefore, to analyze diffusion distance layer larger than 50  m.
m.