Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -xGeO
-xGeO with
with  = 0.09 and 0.15
= 0.09 and 0.15Kakimoto, Kazuo*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Katori, Hiroko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054707_1 - 054707_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe GeO
GeO with andalusite structure
with andalusite structureKakimoto, Kazuo*; Takada, Saki*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054704_1 - 054704_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sb
Sb O
O F
F observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffraction
observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffractionShimono, Seiya*; Ishibashi, Hiroki*; Nagayoshi, Yusuke*; Ikeno, Hidekazu*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Ichihashi, Katsuya*; Nishihara, Sadafumi*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 163, p.110568_1 - 110568_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.94(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
 Sr
Sr NiO
NiO studied by neutron diffraction
studied by neutron diffractionKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Fujita, Masaki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Torii, Shuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Miao, P.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 88(11), p.114602_1 - 114602_6, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:95.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 620(2-3), p.159 - 165, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:79 Percentile:97.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)The J-PARC 1-MW pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS was successfully launched on 30th of May 2008. To demonstrate the unique features of the moderator design and the neutronic performance of JSNS the neutron spectral intensity, absolute neutron flux, and time structure of the neutron pulse shapes etc have been measured using several neutron instruments since then. The measured energy spectra clearly revealed the feature of the para-hydrogen, as expected when designing the moderator. The measured neutron flux below 0.4 eV agreed with the corresponding design value within  20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
Maekawa, Fujio; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Noboru*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/07
Efforts have been made to characterize neutronic performance of JSNS. A NOBORU instrument was mainly used for this purpose while some other instruments were used when needed. The followings were confirmed. (1) Judging from a measured spectral shape, a para-hydrogen fraction in the hydrogen moderator was very close to unity as expected due to introduction of catalyst in a hydrogen circulation system. (2) Measured data for absolute spectral intensity and pulse shapes agreed very well with simulation calculations, and suggested adequacy of the neutron source designs. (3) The world's highest resolution of 0.035 % was recorded at the powder diffractometer SuperHRPD. (4) A total neutron flux of 3  10
10 n/s/cm
n/s/cm was confirmed at the chopper instrument 4SEASONS when it was normalized to 1 MW. The flux is the world's highest among existing spallation neutron sources, and is comparable to fluxes at intense reactor sources even in time-averaged value.
was confirmed at the chopper instrument 4SEASONS when it was normalized to 1 MW. The flux is the world's highest among existing spallation neutron sources, and is comparable to fluxes at intense reactor sources even in time-averaged value.
Harjo, S.; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Torii, Shuki; Ishigaki, Toru; Yonemura, Masao*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(Part 2), p.1025 - 1028, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.85(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ibaraki Prefecture Materials Design Diffractometer of J-PARC is a time-of-flight neutron powder diffractometer with the resolution as good as 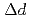 /
/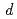 = 0.16 % (almost constant value) for
= 0.16 % (almost constant value) for 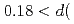
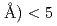 (L1 of 26.5 m). Since this diffractometer has many detectors covering wide 2
(L1 of 26.5 m). Since this diffractometer has many detectors covering wide 2 range, measurements with wide
range, measurements with wide 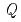 range,
range, 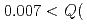
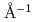
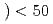 , i.e., PDF analysis and small angle scattering can also be performed. Designing of neutron guide is therefore very important to enhance the performances mentioned above without sacrificing beam intensity. Non-parallel guides including elliptical ones have been compared with a linear-straight guide using the McStas simulation. The elliptical guide having the exit focal points away behind the sample position is available to increase the neutron flux at the sample but give a slight lowering of the instrumental resolution. This elliptical guide gives also Garland peaks at short wavelengths that may give large ambiguities in powder diffraction measurements. Therefore, the linear-straight guide is considered as the best choice for this instrument to keep a good resolution and also a relatively high flux.
, i.e., PDF analysis and small angle scattering can also be performed. Designing of neutron guide is therefore very important to enhance the performances mentioned above without sacrificing beam intensity. Non-parallel guides including elliptical ones have been compared with a linear-straight guide using the McStas simulation. The elliptical guide having the exit focal points away behind the sample position is available to increase the neutron flux at the sample but give a slight lowering of the instrumental resolution. This elliptical guide gives also Garland peaks at short wavelengths that may give large ambiguities in powder diffraction measurements. Therefore, the linear-straight guide is considered as the best choice for this instrument to keep a good resolution and also a relatively high flux.
Nakajima, Kenji; Nakatani, Takeshi; Torii, Shuki; Higemoto, Wataru; Otomo, Toshiya*
JAEA-Technology 2005-005, 44 Pages, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Torii, Shuki; Moriai, Atsushi
JAEA-Technology 2005-004, 31 Pages, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Harjo, S.; Moriai, Atsushi; Torii, Shuki; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Suzuya, Kentaro; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; Tomota, Yo*; Akita, Koichi*; Akiniwa, Yoshiaki*
Materials Science Forum, 524-525, p.199 - 204, 2006/00
An engineering diffractometer designed to solve many problems in materials science and engineering including investigations of stresses and crystallographic structures within engineering components is now being developed at J-PARC project. This instrument views a decoupled-poisoned liquid H moderator, and the primary and the secondary flight paths are 40 m and 2.0 m, respectively, for 90 degree scattering detector banks. The optimization of this instrument has been performed with a Monte Carlo simulation, and an appropriate resolution of less than 0.2 % in
moderator, and the primary and the secondary flight paths are 40 m and 2.0 m, respectively, for 90 degree scattering detector banks. The optimization of this instrument has been performed with a Monte Carlo simulation, and an appropriate resolution of less than 0.2 % in  d/d has been confirmed. A prototyped radial collimator to define a gauge width of 1 mm has been designed and manufactured. From performance tests conducted at the neutron diffractometer for residual stress analysis RESA, the normal distribution with a full width at half maximum of 1.0 mm was obtained in a good agreement with the simulation.
d/d has been confirmed. A prototyped radial collimator to define a gauge width of 1 mm has been designed and manufactured. From performance tests conducted at the neutron diffractometer for residual stress analysis RESA, the normal distribution with a full width at half maximum of 1.0 mm was obtained in a good agreement with the simulation.
 (OH)
(OH) X (X = Cl, Br)
X (X = Cl, Br)Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Harjo, S.; Arai, Masatoshi; Ohara, Takashi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed the software framework in MLF computing environment from 2006 to 2008. The software framework is the fundamental software for neutron and muon experimental instruments in J-PARC/MLF. Currently, the software framework is installed at 4D Space Access Neutron Spectrometer (BL01), IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer (BL03), Cold-Neutron Disk-Chopper Spectrometer (BL14), Engineering Materials Diffractometer (BL19) and High Intensity Total Diffractometer (BL21). The features of experimental control, analysis, visualization and authorization are already implemented in the software framework. In this year, we will start the development to introduce the feature of database. We will present the current status and future plan of the software framework.
Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Kambara, Wataru; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Torii, Shuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Suzuki, Junichi; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Kambara, Wataru; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Torii, Shuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Kaneko, Koji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
no journal, ,
Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC started the user program in December 2008. Various neutron experiments are currently performed there in wide range of scientific researches and industrial applications. Standardization of sample environment (SE) equipments is one of the most important things at the beginning stage. Especially in our country, it often happens that each instrument carries and operates SE devices independently. This situation results in an excess of the cost and incompatibility among the instruments unless we have any guidelines. Thus the SE team has discussed the SE-protocol, in which flange size, thermometers, controllers etc. are standardized. This should bring about saving the cost and manpower and increasing compatibility. The SE team is now discussing user support system in SE, preparation of the SE area, and so on. The technical staff members started working on practical things such as cooling test of cryostats.
 -BaTiO3
-BaTiO3 system studied by neutron and X-ray powder diffraction
system studied by neutron and X-ray powder diffractionKiyanagi, Ryoji; Yamazaki, Tadashi*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Oyama, Kenji*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Zhang, J.*; Kamiyama, Takashi
no journal, ,
 Sr
Sr NiO
NiO studied by high-resolution neutron diffraction
studied by high-resolution neutron diffractionKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Fujita, Masaki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Torii, Shuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Miao, P.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 (OH)
(OH) X (X = Cl, Br)
X (X = Cl, Br)Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English