Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Honda, Akira; Toshiyasu, Suguro,; Sasaki, Ryoichi
JNC TN8400 2004-029, 43 Pages, 2005/03
Radioactive Iodine in the spent nuclear fuel is trapped by Iodine-adsorber in the off-gas process of reprocessing plant. The radioactive iodine includes very long half-lived nuclide (I-129;Half life=1.57x10 y).The I-129 cannot be expected to decay due to containment by the barrier system because of its long half life. The Iodine have soluble and poorly sorbing nature in the geological disposal condition, because the element can take the chemical form of I
y).The I-129 cannot be expected to decay due to containment by the barrier system because of its long half life. The Iodine have soluble and poorly sorbing nature in the geological disposal condition, because the element can take the chemical form of I in the reducing condition such as the condition of deep underground. Therefore Iodine can migrate in barrier system easily and strongly contribute to the peak of dose in the performance assessment of TRU waste disposal. An effective measure for reducing the dose peak is the controlled release of Iodine from the waste package in the low flux. The solidification by the copper matrix was proposed as one of the previous controlled release technology by JNC. The release rate of I-129 from the waste package solidified by the copper matrix was estimated. The corrosion rate of copper matrix was estimated as the sum of those both in the oxdizing and reducing conditions. The rates and periods of I-129 release were estimated under the assumption of congruent release of I-129 with corrosion of the copper matrix. The total release rate and period in the FRHP groundwater case were 3.11X10
in the reducing condition such as the condition of deep underground. Therefore Iodine can migrate in barrier system easily and strongly contribute to the peak of dose in the performance assessment of TRU waste disposal. An effective measure for reducing the dose peak is the controlled release of Iodine from the waste package in the low flux. The solidification by the copper matrix was proposed as one of the previous controlled release technology by JNC. The release rate of I-129 from the waste package solidified by the copper matrix was estimated. The corrosion rate of copper matrix was estimated as the sum of those both in the oxdizing and reducing conditions. The rates and periods of I-129 release were estimated under the assumption of congruent release of I-129 with corrosion of the copper matrix. The total release rate and period in the FRHP groundwater case were 3.11X10 Bq y
Bq y and 1.64x10
and 1.64x10 y(Initiated at 10
y(Initiated at 10 y and finalized at 1.64x10
y and finalized at 1.64x10 y) respectively. The total release rate and period in the SRHP groundwater case were 9.03x10
y) respectively. The total release rate and period in the SRHP groundwater case were 9.03x10 Bq y
Bq y and 5.66x10
and 5.66x10 y(Initiated at 10
y(Initiated at 10 y and finalized at 5.76x10
y and finalized at 5.76x10 y).
y).
Toshiyasu, Suguro,; Notoya, Shin; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Nakamura, Ryosuke*; Shibutani, Tomoki; Kuroha, Mitsuhiko; Kamei, Gento
JNC TN8430 2004-004, 27 Pages, 2005/01
In terms of safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on plutonium sorption on cementitious materials have been obtained by means of a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate, the authors carried out the experiments using ordinary portland cement (OPC) under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g
. Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g , Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84
, Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84 10
10 M, Temperature; 25
M, Temperature; 25 5
5 C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (
C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (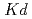 ) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g
) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g in case of L/S=100mL g
in case of L/S=100mL g . Similarly the
. Similarly the 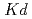 ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g
ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g at L/S=1000mL g
at L/S=1000mL g . These
. These 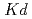 values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g
values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g as a conservative
as a conservative 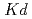 value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.
value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.