Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
 Al
Al O
O
Toyama, Takenori*; Saito, Takashi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Agui, Akane; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 49(5), p.2492 - 2495, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:74.69(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 solution for identification of fluoride species of Db
solution for identification of fluoride species of DbToyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Murakami, Masashi*; Sato, Daisuke*; Motoyama, Risa*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Komori, Yukiko*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
The purpose of the present study is characterization of fluoride complexes of Db. In this study, we investigated anion-exchange behavior of Nb and Ta, lighter homologs of Db, in 1.0-24 M HF/2.0 M HNO solutions as a model experiment of Db.
solutions as a model experiment of Db. 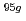 Nb and
Nb and 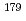 Ta produced at JAEA tandem accelerator and RIKEN AVF cyclotron, respectively, were prepared as non-carrier-added radiotracers by an ion exchange method. Batch experiments were performed with anion-exchange resin. As a result, distribution coefficients (
Ta produced at JAEA tandem accelerator and RIKEN AVF cyclotron, respectively, were prepared as non-carrier-added radiotracers by an ion exchange method. Batch experiments were performed with anion-exchange resin. As a result, distribution coefficients (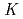
 ) of Nb showed a sharp increase at
) of Nb showed a sharp increase at  6 M HF while those of Ta had a monotonic decrease as increasing HF concentration. This suggests that Nb forms fluoride complexes from oxy fluoride one at
6 M HF while those of Ta had a monotonic decrease as increasing HF concentration. This suggests that Nb forms fluoride complexes from oxy fluoride one at  6 M HF and Ta exists as fluoride complexes under the conditions. It is expected that chemical species of Db fluorides are characterized in its anion-exchange experiments under the present conditions.
6 M HF and Ta exists as fluoride complexes under the conditions. It is expected that chemical species of Db fluorides are characterized in its anion-exchange experiments under the present conditions.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Biotite is known as a host phase that retains uranium (U) in uranium deposits at Ningyo-Toge and Tono, and it is expected that the distribution of U in biotite will provide insight into the concentration and long-term immobilization of U. However, biotite contains rubidium (Rb), which interferes with X-ray fluorescence analysis, making it difficult to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite by measurement using a conventional solid state detector (SSD). In this study, we developed a method to use a transition edge sensor (TES) as a detector in microbeam X-ray fluorescence analysis, which enables us to detect X-ray fluorescence with an energy resolution of about 20 eV and to obtain a Rb K line at 13.373 keV and a U L
line at 13.373 keV and a U L line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
When muons are injected into a deuterium thin film target, muon molecules are formed. The muons released after intramolecular fusion (recycling muons) are important for the development of slow muon beams. In this study, corresponding to an experiment in which recycling muons are transported using a coaxial transport tube, the energy distribution of scattered muons, muons after deceleration, and background radiation due to bremsstrahlung by decay electrons and neutrons are analyzed by numerical simulations.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The reduction of uranium on biotite was studied to obtain insight into the immobilization of uranium in the environment. The chemical species of uranium in biotite were studied using a superconducting transition edge sensor and an X-ray emission spectrometer to remove interference from rubidium in biotite. As a result, the speciation of uranium in biotite collected from former uranium deposits was possible. The XANES spectra of the biotite indicated that the uranium in the biotite was partially reduced.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are attempting to observe regenerative muons emitted from the surface of a solid hydrogen thin film by muon-catalyzed fusion by irradiating the film with muons that have the same charge as electrons and 207 times the mass of electrons. The main background factors in detecting regenerative muons are scattered muons from the accelerator, which are slowed down to the same level as regenerative muons by the target, and bremsstrahlung generated by the components of the device. The results show that there is little scattering within the solid hydrogen, and that the dominant slowing down process is at the Al foil upstream of the solid hydrogen target. The energy distribution of Bremsstrahlung at the X-ray detection position will be reported.
Ikemoto, Megumi*; Somekawa, Jun*; Neki, Arata*; Konishi, Ren*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have been studying on muon beam quality improvement by moderating 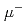 generated by an accelerator with a thin Si film, and then decelerating and focusing the beam in an electrostatic field. In this study, numerical simulation of an experiment in which
generated by an accelerator with a thin Si film, and then decelerating and focusing the beam in an electrostatic field. In this study, numerical simulation of an experiment in which 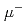 of a few MeV is injected into a 0.5~mm thick Si plate and
of a few MeV is injected into a 0.5~mm thick Si plate and 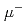 , which is decelerated to a few keV, is extracted electrostatically is performed using charged particle orbit software (SIMION). The flight time to the end of the transport tube and the transport efficiency change with a slight shift of the muon launch position, suggesting that the muon transport process is sensitive to the initial conditions.
, which is decelerated to a few keV, is extracted electrostatically is performed using charged particle orbit software (SIMION). The flight time to the end of the transport tube and the transport efficiency change with a slight shift of the muon launch position, suggesting that the muon transport process is sensitive to the initial conditions.