Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 As
As and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS analyses
and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS analysesLi, S.*; Toyoda, Masayuki*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Ito, Masayuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Otani, Akira*; Matsumura, Daiju; Asano, Shun*; Mizuki, Junichiro*; et al.
Physica C, 555, p.45 - 53, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.97(Physics, Applied) -dependence of local distortions in BaFe
-dependence of local distortions in BaFe As
As and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS methods. Although PDF data exhibit anomaly at the structure transition temperature, EXAFS data exhibit no anomaly. Data supporting the local orthorhombicity at 300 K in the tetragonal phase for BaFe
and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS methods. Although PDF data exhibit anomaly at the structure transition temperature, EXAFS data exhibit no anomaly. Data supporting the local orthorhombicity at 300 K in the tetragonal phase for BaFe As
As . Arguments on the origins of the 4-fold symmetry breaking in the ground average structure of the tetragonal phase.
. Arguments on the origins of the 4-fold symmetry breaking in the ground average structure of the tetragonal phase.
Ebana, Minoru; Noda, Kimio; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Soma, Susumu; Mikami, Satoshi; Toyoda, Motoko; Oyanagi, Katsumi*
PNC TN8410 98-075, 36 Pages, 1998/07
None
Ebana, Minoru; Ozeki, Kiyoshi; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Mikami, Satoshi; Toyoda, Motoko; Hirosawa, Masaya*; Oyanagi, Katsumi*
PNC TN8410 97-292, 17 Pages, 1997/09
None
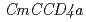 ) in flower color mutation of "Jimba"
) in flower color mutation of "Jimba"Omiya, Akemi*; Toyoda, Tomomi*; Watanabe, Hideki*; Enomoto, Keishi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshioka, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 O
O ferrite determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction methods
ferrite determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction methodsTakayasu, Shunichi*; Yoshizaki, Jumpei*; Okube, Maki*; Toyoda, Takeshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Sasaki, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Site preferences of Ti and Mn and the magnetic structure of M-type BaTiMnFe O
O ferrite were analyzed using the X rays and neutron powder diffraction method. The intensity difference on the magnetic scattering was clearly observed below and above the
ferrite were analyzed using the X rays and neutron powder diffraction method. The intensity difference on the magnetic scattering was clearly observed below and above the  c, showing the ferrimagnetic spin arrangement along with the
c, showing the ferrimagnetic spin arrangement along with the  axis. Site-occupancy refinements give the results that Ti ions occupy the 4
axis. Site-occupancy refinements give the results that Ti ions occupy the 4 1 (24%), 2
1 (24%), 2 (15%) and 2
(15%) and 2 (15%) sites, while Mn ions prefer to 4
(15%) sites, while Mn ions prefer to 4 2 (24%) and 12
2 (24%) and 12 (24%). Magnetic moments were obtained from the Rietveld refinements, which are 3.56, 3.37, -3.86, -3.72 and 3.68
(24%). Magnetic moments were obtained from the Rietveld refinements, which are 3.56, 3.37, -3.86, -3.72 and 3.68 
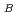 at
at  = 8 K for 2
= 8 K for 2 , 2
, 2 , 4
, 4 1, 4
1, 4 2 and 12
2 and 12 sites, respectively.
sites, respectively.
 O
O by neutron and X-ray diffraction
by neutron and X-ray diffractionTakayasu, Shunichi*; Yoshizaki, Jumpei*; Okube, Maki*; Toyoda, Takeshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Sasaki, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Hexagonal barium ferrites have been traditionally used as permanent magnets and microwave devices because of their high coercivity and large uniaxial anisotropy. It is recognized that the magnetic anisotropy can be optimized by Fe ion for several magnetic and non-magnetic ions, which makes M-type ferrites suitable for microwave absorber in 1 - 75 GHz range. In this study to use neutron and X-ray powder diffraction, site preference and magnetic structure of iron sites on BaTiCoFe
ion for several magnetic and non-magnetic ions, which makes M-type ferrites suitable for microwave absorber in 1 - 75 GHz range. In this study to use neutron and X-ray powder diffraction, site preference and magnetic structure of iron sites on BaTiCoFe O
O are examined.
are examined.