Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Kenji*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi
Zairyo, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
Suzuki, Kenji*; Kura, Komoe*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 71(12), p.1005 - 1012, 2022/12
This paper describes a stress measurement from a welded part of an austenitic stainless steel using synchrotron X-rays. Difficulty measuring the X-ray stress of the welded part is caused by the broadening of the diffraction spot in the radial and circumferential directions. The bending strains of the rectangular bar made of the welded part were measured using synchrotron white X-rays and the double exposure method. To improve the energy resolution, monochromatic synchrotron X-ray of 70 keV was used. The diffraction pattern showed the sharp arc like a pattern from texture material. The diffraction profile was obtained from the integral of the diffraction intensity in the direction of the circumference. The diffraction angle was determined using the double exposure method. As a result, the distribution of the residual stresses of the welded part could be measured.
Suzuki, Kenji*; Yamada, Minami*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*
Zairyo, 71(4), p.347 - 353, 2022/04
We have already succeeded in the residual stress of aluminum alloys using the double exposure method (DEM) with 30 keV synchrotron radiation X-rays. However, the DEM has not be applied in the range of high-energy synchrotron X-rays. In this study, the stress measurements of a shrink-fitted ring using the DEM with synchrotron monochromatic X-rays beyond about 70 keV were performed. A CdTe pixel detector and a CCD camera were used as a detector. The shrink-fitted specimen of SUS304 was quasi-coarse grains of 43 micro-meters, and the diffraction rings were spotty. Despite quasi-coarse grains, it was possible to measure the stresses of the shrink-fitted specimen using the DEM. As a result, the DEM is excellent method to measures the stress for coarse grained materials. In addition, it is better to make the length between the detection positions longer to improve precision of the DEM. On the other hand, it was ineffective to increase the positions of detection.
Suzuki, Kenji*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(3), p.25_1 - 25_14, 2020/09
It is difficult to evaluate stress by the strain scanning method using a conventional diffractometer and a point detector since the two-dimensional diffraction pattern of a material composed of coarse grains does not have a ring but a spotty. To solve this problem, we proposed a double exposure method using a two-dimensional detector and monochromatized X-rays. In this study, we have developed a technique to apply that technique to white X-rays. The diffraction obtained by irradiating white X-rays for a material with of coarse grains becomes a Laue spot. Therefore, we have carried out developing a CdTe pixel two-dimensional detector that can limit the energy to be detected, and we evaluated the stress using that detector. As a result, we succeeded to measure the strain distribution of a bending specimen made to austenitic stainless steel. In the future, we would like to improve this technology and apply it to actual machine materials.
Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Kawase, Morihiro*; Wu, S.*; Hurukawa, Yukihito*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Sato, Masugu*; Hirono, Toko*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(1), p.C01044_1 - C01044_7, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:23.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been developing CdTe pixel detectors combined with a Schottky diode sensor and photon-counting ASICs. The hybrid pixel detector was designed with a pixel size of 200 micro-meter by 200 micro-meter and an area of 19 mm by 20 mm or 38.2 mm by 40.2 mm. The photon-counting ASIC, SP8-04F10K, has a preamplifier, a shaper, 3-level window-type discriminators and a 24-bits counter in each pixel. The single-chip detector with 100 by 95 pixels successfully operated with a photon-counting mode selecting X-ray energy with the window comparator and stable operation was realized at 20 C. We have performed a feasibility study for a white X-ray microbeam experiment. Laue diffraction patterns were measured during the scan of the irradiated position in a silicon steel sample. The grain boundaries were identified by using the differentials between adjacent images at each position.
C. We have performed a feasibility study for a white X-ray microbeam experiment. Laue diffraction patterns were measured during the scan of the irradiated position in a silicon steel sample. The grain boundaries were identified by using the differentials between adjacent images at each position.
Toyokawa, Takuya; Usami, Koji; Shiina, Hidenori; Onozawa, Atsushi
Proceedings of 49th Conference on Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2012) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2012/09
Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi; Toyokawa, Hidenori*
Hozengaku, 11(2), p.99 - 106, 2012/07
An area detector technique has to be applied to the strain scanning method for materials with coarse grains. A new rotating slit system was designed for a 2-dimensional (2D) detector strain scanning method. The rotating slit system can focus the 2D detector on the center of the goniometer, and the gauge volume is made by the rotating slit system. The stress measurements were examined with the rotating slit and 2D detector. The measured diffraction spots shifted for the 2D strain scanning. The magnitude of the shift of the diffraction spot was very large as compared with the shift due to the strain. This phenomenon was caused by interaction between the gauge volume and the coarse grain. That is a coarse grain effect. To overcome the coarse grain effect, we propose a diffraction spot trace method (DSTM), which is constructed by the rotating slit and the PILATUS detector. The bending stress distribution of the coarse grain aluminum alloy was measured by DSTM. The measured stress was consistent with the applied stress.
Inami, Toshiya; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Terada, Noriki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 150, p.042069_1 - 042069_4, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:60.48(Thermodynamics) Pb(
Pb( He,
He,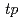 ) reaction at 410 MeV
) reaction at 410 MeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Abend, H.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Van den Berg, A. M.*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Gal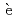 s, S.*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
s, S.*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 731, p.121 - 128, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.29(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 (
(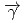 ,
,
 )
) and
and  (
(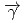 ,
,
 )
)
 reactions for
reactions for 
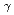 =1.5-2.4 GeV
=1.5-2.4 GeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Sumihama, Mizuki*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Dat , S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 = +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutron
= +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutronNakano, Takashi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Date, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(1), p.012002_1 - 012002_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:1023 Percentile:99.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Pb(
Pb( He,
He,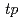 ) reaction at 410 MeV
) reaction at 410 MeVZegers, R. G. T.; Abend, H.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Van den Berg, A. M.*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Gal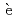 s, S.*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
s, S.*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 90(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_4, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 O(
O(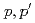 ) reaction at forward angles and structure of the spin-dipole resonances
) reaction at forward angles and structure of the spin-dipole resonancesKawabata, Takahiro*; Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; Ito, M.*; Nakamura, M.*; Sakaguchi, Harutaka*; Takeda, H.*; Taki, T.*; Uchida, Makoto*; Yasuda, Yusuke*; Yosoi, Masaru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 65(6), p.064316_1 - 064316_12, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:69.49(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 clusters in
clusters in  Li and
Li and  Li
LiNakayama, Shintaro*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Daito, Izuru*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Fushimi, Kenichi*; Greenfield, M. B.*; Kori, Hideki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 87(12), p.122502_1 - 122502_4, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:71.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ni via the (
Ni via the (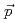 ,
, 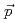 ') reaction at 0
') reaction at 0
Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Daito, Izuru*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Hatanaka, Kichiji*; Hosono, K.*; Ihara, F.*; Ito, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 187(1-2), p.58c - 63c, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
 analog state in
analog state in 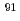 Nb populated by the
Nb populated by the  Zr(
Zr( , t) reaction
, t) reactionVan der Molen, H. K. T.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Van den Berg, A. M.*; Daito, Izuru*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Harakeh, M. N.*; Ihara, F.*; Inomata, Toru*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 502(1-4), p.1 - 8, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 O (p,p') experiment
O (p,p') experimentKawabata, Takahiro*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Hara, Keigo*; Hatanaka, Kichiji*; Hosono, K.*; Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 459(1-2), p.171 - 176, 2001/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:75.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 He
HeNakayama, Shintaro*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Daito, Izuru*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Fushimi, Kenichi*; Inomata, Toru*; Kori, Hideki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 85(2), p.262 - 265, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:88.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Krasznahorkay, A.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Van Aarle, P.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi; Daito, Izuru*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Harakeh, M. N.*; Inomata, Toru*; J necke, J.*; et al.
necke, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 82(16), p.3216 - 3219, 1999/04
Times Cited Count:194 Percentile:96.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shobu, Takahisa; Kim, S.*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English