Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ban, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Hideya*; Hotoku, Shinobu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
A continuous counter-current extraction experiment was performed by mixer-settler extractors to recover minor actinides (MA; Am and Cm) from high-level liquid waste. Using hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) as an extractant, 0.17 g of MA was recovered in a MA fraction.
Yamagishi, Isao; Hato, Shinji*; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sagawa, Yusuke*
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-002, 63 Pages, 2024/07
Adsorption columns filled with zeolite are used to treat contaminated water containing radioactive cesium generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. As the contaminated water treatment progresses, the radioactive cesium in the adsorption column becomes highly concentrated, and the adsorption column becomes a high radiation source. To evaluate the radiation effects such as decay heat and radiolytic hydrogen production in the adsorption column, the concentration of radioactive cesium in the adsorption column is necessary, but since it is difficult to evaluate the concentration by measurement, it is estimated by simulation. In this research, a zeolite column adsorption dynamics simulation (Zeolite Adsorption Column: ZAC) code was developed to calculate the concentration of radioactive materials such as radioactive cesium in a zeolite filled adsorption column when they are injected into the column. The code was validated through comparison of calculation results with existing codes and experimental results of small column tests. This report presents the details of the model, the handling of the code, and the validity of the results for the developed code.
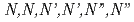 -hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) using mixer-settler extractors in a hot cell
-hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) using mixer-settler extractors in a hot cellBan, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Hideya*; Hotoku, Shinobu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 31(1), p.1 - 11, 2024/00
A demonstration test was performed to separate minor actinides (MA; Am and Cm) by 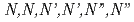 -hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) as an extractant using mixer-settler extractors installed in a hot cell. A high-level liquid waste containing MA, and rare earths (RE; Y, La, Nd, and Eu) was used as the feed. HONTA diluted to 0.05 mol/dm
-hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) as an extractant using mixer-settler extractors installed in a hot cell. A high-level liquid waste containing MA, and rare earths (RE; Y, La, Nd, and Eu) was used as the feed. HONTA diluted to 0.05 mol/dm in
in  -dodecane was fed as the organic phase, and a part of the organic phase was reused without solvent regeneration. HONTA effectively extracted MA, whereas RE were less extractable. Consequently, the Y, La, Nd, and Eu ratios distributed to a RE fraction were
-dodecane was fed as the organic phase, and a part of the organic phase was reused without solvent regeneration. HONTA effectively extracted MA, whereas RE were less extractable. Consequently, the Y, La, Nd, and Eu ratios distributed to a RE fraction were  99.9%, 99.2%, 61.8%, and 81.4%, respectively. The Am and Cm ratios distributed to an MA fraction were 86.8% and 74.7%, respectively, and a substantial amount of MA (0.12 g) was recovered in the MA fraction by the end of the cumulative duration of 40 h.
99.9%, 99.2%, 61.8%, and 81.4%, respectively. The Am and Cm ratios distributed to an MA fraction were 86.8% and 74.7%, respectively, and a substantial amount of MA (0.12 g) was recovered in the MA fraction by the end of the cumulative duration of 40 h.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sato, Takumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(3), p.97 - 107, 2023/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has chosen nitride fuel as the first candidate for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven systems (ADS). The pyrochemical method has been considered for reprocessing spent MA nitride fuels, because their decay heat should be very large for aqueous reprocessing. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of decay heat on the pyrochemical reprocessing of MA nitride fuels. On the basis of the estimated decay heats and the temperature limits of the materials that are to be handled in pyrochemical reprocessing, quantities adequate for handling in argon gas atmosphere were evaluated. From these considerations, we proposed that an electrorefiner with a diameter of 26 cm comprising 12 cadmium (Cd) cathodes with a diameter of 4 cm is suitable. On the basis of the size of the electrorefiner, the number necessary to reprocess spent MA fuels from 1 ADS in 200 days was evaluated to be 25. Furthermore, the amount of Cd-actinides (An) alloy to produce An nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined reaction process was proposed to be about one-quarter that of Cd-An cathode material. The evaluated sizes and required numbers of equipment support the feasibility of pyrochemical reprocessing for MA nitride fuels.
Sugawara, Takanori; Moriguchi, Daisuke*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Takano, Masahide; Nishihara, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2021-008, 63 Pages, 2021/10
This study aims to perform the neutronics calculations for accelerator-driven system (ADS) with a new fuel composition based on the SELECT process developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency because the previous studies had used the ideal MA (minor actinide) fuel composition without uranium and rare earth elements. Through the neutronics calculations, it is shown that two calculation cases, with/without neptunium, satisfy the design criteria. Although the new fuel composition includes uranium and rare earth elements, the ADS core with the new fuel composition is feasible and consistent with the partitioning and transmutation (P&T) cycle. Based on the new fuel composition, the heat removal during fuel powder storage and fuel assembly assembling is evaluated. For the fuel powder storage, it is found that a cylindrical tube container with a length of 500 [mm] and a diameter of 11 - 21 [mm] should be stored under water. For the fuel assembly assembling, CFD analysis indicates that the cladding tube temperature would satisfy the criterion if the inlet velocity of air is larger than 0.5 [m/s]. Through these studies, the new fuel composition which is consistent with the P&T cycle is obtained and the heat removal with the latest conditions is investigated. It is also shown that the new fuel composition can be practically handled with respect to heat generation, which is one of the most difficult points in handling MA fuel.
Sakamoto, Atsushi; Kibe, Satoshi*; Kawanobe, Kazunori*; Fujisaku, Kazuhiko*; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Suzuki, Hideya*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Tatsuro
JAEA-Research 2021-003, 30 Pages, 2021/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing a solvent extraction process called SELECT to recover minor actinides (MA) from spent nuclear fuel. In the SELECT process, TDdDGA, HONTA, and ADAAM are used as the extractants for MA + Ln corecovery, MA/Ln separation and Am/Cm separation, respectively. These extractants do not contain phosphorus (P), and consist of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N). In this study, in order to give beneficial information for designing flowsheet, the mass transfer coefficients of Ln between HNO solution and TDdDGA or HONTA / n-dodecane solvent were evaluated by the single drop technique. Prior to the evaluation of mass transfer coefficient, we had optimized the structure of the single drop apparatus to improve accuracy of the measurement. Based on the mass transfer coefficients obtained in HNO
solution and TDdDGA or HONTA / n-dodecane solvent were evaluated by the single drop technique. Prior to the evaluation of mass transfer coefficient, we had optimized the structure of the single drop apparatus to improve accuracy of the measurement. Based on the mass transfer coefficients obtained in HNO / TDdDGA-n-dodecane system, Ln behaviors in the counter-current extraction and back-extraction using mixer-settlers and centrifugal contactors were estimated by simple calculation, and they had a good agreement with our previous experimental results. We also confirmed the mass transfer coefficients of Ln in HNO
/ TDdDGA-n-dodecane system, Ln behaviors in the counter-current extraction and back-extraction using mixer-settlers and centrifugal contactors were estimated by simple calculation, and they had a good agreement with our previous experimental results. We also confirmed the mass transfer coefficients of Ln in HNO / HONTA - n-dodecane system are under 10
/ HONTA - n-dodecane system are under 10 m/s.
m/s.
Toigawa, Tomohiro; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Kai, Takeshi; Furuta, Takuya; Kumagai, Yuta; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(1), p.74 - 89, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.50(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Absorbed-dose estimation is essential for evaluation of the radiation feasibility of minor-actinide-separation processes. We propose a dose-evaluation method based on radiation permeability, with comparisons of heterogeneous structures seen in the solvent-extraction process, such as emulsions forming in the mixture of the organic and aqueous phases. A demonstration of radiation-energy-transfer simulation is performed with a focus on the minor-actinide-recovery process from high-level liquid waste with the aid of the Monte Carlo radiation-transport code PHITS. The simulation results indicate that the dose absorbed by the extraction solvent from alpha ray depends upon the emulsion structure, and that from beta and gamma ray depends upon the mixer-settler-apparatus size. Non-negligible contributions of well-permeable gamma rays were indicated in terms of the plant operation of the minor-actinide-separation process.
Morita, Yasuji; Fukushima, Masahiro; Kashima, Takao*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-013, 38 Pages, 2020/09
Critical Masses of Cm, Am and the mixture were calculated in metal-water mixtures with water reflector as a basic data for criticality safety assessment of minor actinide separation process. In the mixture of Cm-244 and Cm-245, higher ratio of Cm-245 gives smaller critical mass, but the amount of Cm-245 in the critical mass can be obtained by concentration of Cm-245 in the Cm mixture without depending on the Cm-245 ratio. Critical mass of Cm isotope mixture with 30% Cm-245 was smaller than that of Pu isotope mixture in the practical reprocessing (71% Pu-239 + 17% Pu-240 + 12% Pu-241). When Cm is separated from other element including Am and the solution is concentrated, measure for the critical accident has to be taken. Critical mass of Am-242m is smaller than that of Cm-245, but the ratio of Am-242m in the Am contained in practical spent fuel is small enough, about several percent, and therefore the critical accident by Am does not have to be considered. That by the mixture of Am and Cm does not either.
Nakamura, Satoshi; Kimura, Takahiro; Ban, Yasutoshi; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
JAEA-Technology 2020-009, 22 Pages, 2020/08
Partitioning and transmutation technology division is planning to measure fission rate ratios that contribute to validate nuclear data of minor actinides (MA). For this purpose, MA sources for fission chambers were prepared using electrodeposition method. The radioactivity of each MA source was quantified, and its uncertainty was evaluated. Seven types of MA sources with different radioactivity were prepared using four nuclides of  Np,
Np,  Am,
Am,  Am, and
Am, and  Cm. A
Cm. A  Cm source solution of which radioactivity was quantified by isotope dilution method was used to prepare working standard sources of
Cm source solution of which radioactivity was quantified by isotope dilution method was used to prepare working standard sources of  Cm. The radioactivities were quantified as 1461 Bq, 2179 Bq, and 2938 Bq for
Cm. The radioactivities were quantified as 1461 Bq, 2179 Bq, and 2938 Bq for  Np sources, 1.428 MBq for
Np sources, 1.428 MBq for  Am source, 370.5 kBq and 89.57 kBq for
Am source, 370.5 kBq and 89.57 kBq for  Am sources, and 2.327 MBq for
Am sources, and 2.327 MBq for  Cm source with, the uncertainty of 0.35% (1
Cm source with, the uncertainty of 0.35% (1 ). This report summarizes the method for preparation and quantification of MA sources, and uncertainty evaluation.
). This report summarizes the method for preparation and quantification of MA sources, and uncertainty evaluation.
Tateno, Haruka; Sato, Takumi; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.224 - 235, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fuel cycle technology for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MAs) using an accelerator-driven system has been developed using the double-strata fuel cycle concept. A mononitride solid solution of MAs and Pu diluted with ZrN is a prime fuel candidate for the accelerator-driven transmutation of MAs. Pyro-reprocessing is suitable for recycling the residual MAs in irradiated nitride fuel with high radiation doses and decay heat. Spent nitride fuel is anodically dissolved, and the actinides are recovered simultaneously into a liquid cadmium cathode via molten salt electrorefining. The process should be designed to achieve the target recovery yield of MAs and the acceptable impurity level of rare earths in the recovered material. We evaluated the material balance during the pyro-reprocessing of spent nitride fuel to gain important insight on the design process. We examined the effects of changing processing conditions on material flow and quantity of waste.
Morita, Yasuji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-015, 45 Pages, 2020/01
Decay heat from radioactive elements in high-level liquid waste (HLLW) and separated solutions in partitioning process was evaluated as a basic data for safety assessment of partitioning process. In the evaluation of HLLW from spent UO fuel burned-up to 45 GWd/t in light water reactor, decay heat value from fission products decreased as the cooling period become longer but heat from actinides, Am and Cm, was almost constant until 50-year cooling. Decay heat density in solutions of Am, Cm and rare earth elements and of Am and Cm without concentration for volume reduction does not exceed the heat density of HLLW, but the concentration should be required to minimize the scale of the partitioning process. Separated solution of Am and Cm must be concentrated to convert the two elements to a solid state to make fuel for transmutation, and the decay heat density of the concentrated solution of Am and Cm is 10 times higher compared with the Pu solution of same element concentration. Higher burn-up UO
fuel burned-up to 45 GWd/t in light water reactor, decay heat value from fission products decreased as the cooling period become longer but heat from actinides, Am and Cm, was almost constant until 50-year cooling. Decay heat density in solutions of Am, Cm and rare earth elements and of Am and Cm without concentration for volume reduction does not exceed the heat density of HLLW, but the concentration should be required to minimize the scale of the partitioning process. Separated solution of Am and Cm must be concentrated to convert the two elements to a solid state to make fuel for transmutation, and the decay heat density of the concentrated solution of Am and Cm is 10 times higher compared with the Pu solution of same element concentration. Higher burn-up UO fuel and MOX fuel in light water reactor and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor were also considered and the evaluated decay heat was compared among the spent fuels.
fuel and MOX fuel in light water reactor and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor were also considered and the evaluated decay heat was compared among the spent fuels.
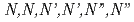 -hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) using mixer-settler extractors in a hot cell
-hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) using mixer-settler extractors in a hot cellBan, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Hideya*; Hotoku, Shinobu; Tsutsui, Nao; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 37(7), p.489 - 499, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.32(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A continuous counter-current experiment to separate minor actinides (MAs: Am and Cm) was performed with 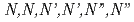 -hexaochyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) as an extractant. Nitric acid of 0.08 M (mol/dm
-hexaochyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) as an extractant. Nitric acid of 0.08 M (mol/dm ) containing MAs and rare earths (REs) recovered from high-level waste was used as the Feed, and the experiment was conducted for 14 h. The ratios of Am and Cm recovered into the MA fraction measured 94.9% and 78.9%, respectively. HONTA hardly extracted Y, La, and Eu in the Feed (99.9% for Y, 99.9% for La, and 96.7% for Eu), most of which were distributed to the RE fraction. A portion of Nd was extracted by HONTA, and consequently the ratio of Nd in the RE fraction was 83.5%. The concentrations of MAs and some REs in each stage were calculated using a simulation code, and the results are consistent with the experimental values. This code indicates that the ratios of MAs in the MA fraction and REs in the RE fraction could be
) containing MAs and rare earths (REs) recovered from high-level waste was used as the Feed, and the experiment was conducted for 14 h. The ratios of Am and Cm recovered into the MA fraction measured 94.9% and 78.9%, respectively. HONTA hardly extracted Y, La, and Eu in the Feed (99.9% for Y, 99.9% for La, and 96.7% for Eu), most of which were distributed to the RE fraction. A portion of Nd was extracted by HONTA, and consequently the ratio of Nd in the RE fraction was 83.5%. The concentrations of MAs and some REs in each stage were calculated using a simulation code, and the results are consistent with the experimental values. This code indicates that the ratios of MAs in the MA fraction and REs in the RE fraction could be  99% by optimizing separation conditions.
99% by optimizing separation conditions.
Morita, Yasuji; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-017, 32 Pages, 2019/02
Potential radiotoxicity defined as a summation of intake dose was estimated for each actinide element to suppose target of recovery ratio of minor actinide (MA). Importance of each element from the viewpoint of the radiotoxicity was evaluated from the evolution of the radiotoxicity and ratio to the total radiotoxicity. In all the 4 types of spent fuels examined, Am is the most important element. For instance, the potential radiotoxicity of Am accounts for 93% of the total radiotoxicity of actinide elements in HLW produced by reprocessing of spent fuel from pressurized water reactor (PWR). Residual Pu after the recovery of 99.5% in reprocessing still gives contribution that cannot be ignored in radiotoxicity. When the burn-up of the UO fuel in PWR increased, the potential radiotoxicity of actinide elements increased almost in proportion to the burn-up, but in case of MOX fuel in PWR and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor, the radiotoxicity of actinide elements increased further. Much consideration is required for the recovery of actinide elements in HLW from different types of fuel.
fuel in PWR increased, the potential radiotoxicity of actinide elements increased almost in proportion to the burn-up, but in case of MOX fuel in PWR and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor, the radiotoxicity of actinide elements increased further. Much consideration is required for the recovery of actinide elements in HLW from different types of fuel.
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(11), p.1275 - 1290, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To reduce environmental burden and thread of nuclear proliferation, multi-recycling fuel cycle with High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) has been investigated. Those problems are solved by incinerating TRans Uranium (TRU) nuclides, which is composed of plutonium and Minor Actinoide (MA), and there is concept to realize TRU incineration by multi-recycling with Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR). In this study, multi-recycling is realized even with thermal reactor by feeding fissile uranium from outside of the fuel cycle instead of breeding fissile nuclide. In this fuel cycle, recovered uranium by reprocessing and natural uranium are enriched and mixed with recovered TRU by reprocessing and partitioning to fabricate fresh fuels. The fuel cycle was designed for a Gas Turbine High Temperature Reactor (GTHTR300), whose thermal power is 600 MW, including conceptual design of uranium enrichment facility. Reprocessing is assumed as existing Plutonium Uranium Redox EXtraction (PUREX) with four-group partitioning technology. As a result, it was found that the TRU nuclides excluding neptunium can be recycled by the proposed cycle. The duration of potential toxicity decaying to natural uranium level can be reduced to approximately 300 years, and the footprint of repository for High Level Waste (HLW) can be reduced by 99.7% compared with GTHTR300 using existing reprocessing and disposal technology. Suppress plutonium is not generated from this cycle. Moreover, incineration of TRU from Light Water Reactor (LWR) cycle can be performed in this cycle.
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 116, p.224 - 234, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Optimization of disposal method and scenario to reduce volume of High Level Waste (HLW) and the footprint in a geological repository for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) has been performed. It was found that HTGR has great advantages to reducing HLW volume and its footprint, which are high burn-up, high thermal efficiency and pin-in-block type fuel, compared with those of LWR and has potential to reduce those more in the previous study. In this study, the scenario is optimized, and the geological repository layout is designed with the horizontal emplacement based on the KBS-3H concept instead of the vertical emplacement based on KBS-3V concept employed in the previous study. As a result, for direct disposal, the repository footprint can be reduced by 20 % by employing the horizontal without change of the scenario. By extending 40 years for cooling time before disposal, the footprint can be reduced by 50 %. For disposal with reprocessing, the number of canister generation can be reduced by 20 % by extending cooling time of 1.5 years between the discharge and reprocessing. The footprint per electricity generation can be reduced by 80 % by extending 40 years before disposal. Moreover, by employing four-group partitioning technology without transmutation, the footprint can be reduced by 90 % with cooling time of 150 years.
Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Hales, B. P.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Shibahara, Yuji*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, p.15 - 22, 2018/01
Neutron nuclear data of long lived fission products (LLFPs) have been required as basic data for the technology of reduce environmental impact involved in high level radioactive wastes (HLW). The innovative large project called by "Impusing Paradigm Change through Disruptive Technologies Program: ImPACT" have been started from October, 2014. In the ImPACT project, some research groups of JAEA engaged in the Project No.2 (Nuclear Reaction Data Measurements), and have started measurements of neutron capture cross-section at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. In our research, we selected cesium-135 ( Cs) nuclide (half life: 2.3
Cs) nuclide (half life: 2.3 10
10 yr.) among LLFPs in the HLW, and decided to measure the neutron capture cross-sections of
yr.) among LLFPs in the HLW, and decided to measure the neutron capture cross-sections of  Cs. When measurement, the
Cs. When measurement, the  Cs sample might contained cecium-137 (
Cs sample might contained cecium-137 ( Cs) as impurities because it's impossible to chemically separate each other. To measure the cross-sections of
Cs) as impurities because it's impossible to chemically separate each other. To measure the cross-sections of  Cs, there should be also needed to know the cross-sections of
Cs, there should be also needed to know the cross-sections of  Cs. In this work, sample maintenance also has been examined especially for selen-79 (
Cs. In this work, sample maintenance also has been examined especially for selen-79 ( Se) nuclide among LLFPs having difficulty in sample preparations. In this oral session, the outline of our research project will be presented together with a research motivation, situations of past reported data, total schedules, progress, future plans, and some of high light data for neutron capture cross-section measurements.
Se) nuclide among LLFPs having difficulty in sample preparations. In this oral session, the outline of our research project will be presented together with a research motivation, situations of past reported data, total schedules, progress, future plans, and some of high light data for neutron capture cross-section measurements.
Suzuki, Hideya; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Kurosawa, Tatsuya*; Sagawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1163 - 1167, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:93.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)A highly practical diamide-type extractant, which is an alkyl diamide amine with 2-ethylhexyl alkyl chains (ADAAM(EH)), was investigated for mutual separation of Am(III) and Cm(III). ADAAM(EH) is a multidentate ligand with one soft N-donor atom and two hard O-donor atoms in its central frame. This tridentate arrangement of donor atoms provides selective binding to Am(III) compared to that with Cm(III) in highly acidic media, resulting in separation factors of up to 5.5. A continuous liquid-liquid extraction and stripping test was conducted using a multistage countercurrent mixer-settler extractor with ADAAM(EH) in n-dodecane. In this test, separation of Am(III) and Cm(III) was achieved with very high yield.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
NEA/NSC/R(2017)3, p.427 - 432, 2017/11
Transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides including minor actinides (MA: Np, Am, Cm) has been studied in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Pb-Bi cooled sub-critical accelerator-driven system (ADS) is regarded as one of the powerful tools for transmutation of MA under the double strata fuel cycle concept. Uranium-free MA-Pu nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for MA transmutation. Reprocessing of spent ADS fuel and reusing MA recovered from the spent ADS fuels is necessary to improve the transmutation ratio. A pyrochemical process has been proposed as the first candidate for reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel for MA transmutation, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA, and feasibility for recovering expensive N-15 in the spent fuels to be reused. This paper overviews the current status of the technology development, including our recent study. Development of the anode suitable for electro-refining of nitride fuels and that of the apparatus for renitridation of the metals recovered in Cd cathode for 100g-Cd scale cold tests are main topics. Evaluation of the batch sizes of each process, which is necessary for estimating the scale of the engineering-apparatus, with considering the decay heat of MA and FP, will also be introduced.
Kibe, Satoshi; Fujisaku, Kazuhiko*; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Suzuki, Hideya; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
JAEA-Research 2016-024, 40 Pages, 2017/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing some flowsheets with TDdDGA (N,N,N,Ntetradodecyldiglycolamide) extractant to recover MA (minor actinide) from raffinate. In this study, countercurrent experiments with the improved flowsheet, e.g. the addition of alcohol into the solvent for preventing the precipitation, were performed using miniature centrifugal contactors in order to compare the extraction/stripping behavior of each element with the mixer-settler type. As a result, no entrainments were observed and sufficient phase separation was achieved by centrifugal contactors without any abnormal fluid behavior, such as overflow. The extraction and stripping of Ln(III) which show the similar tendencies as MA could be achieved successfully, especially their stripping proceeded more efficiently in centrifugal contactors. This might be due to the increase in stripping rates by improving the flowsheet and to superior phase separation performance of centrifugal contactors.
Suzuki, Hideya; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Analytical Sciences, 33(2), p.239 - 242, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:66.96(Chemistry, Analytical)Alkyl diamide amine (ADAAM), a new high-performance reagent with a simple structure, was examined for the mutual separation of Am(III) and Cu(III). The combination of ADAAM and Tetraethyldiglycolamide (TEDGA) as a masking agent shows selectivity for Am(III) over Cm(III) in highly acidic media with separation factors up to 41.