Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 162(15), p.154102_1 - 154102_11, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Scientific knowledge of low-energy electrons resulting from water radiolysis is required to estimate radiation DNA damage. However, since the analysis of water radiolysis is very complex, this study focuses on the experimental values of low-energy electrons related to simple water photolysis and those generated by photoirradiation of electrodes in water. Both experimental analyses involve the presence or absence of a Coulomb field in the parent ion. In this study, we analyzed these experimental values using a calculation code that combines Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics methods. As a result, it was shown that the code reproduced the experimental values even under different experimental conditions, and the code was validated. The calculation code will be a powerful tool for analyzing the interaction between low-energy electrons and DNA, and is expected to be applied to elucidate the formation mechanism of radiation DNA damage.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Ito, Yuma*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.60_1 - 60_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Radiation DNA damage is formed from direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is the interaction between DNA and a radiation, while the indirect effect is the chemical reaction between DNA and radiolytic chemical species. We believed that when the direct effect is induced, multiple lesions are formed within 10 base pairs (about 3.4 nm) of DNA. The damage reduces repair efficiency and induces biological effects. In this study, DNA damage induced by only indirect effects was quantitatively evaluated. Our results indicated that the multiple damage is formed when only 10s of eV energy is deposited to water in the vicinity of DNA, although its formation probability is less than 1%. In other words, the possibility of late biological effects cannot be excluded simply by imparting energy to water in the extreme vicinity of DNA without direct interaction between radiation and DNA. Our results are one of the most important findings for understanding low-dose radiation risk.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.24722_1 - 24722_15, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Scientific insight of water radiolysis is essential to estimate the direct and indirect effects of radiation DNA damage. Secondary electrons produced by water radiolysis are responsible for both effects. Here, we use a first-principles code to calculate the femtosecond dynamics of secondary electrons produced as a result of 20-30 eV energy deposition to water and analyze the formation mechanism of radiolytic chemical species produced in a nano-size ultra-small space region. From the results, it was clarified that the chemical species produced by water radiolysis begin to densify in the ultra-small region of a few nanometers when the deposition energy exceeds 25 eV. Our results provide important scientific insights into the formation of clustered DNA damage, which is believed to cause biological effects such as cell death.
Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Majima, Takuya*; Saito, Manabu*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 161(10), p.104503_1 - 104503_8, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Although fast ion beams can damage DNA by chemical products such as secondary electrons produced by their interaction with water in living cells, the process of formation of these chemical products in the Bragg peak region used in particle therapy is not fully understood. To investigate this process, we performed experiments to evaluate the yields of radiolytic products produced when a liquid water jet in vacuum is irradiated with a MeV-energy carbon beam. In addition, ionization processes in water due to incident ions and secondary electrons were simulated using a radiation transport Monte Carlo code. The results indicated that the primary source of ionization in water is secondary electrons. Finally, we show that these elementary processes contribute to the development of radiation biophysics and biochemistry to study the formation mechanism of DNA damage.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(46), p.32371 - 32380, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.10(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Although scientific knowledge of photolysis and radiolysis of water is widely used in the life sciences and other fields, the formation mechanism of the spatial distribution of hydrated electrons (spur) resulting from energy deposition to water is still not well understood. The chemical reaction times of hydrated electrons, OH radicals, and H O
O in the spur strongly depend on the spur radius. In our previous study, we elucidated the mechanism at a specific given energy (12.4 eV) by first-principles calculations. In the present study, we performed first-principles calculations of the spur radius at the deposition energies of 11-19 eV. The calculated spur radius is 3-10 nm, which is consistent with the experimental prediction (~4 nm) for the energy range of 8-12.4 eV, and the spur radius gradually increases with increasing energy. The spur radius is a new scientific knowledge and is expected to be widely used for estimating radiation DNA damage.
in the spur strongly depend on the spur radius. In our previous study, we elucidated the mechanism at a specific given energy (12.4 eV) by first-principles calculations. In the present study, we performed first-principles calculations of the spur radius at the deposition energies of 11-19 eV. The calculated spur radius is 3-10 nm, which is consistent with the experimental prediction (~4 nm) for the energy range of 8-12.4 eV, and the spur radius gradually increases with increasing energy. The spur radius is a new scientific knowledge and is expected to be widely used for estimating radiation DNA damage.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(11), p.7076 - 7086, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.12(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Scientific insights of water radiolysis are widely used in the life sciences and so on, however, the formation mechanism of radicals, a product of water radiolysis, is still not well understood. We are challenging to develop a simulation code to solve this formation mechanism from the viewpoint of radiation physics. Our first-principles calculations have revealed that the behavior of secondary electrons in water is governed not only by collisional effects but also by polarization effects. Furthermore, from the predicted ratio of ionization to electronic excitation, based on the spatial distribution of secondary electrons, we successfully reproduce the initial yield of hydrated electrons predicted in terms of radiation chemistry. The code provides us a reasonable spatiotemporal connection from radiation physics to radiation chemistry. Our findings are expected to provide newly scientific insights for understanding the earliest stages of water radiolysis.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Kinoshita, Ryoma*; Sasaki, Yuji
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 168(7), p.076508_1 - 076508_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Electrochemistry)It is important to develop solvent extraction and electrodeposition processes for platinum group metals in order to reduce the volume of secondary wastes. In this study, the electrodeposition behavior of the extracted Pt(IV) complex in a phosphonium-based ionic liquid (IL) was investigated by using an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). The charge transfer reaction Pt(IV) + 2e(-)  Pt(II) was observed at -0.53 V and the electrodeposition reaction Pt(II) + 2e(-)
Pt(II) was observed at -0.53 V and the electrodeposition reaction Pt(II) + 2e(-)  Pt(0) proceeded at -1.65 V in this system. Moreover, consecutive solvent extraction and electrodeposition of Pt metal in Alamine336/IL system were performed at 10 cycles. High extraction percentage (E
Pt(0) proceeded at -1.65 V in this system. Moreover, consecutive solvent extraction and electrodeposition of Pt metal in Alamine336/IL system were performed at 10 cycles. High extraction percentage (E  95.1 %) and good current efficiency (
95.1 %) and good current efficiency (
 85.8 %) were maintained in the first to sixth cycles. The XPS Pt-4f (7/2) spectrum confirmed that all the electrodeposits were in the metallic state.
85.8 %) were maintained in the first to sixth cycles. The XPS Pt-4f (7/2) spectrum confirmed that all the electrodeposits were in the metallic state.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 168(5), p.056502_1 - 056502_7, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.37(Electrochemistry)The coordination states of multivalent dysprosium complexes of potassium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide (K[NTf ]) were investigated by Raman spectroscopy. The solvation number, n, of the dysprosium complexes was determined to be 4.12 for Dy(II) and 5.09 for Dy(III). Electrochemical analysis revealed that the reduction peak of [Dy-III(NTf
]) were investigated by Raman spectroscopy. The solvation number, n, of the dysprosium complexes was determined to be 4.12 for Dy(II) and 5.09 for Dy(III). Electrochemical analysis revealed that the reduction peak of [Dy-III(NTf )(5)](2-) at approximately +0.81 V at 483 K is based on an electrodeposition reaction from [Dy-III(NTf
)(5)](2-) at approximately +0.81 V at 483 K is based on an electrodeposition reaction from [Dy-III(NTf )(5)](2-) to Dy(0). The nucleation behavior of [Dy-III(NTf
)(5)](2-) to Dy(0). The nucleation behavior of [Dy-III(NTf )(5)](2-) was evaluated using chronoamperometry. The results indicated that the nucleation mechanism of Dy nuclei changed from instantaneous to progressive nucleation when the overpotential became more negative than the deposition potential of Dy(0). The electrodeposits were identified as mostly the metallic state by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
)(5)](2-) was evaluated using chronoamperometry. The results indicated that the nucleation mechanism of Dy nuclei changed from instantaneous to progressive nucleation when the overpotential became more negative than the deposition potential of Dy(0). The electrodeposits were identified as mostly the metallic state by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Kinoshita, Ryoma*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 168(5), p.056501_1 - 056501_6, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.88(Electrochemistry)The extraction behavior of Ir(IV) in a phosphonium-based ionic liquid (IL) system, triethyl-n-pentyl phosphonium bis(trifluoromethyl-sulfonyl)amide ([P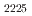 ][NTf
][NTf ]), was investigated using an amine extractant. Voltammetry-based electrochemical analysis revealed that the reduction of Ir(IV) proceeded via an intermediate Ir(III) species in two steps, namely, Ir(IV) + e(-)
]), was investigated using an amine extractant. Voltammetry-based electrochemical analysis revealed that the reduction of Ir(IV) proceeded via an intermediate Ir(III) species in two steps, namely, Ir(IV) + e(-)  Ir(III) and Ir(III) + 3e(-)
Ir(III) and Ir(III) + 3e(-)  Ir(0). Diffusion coefficients of the extracted Ir(IV) species in the IL were determined over the temperature range of 298-373 K using semi-integral and semi-differential analyses, and values obtained from the two analyses were consistent with each other. Furthermore, consecutive solvent extraction and electrodeposition of Ir metal in the IL bath were performed for 10 cycles. The entire Ir electrodeposit was in the metallic state, as is evident from the 4f (7/2) spectrum obtained by XPS.
Ir(0). Diffusion coefficients of the extracted Ir(IV) species in the IL were determined over the temperature range of 298-373 K using semi-integral and semi-differential analyses, and values obtained from the two analyses were consistent with each other. Furthermore, consecutive solvent extraction and electrodeposition of Ir metal in the IL bath were performed for 10 cycles. The entire Ir electrodeposit was in the metallic state, as is evident from the 4f (7/2) spectrum obtained by XPS.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Hydrometallurgy, 199, p.105539_1 - 105539_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.99(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The synergistic solvent extraction of lanthanide(III) with mixtures of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA, A) and monoisodecyl phosphoric acid (MIDPA, B) in phosphonium-based ionic liquid was investigated. In the case of D2EHPA or MIDPA single extractant system, Ln(III) (Ln = Pr and Nd) was extracted as [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (
HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (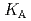 ,
, 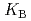 and
and 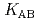 ) and the formation constants (
) and the formation constants (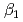 ,
, 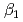 and
and 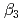 ), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA
), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA B
B or [DyHA
or [DyHA B
B ] was more stable than [LnA
] was more stable than [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji; Ono, Ryoma*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(1), p.597 - 607, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.32(Chemistry, Analytical)To achieve trichotomic separation of light lanthanides (Ln), heavy Ln, and Am, batchwise multi-stage extractions using tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA) extractant from organic acids are studied. Malonic acid (MA) has high solubility in water and is used as the main component of the aqueous phase. It is clear that the separation factor (SF) for Nd/Am from MA and that for La/Am from MA + HNO are both around 30. The light Ln (e.g., La and Ce) flowed-out in 1 M MA+0.05 M HNO
are both around 30. The light Ln (e.g., La and Ce) flowed-out in 1 M MA+0.05 M HNO (1st soln.), Am is recovered into 3 M MA (2nd soln.), and middle and heavy Ln (Nd and other heavy Ln) are back-extracted into 0.1 M TEDGA/water (3rd soln.). This extraction method can give 95% recovery of Am with total Ln of less than 16% present in high-level radioactive waste.
(1st soln.), Am is recovered into 3 M MA (2nd soln.), and middle and heavy Ln (Nd and other heavy Ln) are back-extracted into 0.1 M TEDGA/water (3rd soln.). This extraction method can give 95% recovery of Am with total Ln of less than 16% present in high-level radioactive waste.
 -diketone extractant and a neutral ligand
-diketone extractant and a neutral ligandMatsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(7), p.764 - 784, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:25.61(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the solvent extraction of four rare earth (RE) elements (Pr, Nd, Tb, and Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnets using mixtures of 1-(2-thienyl)-4,4,4,-trifluoro-1,3-butanedione (Htta) or 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-phenyl-1,3-butanedione (Hbfa) chelating extractants and tri-n-octylphosphine oxide (TOPO) neutral ligand in phosphonium based ionic liquids. A synergistic effect was observed for the extraction of the RE elements with the combination of extractant and neutral ligand. The separation of Tb(III) and Dy(III) from other RE(III) components was performed with seven extraction cycles.
Sasaki, Yuji; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1303 - 1309, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.03(Chemistry, Analytical)The mutual separation of lanthanides is studied by multi-stage extraction using extractant, DGA (diglycolamide) compounds. Tetraoctyl-DGA (TODGA) has a high extractability to lanthanides and relatively high separation factor (SF) between Dy and Nd (SF: over 20). The complete separation with such SF value can be achieved by multi-stage extraction. Less information on multi-stage extraction compared to batch extraction is presented up to now, thus we conduct the basic study about that. Confirming the experimental data to be identical to the calculation, the sample solution including both metals is employed for the batchwise multi-stage extraction. Ninety-seven % of Dy with under detection limit of Nd can be recovered into the organic phase from Nd with ten times higher concentration than Dy using the condition, 0.1 M TODGA/n-dodecane and 0.3 M HNO by multi-stage extraction of 9
by multi-stage extraction of 9 9 for organic and aqueous phases.
9 for organic and aqueous phases.
Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Kai, Takeshi; Kitajima, Kensei*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Majima, Takuya*; Saito, Manabu*
European Physical Journal D, 74(10), p.212_1 - 212_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.91(Optics)Fundamental study of interaction between biomolecules and heavy ions in water is very important to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects. A heavy ion irradiation experiment into droplet target assumed as a biological system in a vacuum was performed to measure production yields of cations and anions for glycine, which was ejected from the droplet target to the vacuum. However, the production mechanisms have been unknown. The PHITS code adapting ion track structure mode was used to analyze the production mechanisms from the dose evaluation at the surface between the vacuum and the water. It is found that induction yields of ionization and excitation, and dissociative electron attachment involved in the secondary electrons were correlated with the production yields of cations and anions of the glycine. The results provide us newly scientific insights to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects.
 -dioctylacetamide and direct electrodeposition from loaded organic phase
-dioctylacetamide and direct electrodeposition from loaded organic phaseMatsumiya, Masahiko*; Song, Y.*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Separation and Purification Technology, 234, p.115841_1 - 115841_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:55.76(Engineering, Chemical)The development of solvent extraction and direct electrodeposition processes is an important task to reduce the volume of secondary wastes. In this study, the extraction of Pd(II) from hydrochloric/chloride media using methylimino-bis-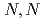 -dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) in three diluents (acetophenone; AP, 1,2-dichloroethane; DCE, or 1-octanol; OC) and the electrochemical behavior of the extracted Pd(II) complex in the MIDOA/AP bath was investigated. Pd(II) was found to be reduced to Pd(0) metal via a two-electron transfer between -2.38 V and -3.40 V. The potentiostatic electrodeposition of the extracted Pd(II) complex enabled us to recover the blackish electrodeposits, which were identified as Pd metal.
-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) in three diluents (acetophenone; AP, 1,2-dichloroethane; DCE, or 1-octanol; OC) and the electrochemical behavior of the extracted Pd(II) complex in the MIDOA/AP bath was investigated. Pd(II) was found to be reduced to Pd(0) metal via a two-electron transfer between -2.38 V and -3.40 V. The potentiostatic electrodeposition of the extracted Pd(II) complex enabled us to recover the blackish electrodeposits, which were identified as Pd metal.
 NiSe
NiSe
Tsuchida, Shun*; Hirose, Yusuke*; Sekikawa, Takuya; Ono, Yoshiaki*; Settai, Rikio*
no journal, ,
Excitonic insulators have the property that the entire crystal becomes an insulator due to the collective behavior of electrons and holes bound together in the crystal, and they have begun to attract attention as a new physical property. In this study, we focused on Ta NiSe
NiSe , which is one of the excitonic insulator candidates, but its synthesis itself is difficult and its physical properties have not yet been clarified. The electrical resistivity of M=Ti, Zr, and Hf at low temperatures is 5 to 6 orders of magnitude lower than that of the parent material. Furthermore, when titanium is substituted for tantalum (M=Ti), the electrical resistivity of samples with composition ratio x less than 0.06 is semiconducting, while the electrical resistivity of the high temperature phase behaves metallic when x = 0.06 or higher. The phase transition shown in this study may be a new insight into the realization of excitonic insulators.
, which is one of the excitonic insulator candidates, but its synthesis itself is difficult and its physical properties have not yet been clarified. The electrical resistivity of M=Ti, Zr, and Hf at low temperatures is 5 to 6 orders of magnitude lower than that of the parent material. Furthermore, when titanium is substituted for tantalum (M=Ti), the electrical resistivity of samples with composition ratio x less than 0.06 is semiconducting, while the electrical resistivity of the high temperature phase behaves metallic when x = 0.06 or higher. The phase transition shown in this study may be a new insight into the realization of excitonic insulators.
Sasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Ban, Yasutoshi; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*; Shimosaka, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
no journal, ,
In order to enlarge the separation factors between trivalent actinide (An) and lanthanide (Ln), which show similar chemical behavior, the use of water-soluble ligand has been studied. In this work, ten of amides and carboxylic acids are employed in TODGA extraction system and their properties are compared. It is noted that complexing ability of amide with Ln is higher than that with carboxylic acid under pH 2, if both reagents have the same central frame. Classifying 14 lanthanides into four groups (La-Nd, Sm-Gd, Gd-Ho, and Er-Lu), the difference of their complexing reactions in each group and the reaction of An will be discussed.
 NiSe
NiSe , 4
, 4Tsuchida, Shun*; Hirose, Yusuke*; Sekikawa, Takuya; Ono, Yoshiaki*; Settai, Rikio*
no journal, ,
Exciton insulators have the property that the entire crystal becomes an insulator due to the collective behavior of electrons and holes bound together in the crystal, and they are beginning to attract attention as a new physical property. In this study, we focused on Ta NiSe
NiSe , which is one of the excitonic insulator candidates, but its synthesis itself is difficult and its physical properties have not yet been clarified. Furthermore, when titanium is substituted for tantalum (M = Ti), the electrical resistivity of the sample with composition ratio x less than 0.06 is semiconducting, while the electrical resistivity of the high-temperature phase behaves metallic when x = 0.06 or higher. The phase transition shown in this study may be a new insight into the realization of excitonic insulators.
, which is one of the excitonic insulator candidates, but its synthesis itself is difficult and its physical properties have not yet been clarified. Furthermore, when titanium is substituted for tantalum (M = Ti), the electrical resistivity of the sample with composition ratio x less than 0.06 is semiconducting, while the electrical resistivity of the high-temperature phase behaves metallic when x = 0.06 or higher. The phase transition shown in this study may be a new insight into the realization of excitonic insulators.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Ito, Yuma*; Yokoya, Akinari*
no journal, ,
Irradiation of living systems forms complex DNA damage that induces biological effects in very rare cases. This complex DNA damage is called cluster damage and is very difficult to detect experimentally. In this study, we have developed physical and chemical codes for analyzing DNA damage, and are working to elucidate the formation mechanism of cluster damage. In this study, we analyzed the results of calculations in a simple system in which energy is deposited to DNA and secondary electrons are emitted, and showed that the formation mechanism of cluster damage strongly depends on the deposition energy to DNA. This scientific insight is expected to contribute to the elucidation of the repair mechanism of DNA damage and lead to the elucidation of radiation biological effects.
Tsuchida, Yusuke; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Sasaki, Yuji; Akama, Takeshi*; Arita, Yuji*
no journal, ,
We study the solvent extraction of soft acid metals, e.g., platinum metals, gold and silver from nitric and hydrochloric acids by commercially available organic compounds with low solubility in water. We would like to know some of the physical parameters obtained from DFT calculations can support the experimental results. The present work show that the extractants having S-donor give high extractability for gold.