Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Parker, J.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao
Scientific Reports (Internet), 15, p.7687_1 - 7687_8, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1A neutron resonance absorption imaging technique to visualize two-dimensional distributions with element discrimination has been developed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. We measured neutron transmission spectra from 1 eV to 100 keV while rotating a sample containing iron, zirconium, nickel, molybdenum, and aluminum rods. The distributions of hafnium (impurity of zirconium) and molybdenum were clearly obtained by a straightforward analysis using the most prominent resonances. Then an analysis using multiple resonances of each element simultaneously was performed finding that the accuracy of elemental identification was improved, and iron and nickel distributions became clearer. However, these analysis methods sometimes have difficulties in the case of overlapping materials since a resonance shape can be deteriorated by those of other materials. Such an example was demonstrated with the case of iron and nickel. To overcome the issue and aiming for further improvement, we proposed a method to fit the transmission spectrum in a wide range assuming the existence of possible elements, successfully visualizing both the distributions of the sample metals and those of hafnium and manganese (impurities of zirconium and iron). The newly introduced analysis technique will contribute to the establishment of a standard analytical procedure for general users of the facility.
 -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
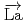 +
+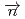
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.45(Physics, Nuclear) -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 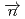 +
+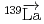 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.17(Physics, Nuclear)Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Abe, Yuta; Oikawa, Kenichi; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Sato, Ikken
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012022_1 - 012022_6, 2023/10
We developed a method to obtain the areal density distribution of boron, which has a large neutron cross section, by means of an energy resolved neutron imaging. Commonly in a measurement of elements with very high neutron sensitivity, the quantitative measurement becomes more difficult with the amount of element due to the neutron self-shielding effect. To avoid this effect, an energy-resolved method using known cross section data was attempted, and a quantitative imaging of such elements was demonstrated at the MLF of J-PARC. This presentation introduces a measurement of melted simulated-fuel assemblies obtained in the research of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant after the severe accident. Energy-dependent neutron transmission rates of the samples were measured by a neutron imaging detector, and were analyzed to obtained the areal density of boron at each position.
Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2023/10
The Japan Research Ractor-3 (JRR-3) is operation resumed on February 26, 2021, and the shared use was also restarted in July, 2021. With the resumption of JRR-3 operation, two imaging facilities called TNRF and CNRF have also resumed their utilization. In this presentation, we report the details of these two neutron facilities.
Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Nagai, Takayuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.10071_1 - 10071_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.61(Multidisciplinary Sciences)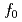 (980) meson decaying into
(980) meson decaying into 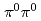 at
at 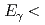 2.4 GeV
2.4 GeVMuramatsu, Norihito*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; LEPS2 BGOegg Collaboration*; 61 of others*
Physical Review C, 107(4), p.L042201_1 - L042201_5, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:26.66(Physics, Nuclear) photoproduction on the proton at
photoproduction on the proton at 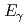 = 1.3-2.4 GeV
= 1.3-2.4 GeVHashimoto, Toshikazu*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; LEPS BGOegg Collaboration*; 58 of others*
Physical Review C, 106(3), p.035201_1 - 035201_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:61.57(Physics, Nuclear)Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Abe, Yuta; Oishi, Yuji*; Kai, Tetsuya; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Masahide; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011074_1 - 011074_6, 2021/03
In the decommissioning of the Fukushima-Daiichi (1F) Nuclear Power Plant, it is essential to understand characteristics of the melted core materials. The estimation of boride in the real debris is of great importance to develop safe debris removal plans. Hence, it is required to investigate the amount of boron in the melted core materials with nondestructive methods. Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis (PGAA) is one of the useful techniques to determine the amount of borides by means of the 478 keV prompt gamma-ray from neutron absorption reaction of boron. Moreover, it is well known that the width of the 478 keV gamma-ray peak is typically broadened due to the Doppler effect. The degree of the broadening is affected by coexisting materials, and can be recognized by the width of the prompt gamma-ray peak. As a feasibility study, the prompt gamma-ray from boride samples were measured using the ANNRI, NOBORU, and RADEN beamlines at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC).
Abe, Yuta; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oishi, Yuji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Ikken
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011075_1 - 011075_6, 2021/03
Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Abe, Yuta; Oishi, Yuji*; Sun, Y.*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Sato, Ikken
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 991, p.164964_1 - 164964_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.63(Instruments & Instrumentation)Peak shape analysis was performed for the energy spectra of Doppler-broadened prompt  -rays generated by neutron capture reactions with various boride or boron samples. Significant differences were observed between nonmetallic and metallic borides. Minor differences between the peak shapes of prompt
-rays generated by neutron capture reactions with various boride or boron samples. Significant differences were observed between nonmetallic and metallic borides. Minor differences between the peak shapes of prompt  -rays from zirconium- and ferro-borons were evaluated by a peak fitting method. The identification of zirconium- and ferro-borons and other types of borides was estimated.
-rays from zirconium- and ferro-borons were evaluated by a peak fitting method. The identification of zirconium- and ferro-borons and other types of borides was estimated.
Higuchi, Yuki*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Nagai, Yasutaka*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(2), p.1062 - 1071, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.09(Chemistry, Physical)This study is the first report on liquid water and ice imaging conducted at a pulsed spallation neutron source facility. Neutron imaging can be utilised to visualise the water distribution inside polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs). Particularly, energy-resolved neutron imaging is a methodology capable of distinguishing between liquid water and ice, and is effective for investigating ice formation in PEFCs operating in a subfreezing environment. The distinction principle is based on the fact that the cross sections of liquid water and ice differ from each other at low neutron energies. In order to quantitatively observe transient freezing and thawing phenomena in a multiphase mixture (gas/liquid/solid) within real PEFCs with high spatial resolution, a pulsed neutron beam with both high intensity and wide energy range is most appropriate. In the validation study of the present work, we used water sealed in narrow capillary tubes to simulate the flow channels of a PEFC, and a pulsed neutron beam was applied to distinguish ice, liquid water and super-cooled water, and to clarify freezing and thawing phenomena of the water within the capillary tubes. Moreover, we have enabled the observation of liquid water/ice distributions in a large field of view (300 mm  300 mm) by manufacturing a sub-zero environment chamber that can be cooled down to -30
300 mm) by manufacturing a sub-zero environment chamber that can be cooled down to -30 C, as a step towards
C, as a step towards  visualisation of full-size fuel cells.
visualisation of full-size fuel cells.
 photoproduction off the proton at
photoproduction off the proton at 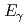 = 1.3-2.4 GeV
= 1.3-2.4 GeVMuramatsu, Norihito*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; LEPS2/BGOegg Collaboration*; 59 of others*
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.025201_1 - 025201_10, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.94(Physics, Nuclear)Abe, Yuta; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oishi, Yuji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Ikken
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
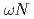 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.19(Physics, Nuclear) ' bound nuclei in the
' bound nuclei in the  C(
C(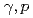 ) reaction with simultaneous detection of decay products
) reaction with simultaneous detection of decay productsTomida, Natsuki*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; LEPS2/BGOegg Collaboration*; 61 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 124(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_7, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary)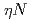 scattering parameters and possible
scattering parameters and possible 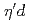 bound state from
bound state from  photoproduction on the deuteron
photoproduction on the deuteronIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; FOREST Collaboration*; 48 of others*
Acta Physica Polonica B, 51(1), p.27 - 32, 2020/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Teshigawara, Makoto; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke*; Ichikawa, Go*; Takata, Shinichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Harada, Masahide; Oi, Motoki; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Kai, Tetsuya; Kawamura, Seiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 929, p.113 - 120, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:88.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)A nano-diamond is an attractive neutron reflection material below cold neutron energy. The total neutron cross section of a nano-diamond was derived from a neutron transmission measurement over the neutron energy range of 0.2 meV to 100 meV because total neutron cross section data were not available. The total cross section of a nano-diamond with particle size of approximately 5 nm increased with a decrease in neutron energy to 0.2 meV. It was approximately two orders of magnitude larger than that of graphite at 0.2 meV. The contribution of inelastic scattering to the total cross section was to be shown negligible small at neutron energies of 1.2, 1.5, 1.9, 2.6, and 5.9 meV in the inelastic neutron scattering measurement. Moreover, small-angle neutron scattering measurements of the nano-diamond showed a large scattering cross section in the forward direction for low neutron energies.
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
no journal, ,
Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Oi, Motoki; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Haga, Katsuhiro
no journal, ,
At J-PARC 1MW spallation neutron source, pulsed neutrons included by 25Hz pulsed proton beam are provided to neutron instruments. Recently, 800 kW proton beam operation is successful, and the proton beam power gradually increases. A neutron instrument observed neutron beams with weak time correction to proton pulse. Therefore, at the neutron instrument to measure neutron pulse characteristics, NOBORU, we tried to measure delayed neutrons. In the measurement, a neutron detector was located on the beam axis in the NOBORU experimental room and pulsed neutrons were measured with flight time after the beam operation stop. Pulse height was also measured to distinguish whether neutron or others. From the results, neutrons could be measured after the beam operation stop. We will present in details in the conference.