Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Takeda, Ryoma; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 61(6), p.248 - 252, 2024/12
A comparative analysis of the 0.2 % yield stress in SUS304L stainless steel revealed that lower strain rates and higher temperatures significantly reduce yield stress. Grain refinement from 68.6  m to 0.59
m to 0.59  m minimally impacted the rate of yield stress reduction at slower strain rates. However, finer grains showed a decrease in yield stress at reactor operating temperature compared to room temperature. In slow strain rate tests under conditions promoting intragranular stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SUS304L with grain sizes of 28.4
m minimally impacted the rate of yield stress reduction at slower strain rates. However, finer grains showed a decrease in yield stress at reactor operating temperature compared to room temperature. In slow strain rate tests under conditions promoting intragranular stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SUS304L with grain sizes of 28.4  m or smaller exhibited similar fracture strains comparable to those at reactor operating temperatures, whereas coarse-grained SUS304L showed reduced fracture strain. Microstructural analysis showed that in smaller grains, over 87 % of the fracture surface was ductile. In particular, SUS304L with 0.59
m or smaller exhibited similar fracture strains comparable to those at reactor operating temperatures, whereas coarse-grained SUS304L showed reduced fracture strain. Microstructural analysis showed that in smaller grains, over 87 % of the fracture surface was ductile. In particular, SUS304L with 0.59  m grains exhibited a higher presence of {111} /
m grains exhibited a higher presence of {111} /  3 boundaries, which decreased with grain growth. These results indicate that grain refinement will suppress intragranular SCC by slowing corrosion progression through increased {111} /
3 boundaries, which decreased with grain growth. These results indicate that grain refinement will suppress intragranular SCC by slowing corrosion progression through increased {111} /  3 boundaries.
3 boundaries.
 Mo adsorption; Utilizing spray-dried mesoporous alumina for clinical-grade generator development
Mo adsorption; Utilizing spray-dried mesoporous alumina for clinical-grade generator developmentAlowasheeir, A.*; Eguchi, Miharu*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Wakabayashi, Ryutaro*; Kimura, Tatsuo*; Ariga, Katsuhiko*; Hatano, Kentaro*; Fukumitsu, Nobuyoshi*; Yamauchi, Yusuke*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 97(10), p.uoae099_1 - uoae099_7, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:37.20(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope separation by modified extraction method
Tc radioisotope separation by modified extraction methodPratama, C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Saptiama, I.*; Marlina, M.*; Triyatna, F.*; Ilhami, A.*; Maria, C. P.*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Teguh, A.*; Prasetyo, I.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2828, p.012025_1 - 012025_12, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Hu, X.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Hori, Junichi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(11), p.6057 - 6063, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Shaimerdenov, A.*; Gizatulin, Sh.*; Sairanbayev, D.*; Bugybay, Zh.*; Silnyagin, P.*; Akhanov, A.*; Fuyushima, Takumi; Hirota, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 548, p.165235_1 - 165235_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)Compared to conditions in other types of installations, cable insulation in nuclear reactors is exposed to mixed conditions (high temperatures, radiation, pressure, humidity, aggressive environments) and at the same time they must maintain their performance characteristics for a long time (about 40-50 years). As a result of irradiation to such conditions, the electrical properties of the cable insulation are degraded, which leads to an increase in current loss. This is because the charge is induced by radiation into the insulator. At the WWR-K reactor, studies were started on the radiation resistance of signal cables with two types of mineral insulation (MgO and Al O
O ). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons
). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons  10
10 cm
cm in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500
in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500  50)
50) C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(6), p.393 - 397, 2023/06
, 65(6), p.393 - 397, 2023/06
no abstracts in English
Seki, Misaki; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Zhang, J.*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hori, Junichi*; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; et al.
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(1), p.2 - 9, 2022/06
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Yoshitaka; Niizeki, Tomotake*; Fukumitsu, Nobuyoshi*; Ariga, Katsuhiko*; Yamauchi, Yusuke*; Malgras, V.*; Kaneti, Y. V.*; Liu, C.-H.*; Hatano, Kentaro*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 95(1), p.129 - 137, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this work, the mechanisms responsible for the adsorption of molybdate ions on alumina are investigated using in-depth surface analyses carried out on alumina specimens immersed in solutions containing different molybdate ions at different pH values. The obtained results reveal that when alumina is immersed in an acidic solution containing molybdate ions, the hydroxyl groups present on the surface are removed to generate positively charged sites, and molybdate ions (MoO
 or AlMo
or AlMo O
O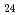 H
H
 ) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo
) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo O
O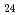 H
H
 , which is more easily desorbed than MoO
, which is more easily desorbed than MoO
 . Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
. Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
 ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope (
ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope ( Mo/
Mo/ Tc) generators.
Tc) generators.
 Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution with alumina columns
Tc elution with alumina columnsFujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; Hori, Junichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2155, p.012018_1 - 012018_6, 2022/01
Technetium-99m ( Tc), the daughter nuclide of Molybdenum-99 (
Tc), the daughter nuclide of Molybdenum-99 ( Mo), is the most commonly used radioisotope in radiopharmaceuticals. The research and development (R&D) for the production of
Mo), is the most commonly used radioisotope in radiopharmaceuticals. The research and development (R&D) for the production of  Mo by the neutron activation method ((n,
Mo by the neutron activation method ((n,  ) method) has been carried out from viewpoints of no-proliferation and nuclear security, etc. Since the specific activity of
) method) has been carried out from viewpoints of no-proliferation and nuclear security, etc. Since the specific activity of  Mo produced by the (n,
Mo produced by the (n,  ) method is extremely low, developing Al
) method is extremely low, developing Al O
O with a large Mo adsorption capacity is necessary to adapt (n,
with a large Mo adsorption capacity is necessary to adapt (n,  )
) Mo to the generator. In this study, three kinds of Al
Mo to the generator. In this study, three kinds of Al O
O specimens with different raw materials were prepared and compared their adaptability to generators by static and dynamic adsorption. MoO
specimens with different raw materials were prepared and compared their adaptability to generators by static and dynamic adsorption. MoO pellet pieces (1.5g) were irradiated with 5 MW for 20 min in the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). Irradiated MoO
pellet pieces (1.5g) were irradiated with 5 MW for 20 min in the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). Irradiated MoO pellet pieces were dissolved in 6M-NaOH aq. In dynamic adsorption, 1 g of Al
pellet pieces were dissolved in 6M-NaOH aq. In dynamic adsorption, 1 g of Al O
O was filled into a PFA tube (
was filled into a PFA tube ( 1.59 mm). The
1.59 mm). The  Mo adsorption capacity of Al
Mo adsorption capacity of Al O
O specimens under dynamic condition was slightly reduced compared to that under static condition. The
specimens under dynamic condition was slightly reduced compared to that under static condition. The  Tc elution rate was about 100% at 1.5 mL of milking in dynamic adsorption, while it was around 56-87% in static adsorption. The
Tc elution rate was about 100% at 1.5 mL of milking in dynamic adsorption, while it was around 56-87% in static adsorption. The  Mo/
Mo/ Tc ratio of dynamic condition was greatly reduced compared to that of static condition. Therefore, the
Tc ratio of dynamic condition was greatly reduced compared to that of static condition. Therefore, the  Tc elution property is greatly affected by the method of adsorbing Mo, e.g., the column shape, the linear flow rate, etc.
Tc elution property is greatly affected by the method of adsorbing Mo, e.g., the column shape, the linear flow rate, etc.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n,  ) method, 3
) method, 3Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Namekawa, Yoji*; Nishikata, Kaori; Daigo, Fumihisa; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2020, P. 136, 2021/08
no abstracts in English
 Mo-adsorption/
Mo-adsorption/ Tc-elution properties of alumina with different surface structures
Tc-elution properties of alumina with different surface structuresFujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Kitagawa, Tomoya*; Matsukura, Minoru*; Hori, Junichi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(3), p.1355 - 1363, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:40.86(Chemistry, Analytical)We prepared three types of Al O
O with different surface structures and investigated
with different surface structures and investigated  Mo-adsorption/
Mo-adsorption/ Tc-elution properties using [
Tc-elution properties using [ Mo]MoO
Mo]MoO that was irradiated in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. Al
that was irradiated in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. Al O
O adsorbed [
adsorbed [ Mo]molybdate ions in solutions at different pH; the lower was the pH, the higher was the Mo-adsorption capacity of Al
Mo]molybdate ions in solutions at different pH; the lower was the pH, the higher was the Mo-adsorption capacity of Al O
O . The
. The  Tc-elution properties of molybdate ion adsorbed Al
Tc-elution properties of molybdate ion adsorbed Al O
O were elucidated by flowing saline. Consequently, it was suggested that
were elucidated by flowing saline. Consequently, it was suggested that  Mo-adsorption/desorption properties are affected by the specific surface of Al
Mo-adsorption/desorption properties are affected by the specific surface of Al O
O and
and  Tc-elution properties are affected by the crystal structure of Al
Tc-elution properties are affected by the crystal structure of Al O
O .
.
Benu, D. P.*; Earnshaw, J.*; Ashok, A.*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Saptiama, I.*; Yuliarto, B.*; Suendo, V.*; Mukti, R. R.*; Fukumitsu, Nobuyoshi*; Ariga, Katsuhiko*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.502 - 507, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:55.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kaminaga, Masanori; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hori, Naohiko; Naka, Michihiro
IAEA-TECDOC-1943, p.45 - 56, 2021/02
The JMTR operation was once stopped in order to have a check & review in August 2006, and the refurbishment and restart of JMTR was finally determined by the national discussion. The refurbishment was started from FY2007, and was finished in March 2011. However, at the end of the FY2010, the Great-Eastern-Japan-Earthquake occurred, and functional tests before the JMTR restart were delayed. On the other hand, based on the safety assessments considering the 2011 earthquake new regulatory requirements have established on Decmber18, 2013 by the NRA. The new regulatory requirements include the satisfaction of integrities for the updated earthquake forces, Tsunami, the consideration of natural phenomena, and the management of consideration in the Beyond Design Basis Accidents (BDBA) to protect fuel damage and to mitigate impact of the accidents. Analyses related to the new regulatory requirements have intensively been performed timely, and an application to the NRA had been submitted in March 27, 2015. After submission of application, seismic resistance assessment of JMTR reactor building was carried out by assuming the standard earthquake ground motion of 810 ga. As the results, it was found that seismic reinforcement work for reactor building and reactor pool wall were required. As a result, it became clear that at least 7 years of reinforcement work period and cost of about 40 billion yen are required for seismic reinforcement and to meet new regulatory standards. At the same time, it was made clear that high availability such as 8 operation cycles per year as originally planned cannot be expected due to aiging problem. For this reason, JAEA positioned JMTR as a decommissioning facility in the mid- and long-term plan of JAEA announced in April 2017. On the other hand, JAEA started to study the construction of a new material testing reactor. The examination results will be compiled by the end of FY2019. In this paper, outline of JMTR decommissioning plan is described.
 for production of
for production of  Tc radioactive isotope
Tc radioactive isotopeSuematsu, Hisayuki*; Sato, Soma*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Niihara, Koichi*; Nanko, Makoto*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies (Internet), 8(4), p.1154 - 1161, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.68(Materials Science, Ceramics)Pulsed electric current sintering of molybdenum trioxide (MoO ) was carried out by one- and two-step pressuring methods for fabrication of irradiation target using production of
) was carried out by one- and two-step pressuring methods for fabrication of irradiation target using production of  Mo and
Mo and  Tc nuclear medicine. At 550
Tc nuclear medicine. At 550 C by the two-step pressurizing method, a relative density of 93.1% was obtained while, by the one-step pressurization method, the relative density was 76.9%. Direct sample temperature measurements were conducted by inserting a thermocouple in a punch. By the two-step pressurizing method, the sample temperature was higher than that by the one-step pressurizing method even almost the same die temperature. From voltage and current waveforms, it was thought that the conductivity of the sample increased by the two-step pressurizing method to increase the sample temperature and the relative density. The two-step pressurization method enables us to prepare dense targets at a low temperature from recycled and coarse-grained
C by the two-step pressurizing method, a relative density of 93.1% was obtained while, by the one-step pressurization method, the relative density was 76.9%. Direct sample temperature measurements were conducted by inserting a thermocouple in a punch. By the two-step pressurizing method, the sample temperature was higher than that by the one-step pressurizing method even almost the same die temperature. From voltage and current waveforms, it was thought that the conductivity of the sample increased by the two-step pressurizing method to increase the sample temperature and the relative density. The two-step pressurization method enables us to prepare dense targets at a low temperature from recycled and coarse-grained  Mo enriched MoO
Mo enriched MoO powder.
powder.
Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1276 - 1286, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of materials of mineral-insulated (MI) cables on their electrical characteristics upon exposure to high-temperature conditions was examined via a transmission test, in the objective of achieving the stability of the potential distribution along the cable length. Occurrence of a voltage drop along the cable was confirmed for aluminum oxide (Al O
O ) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al
) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al O
O and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires (
and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires ( ) and the distance between them (
) and the distance between them ( ) were varied. Considering the variation of
) were varied. Considering the variation of  , the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio
, the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio 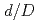 of 0.35, obtained by dividing
of 0.35, obtained by dividing  with that of the insulating material (
with that of the insulating material ( ). In case of varying
). In case of varying  , a minimum voltage drop was l/
, a minimum voltage drop was l/ of 0.5.
of 0.5.
Seki, Misaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (62), p.9 - 19, 2020/09
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been contributing to various research and development activities such as the fundamental research of nuclear materials/fuels, safety research and development of power reactors, and radioisotope production since the beginning of the operation in 1968. JMTR, however, was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017 and it is taken an inspection of a plan concerning decommissioning because the performance of JMTR does not confirm with the stipulated earthquake resistance. As aluminum and beryllium are used for the core structural materials in JMTR, it is necessary to establish treatment methods of these materials for the fabrication of stable wastes. In addition, a treatment method for the accumulated spent ion-exchange resins needs to be examined. This report describes the overview of these examination situations.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n, ) method, 2
) method, 2Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Namekawa, Yoji*; Nishikata, Kaori; Kato, Yoshiaki; Sayato, Natsuki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 157, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Seki, Misaki; Ishikawa, Koji*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 279, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Seki, Misaki; Ishikawa, Koji*; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 257, 2019/08
no abstracts in English