Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Goto, Minoru; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Ueta, Shohei; Nakano, Masaaki*; Honda, Masaki*; Tachibana, Yukio; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Aihara, Jun; Fukaya, Yuji; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.507 - 513, 2015/09
A concept of a plutonium burner HTGR named as Clean Burn, which has a high nuclear proliferation resistance, had been proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In addition to the high nuclear proliferation resistance, in order to enhance the safety, we propose to introduce PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.

 ground quartet systems Sm
ground quartet systems Sm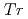
 Al
Al (
(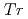 : Ti, V, Cr)
: Ti, V, Cr)Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Sakai, Akito*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(Suppl.B), p.SB050_1 - SB050_4, 2012/12
Recently, 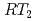 Al
Al compounds (
compounds ( : rare earth,
: rare earth,  : transition metal) have attracted much attention due to interesting physical properties closely related to their caged-structure. Each
: transition metal) have attracted much attention due to interesting physical properties closely related to their caged-structure. Each  ion is confined in a Frank-Kasper cage consisting of 16 Al atoms and the large coordination number leads to strong
ion is confined in a Frank-Kasper cage consisting of 16 Al atoms and the large coordination number leads to strong  -
- hybridization. In addition, the Frank-Kasper cage allows various multipole degrees of freedom for the
hybridization. In addition, the Frank-Kasper cage allows various multipole degrees of freedom for the  -electrons at low
-electrons at low  because of a highly symmetric crystalline-electric-field (CEF). Among the
because of a highly symmetric crystalline-electric-field (CEF). Among the 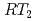 Al
Al series, Pr
series, Pr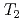 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V) and Sm
: Ti, V) and Sm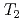 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) exhibit both these features. The
: Ti, V, Cr) exhibit both these features. The 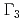 ground doublet systems Pr
ground doublet systems Pr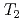 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V) show a phase transition at
: Ti, V) show a phase transition at 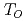 = 2.0K (Ti) and 0.6K (V). The order parameter is believed to be an electric quadrupole active in the
= 2.0K (Ti) and 0.6K (V). The order parameter is believed to be an electric quadrupole active in the 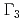 subspace. A possibility of the quadrupole Kondo effect has been discussed based on characteristic
subspace. A possibility of the quadrupole Kondo effect has been discussed based on characteristic  -dependence in specific heat, resistivity, and magnetic susceptibility. The
-dependence in specific heat, resistivity, and magnetic susceptibility. The 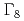 ground quartet systems Sm
ground quartet systems Sm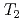 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) also exhibit a phase transition at
: Ti, V, Cr) also exhibit a phase transition at 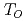 = 6.4K (Ti), 2.3K (V), and 1.8K (Cr). A nuclear specific heat study in SmTi
= 6.4K (Ti), 2.3K (V), and 1.8K (Cr). A nuclear specific heat study in SmTi Al
Al suggests that the primary order parameter is a magnetic dipole in spite of field-insensitive nature of the phase boundary. A possible importance of a secondarily ordered octupole moment was discussed. We here present a microscopic study of PrTi
suggests that the primary order parameter is a magnetic dipole in spite of field-insensitive nature of the phase boundary. A possible importance of a secondarily ordered octupole moment was discussed. We here present a microscopic study of PrTi Al
Al and Sm
and Sm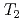 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) using muon spin relaxation. In PrTi
: Ti, V, Cr) using muon spin relaxation. In PrTi Al
Al , no additional local field was observed in the ordered phase. This strongly supports the quadrupole ordering scenario. On the other hand, an appearance of a coherent local field was observed below
, no additional local field was observed in the ordered phase. This strongly supports the quadrupole ordering scenario. On the other hand, an appearance of a coherent local field was observed below 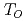 in Sm
in Sm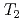 Al
Al . This is consistent with the primary magnetic dipole ordering. The frequency distribution suggests that the magnetic structure is possibly different between the Sm
. This is consistent with the primary magnetic dipole ordering. The frequency distribution suggests that the magnetic structure is possibly different between the Sm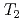 Al
Al compounds.
compounds.
 SR evidence of nonmagnetic order and
SR evidence of nonmagnetic order and 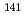 Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism in the cubic
Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism in the cubic 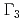 ground doublet system PrTi
ground doublet system PrTi Al
Al
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Luetkens, H.*; Baines, C.*; Sakai, Akito*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(11), p.113703_1 - 113703_4, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:77.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 131(26), p.9180 - 9181, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report here on the successful oxidation of element 102, nobelium (No), on an atom-at-a-time scale in 0.1 M  -hydroxyisobutyric acid (
-hydroxyisobutyric acid ( -HIB) solution using newly developed flow electrolytic column chromatography. It is found that the most stable No
-HIB) solution using newly developed flow electrolytic column chromatography. It is found that the most stable No is oxidized to No
is oxidized to No within 3 min and that the oxidized No complex with
within 3 min and that the oxidized No complex with  -HIB holds the trivalent state in the column above the applied potential of 1.0 V.
-HIB holds the trivalent state in the column above the applied potential of 1.0 V.
Hattori, Takanori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Materia, 47(10), p.507 - 512, 2008/10
We investigate pressure-induced structural changes in liquids of tetrahedrally bonded materials by a synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The liquids show various structural changes, depending on their ionic characters in the chemical bonds. The liquids with a small ionic character, such as GaSb, InSb, InAs, show continuous structural changes over a wide pressure region of about 20 GPa. In contrast, those with a large ionic character, such as CdTe, AgI, show drastic structural changes within a narrow pressure region of  2 GPa. We discuss the effect of the ionicity on the pressure-induced structural changes in liquid and compare the effect with that in the crystalline phases.
2 GPa. We discuss the effect of the ionicity on the pressure-induced structural changes in liquid and compare the effect with that in the crystalline phases.
Yan, X.; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Ohashi, Kazutaka; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Nuclear Technology, 163(3), p.401 - 415, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)A rupture of primary piping in HTGR represents a design basis event. In such a loss of coolant event a safety issue remains graphite oxidation damage to fuel and core should major air ingress take place through the breached primary boundary. The present study deals with the two most probable cases of air ingress. The first results from rupture of a standpipe. A design change proposed in the vessel top structure intends to rule out any probability of a standpipe rupture. The feasibility of the modified structure is evaluated. The second case results from rupture of a main coolant pipe. Experiment and analysis are performed to gain understanding of the multi-phased air ingress phenomena and accordingly a new mechanism of sustained counter-air diffusion is proposed that is fully passive and effective in preventing major air ingress in the event of main coolant pipe rupture. The results of the present study may lead to improved safety and economic design of the HTGR.
Shimojo, Fuyuki*; Miyata, Yasuhisa*; Sugahara, Takayuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 98, p.042016_1 - 042016_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The structural and bonding properties of liquid InAs under pressure are investigated by ab initio molecular-dynamics simulations. The calculated structure factors are in good agreement with the recent X-ray diffraction measurements over a wide range of pressure. It is shown that the pressure dependence of the spatial correlation between atoms depends on the species of atomic pairs reflecting the strength of the covalent bonding. A detailed investigation of the pair distribution functions confirms that different pressure-induced structural changes occur below and above 6-10 GPa. It is suggested that such structural changes are related to the reduction of the covalent nature under pressure.
Hattori, Takanori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Miyata, Yasuhisa*; Sugahara, Takayuki*; Shimojo, Fuyuki*
Physical Review B, 76(14), p.144206_1 - 144206_10, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the pressure-induced structural changes of liquid III-V compounds systematically, the pressure dependence of liquid InAs was investigated using the synchrotron X-ray diffraction and an 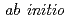 molecular dynamics simulation (AIMD). The X-ray diffraction experiments revealed that the liquid changes its compression behavior from a nearly uniform type to a nonuniform one around 9 GPa. Corresponding to this change, the coordination number CN, which is maintained up to 9 GPa, markedly increases from 6.0 to 7.5. The AIMD simulation revealed that this change is related to the change in the pressure dependence of all three pair correlations. In particular, a marked change is observed in the As-As correlation; in the low pressure region the position of the first peak in
molecular dynamics simulation (AIMD). The X-ray diffraction experiments revealed that the liquid changes its compression behavior from a nearly uniform type to a nonuniform one around 9 GPa. Corresponding to this change, the coordination number CN, which is maintained up to 9 GPa, markedly increases from 6.0 to 7.5. The AIMD simulation revealed that this change is related to the change in the pressure dependence of all three pair correlations. In particular, a marked change is observed in the As-As correlation; in the low pressure region the position of the first peak in 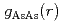 ,
, 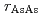 , increases with maintaining the CN
, increases with maintaining the CN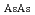 , but in the high pressure region the
, but in the high pressure region the 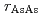 stops increasing and the CN
stops increasing and the CN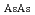 begins to increase. The results for InAs are compared with those for GaSb and InSb and the systematics of the pressure-induced structural change of liquid III-V compounds are dicussed.
begins to increase. The results for InAs are compared with those for GaSb and InSb and the systematics of the pressure-induced structural change of liquid III-V compounds are dicussed.
Narushima, Takashi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Hinzmann, A*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Physical Review B, 76(10), p.104204_1 - 104204_8, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid Sn was investigated up to 19.4 GPa by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Upon compression up to about 3-6 GPa, the structural features, which reflect the anisotropic local structure become less prominent; i.e., the hump on the high- side of the first peak in the structure factor
side of the first peak in the structure factor 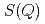 becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in
becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in 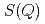 ,
, 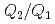 , decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
, decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
Hattori, Takanori; Taga, Naohito*; Takasugi, Yukinobu*; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2005, Part A, p.42 - 43, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 73(5), p.054203_1 - 054203_9, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:68.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid CdTe was investigated at pressures up to 23.5GPa using synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The structure factor, S(Q), and the pair distribution function, g(r), drastically change in two pressure regions, 1.8-3.0 GPa and 7.0-9.0 GPa, accompanied with marked increase in the average coordination number, CN. These findings suggest that there exists at least three stable liquid forms below 23.5GPa. The pressure interval of the structural change is much smaller compared to other liquids of tetrahedrally bonded materials. Comparing the shapes of S(Q) and g(r), and other structural parameters with the respective data for the reference materials reveals that the lowest- and intermediate-pressure forms have the same local structures as the crystalline counterpart (zinc-blende-like local structure and a NaCl-like local structure), while the highest-pressure form has a different local structure from that in the crystalline form.
Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Maekawa, Isamu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(3), p.257 - 267, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(36), p.6085 - 6103, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:92.19(Physics, Condensed Matter)X-ray structural studies on several elemental liquids under high pressure are reviewed. Combination of synchrotron radiation sources and large volume presses enables us to carry out in-situ structural measurements on liquids at high pressures up to several GPa. The measurements have revealed that compressions of liquid alkali metals are almost uniform, whereas those of liquids that have covalent components in bonding are mostly anisotropic. In some elements, different types of volume dependence of the nearest neighbour distances are observed in different pressure ranges. This behaviour suggests that the liquid phase can be divided in regions. Although most of the observed structural changes are continuous, a discovery of an abrupt structural change in liquid phosphorus, which is completed over a pressure range of less than 0.05 GPa around 1GPa and 1050  C, supports existence of a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition.
C, supports existence of a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Mizutani, Takeshi; Utsumi, Wataru; Shimomura, Osamu; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Physica Status Solidi (B), 223(2), p.401 - 404, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:66.81(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Kozaburo*; Inui, Masanori*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 42(1), p.33 - 40, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori; Shimomura, Osamu; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 250-252(Part2), p.537 - 541, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Tamura, Kozaburo*; Inui, Masanori*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Shimomura, Osamu
Hoshako, 12(1), p.17 - 23, 1999/02
no abstracts in English
Morimoto, Yoshiki*; Kato, Sayuri*; Toda, Naohiro*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Yaoita, Kenichi*; Shimomura, Osamu
Review of High Pressure Science and Technology, 7, p.245 - 247, 1998/03
X-ray diffraction for liquid Rb and liquid Na has been measured under pressure up to 6 GPa using synchrotron radiation. Volume dependences of static structure factor 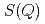 and pair distribution function
and pair distribution function 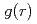 were obtained to the volume range
were obtained to the volume range 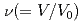 of 0.52 for liquid Rb and
of 0.52 for liquid Rb and  of 0.73 for liquid Na to investigate the effect of the electronic change on the structure of liquid metals. With increasing pressure, the peaks of
of 0.73 for liquid Na to investigate the effect of the electronic change on the structure of liquid metals. With increasing pressure, the peaks of 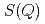 of both liquid Rb and liquid Na shift towards higher
of both liquid Rb and liquid Na shift towards higher  , and the heights of the first peak increase. Theses volume dependences of the structural data are compared with those for other metals under pressure and expanded fluids.
, and the heights of the first peak increase. Theses volume dependences of the structural data are compared with those for other metals under pressure and expanded fluids.
Toda, Naohiro*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Review of High Pressure Science and Technology, 7, p.647 - 649, 1998/03
The electrical conductivity  has been measured at pressures
has been measured at pressures  to 8 GPa and temperatures
to 8 GPa and temperatures  of 77-300K in evaporated amorphous Ge (a-Ge), a-Ge-Cu alloys and a-Ge-Al alloys. The
of 77-300K in evaporated amorphous Ge (a-Ge), a-Ge-Cu alloys and a-Ge-Al alloys. The  dependence of
dependence of  is well described by a power lw at low temperatures below 150 K, which is expemcted from a multi-phonon tunneling transition process model with weak electron-lattice coupling, rather than the Mott's variable range hopping conduction model. The exponent
is well described by a power lw at low temperatures below 150 K, which is expemcted from a multi-phonon tunneling transition process model with weak electron-lattice coupling, rather than the Mott's variable range hopping conduction model. The exponent  in the power law changes with increasing pressure. For both a-Ge
in the power law changes with increasing pressure. For both a-Ge Cu
Cu and a-Ge
and a-Ge Al
Al alloys, d(ln
alloys, d(ln  )/d
)/d show positive values in the low pressure region and negative values in the high pressure region. Results are discussed from several hopping conduction models.
show positive values in the low pressure region and negative values in the high pressure region. Results are discussed from several hopping conduction models.
Mori, Yuki*; Kato, Sayuri*; Mori, Hiroko*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Review of High Pressure Science and Technology, 7, p.353 - 355, 1998/03
The temperature dependence of phase transitions in GaSb, AlSb, GaAs, GaP, InAs, ZnSe, and CdTe are studied by X-ray diffraction measurements under pressure upto 30 GPa at temperatures of 90-300K. The phase transitions depend on paths in a pressure-temperature phase diagram. The structure of the recovered phase after decompression depends on the ionicity in bonding: amorphous for small ionicity, the stable zincblende structure for large ionicity, and microcrystalline or moderate ionicity. These results are discussed by using a configuration-coordinate model.