Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Goto, Minoru; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Ueta, Shohei; Nakano, Masaaki*; Honda, Masaki*; Tachibana, Yukio; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Aihara, Jun; Fukaya, Yuji; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.507 - 513, 2015/09
A concept of a plutonium burner HTGR named as Clean Burn, which has a high nuclear proliferation resistance, had been proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In addition to the high nuclear proliferation resistance, in order to enhance the safety, we propose to introduce PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Tachibana, Yukio; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
FAPIG, (190), p.20 - 24, 2015/07
In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat in HTGRs must be removed by radiation, thermal conduction and natural convection. Passive heat removal performance is of primary concern for enhancing inherent safety features of HTGRs. Therefore, the thermal hydraulic analyses for normal operation and a loss of forced cooling accident are conducted by using thermal hydraulic CFD code. And further, a multi-hole type fuel block of MHTGR is also modeled and the flow and heat transfer characteristics are compared with a pin-in-block type fuel block.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Passive heat removal performance of the reactor vessel cavity cooling system (RCCS) is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat must be removed by radiation and natural convection of RCCS. Thus thermal hydraulic analysis of reactor internals and RCCS is powerful means for evaluation of the heat removal performance of RCCS. The thermal hydraulic analyses using CFD computation tools are conducted for normal operation of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and are compared to the temperature distribution of measured data. The calculated temperatures on outer faces of the permanent side reflector (PSR) blocks are in fair agreement with measured data. The transient analysis for decay heat removal mode in HTTR is also conducted.
 C high temperature gas-cooled reactor
C high temperature gas-cooled reactorNakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The conceptual core design study of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is performed. The major specifications are 600 MW thermal output, 950 C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release,
C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release, 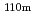 Ag and
Ag and  Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Yan, X.; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Ohashi, Kazutaka; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Nuclear Technology, 163(3), p.401 - 415, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)A rupture of primary piping in HTGR represents a design basis event. In such a loss of coolant event a safety issue remains graphite oxidation damage to fuel and core should major air ingress take place through the breached primary boundary. The present study deals with the two most probable cases of air ingress. The first results from rupture of a standpipe. A design change proposed in the vessel top structure intends to rule out any probability of a standpipe rupture. The feasibility of the modified structure is evaluated. The second case results from rupture of a main coolant pipe. Experiment and analysis are performed to gain understanding of the multi-phased air ingress phenomena and accordingly a new mechanism of sustained counter-air diffusion is proposed that is fully passive and effective in preventing major air ingress in the event of main coolant pipe rupture. The results of the present study may lead to improved safety and economic design of the HTGR.
Shibata, Taiju; Sumita, Junya; Baba, Shinichi; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.728 - 733, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.1698 - 1703, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.143 - 147, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Shibata, Taiju; Sumita, Junya; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo
FAPIG, (169), p.13 - 17, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Maekawa, Isamu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(3), p.257 - 267, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Makoto*; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*; Ito, Tsutomu*; Sakuma, Takaaki*; Shibata, Taiju; Baba, Shinichi; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Ibaraki Koenkai (2004) Koen Rombunshu (No.040-3), p.57 - 58, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Sumita, Junya; Nakano, Masaaki*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro
JAERI-Tech 2004-055, 25 Pages, 2004/08
Neutron irradiation remarkably reduces the thermal conductivity of graphite, and the reduced thermal conductivity is recovered by annealing effect if the graphite is heated above the irradiation temperature. Therefore, it is expected that the reduced thermal conductivity of graphite components in the HTGR could be recovered by the annealing effect in accidents, such as a depressurization accident. Then, an analytical investigation of the annealing effect on thermal performance of a HTGR core was carried. The analysis showed that the annealing effect reduces the maximum fuel temperature about 70 C, and it is important to introduce the annealing effect appropriately in the temperature analysis of the core components and reactor internals. In addition, an annealing test method was investigated to evaluate the effect quantitatively, and the test plan was made.
C, and it is important to introduce the annealing effect appropriately in the temperature analysis of the core components and reactor internals. In addition, an annealing test method was investigated to evaluate the effect quantitatively, and the test plan was made.
Hattori, Takanori; Mori, Tetsuji*; Narushima, Takashi*; Funamori, Nobumasa*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
no journal, ,
In the previous studies for the pressure-induced structural changes in liquids of tetrahedrally bonded materials, the followings are elucidated. (1) With increasing pressure, the anisotropy in local structures becomes smaller and liquids approach simple liquid metals. (2) The pressure-induced changes become less prominent and the liquids take a unique structure which does not change by compression. (3) As a result, the liquid preserves anisotropy in the local structure at pressures where the crystalline counterpart loses the anisotropy. In our previous studies, the pressure-induced changes were analyzed with the distorted crystalline model. However, this model assumes the existence of the crystalline-type local structure. In the present study, we analyzed it with a RMC method, which does not involve such assumption. Based on the results, we discuss the high-pressure evolution of the local structures in the liquids.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Murakami, Tomoyuki; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Sumita, Junya; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tachibana, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Tachibana, Yukio
no journal, ,
Passive heat removal performance is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat of fuels must be removed to graphite blocks by radiation, thermal conduction and natural convection in block-type HTGR. Because the temperature of fuels is strongly affected by natural convection of coolant in core region, it becomes important to estimate the behavior of natural convection in core region precisely. The numerical study is performed using thermal hydraulic CFD code with one column-model of fuel blocks which is represented explicitly as individual coolant channels in the fuel block. The thermal hydraulic analyses are conducted for normal operation and loss of forced cooling accident conditions, as results, the flow and heat transfer characteristics of fuel blocks are quantitatively evaluated both in forced convection mode and natural convection mode. The 30 sector model of limited core region is also developed for CFD calculation of natural convection flow pattern in core. The mass flow rate of upward flow is considerably reduced from one column model. And further, multi-hole type fuel blocks of MHTGR are also modeled and compare the flow and heat transfer characteristics between multi-hole type and pin-in-block type fuel block. The multi-hole type fuel block raise more natural convection flow in core region than pin-in-block type.
sector model of limited core region is also developed for CFD calculation of natural convection flow pattern in core. The mass flow rate of upward flow is considerably reduced from one column model. And further, multi-hole type fuel blocks of MHTGR are also modeled and compare the flow and heat transfer characteristics between multi-hole type and pin-in-block type fuel block. The multi-hole type fuel block raise more natural convection flow in core region than pin-in-block type.
Yan, X.; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Okamoto, Futoshi*
no journal, ,
Safety goal for VHTR considers rupture of main primary piping as design basis accident in which animportant safety issue remains to be potential fuel and core graphite oxidation in case of significant air ingressinto the reactor core through the breached primary piping. The present study analyzes the air ingress behaviorand newly proposes a sustained counter-air diffusion (SCAD) mechanism for its practical prevention.
Koike, Kazuhiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Satoru; Namekawa, Takashi; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Hashimoto, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English