Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Ida, Mizuho*; Ito, Yuzuru; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Edao, Yuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 66(1), p.46 - 56, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Fukada, Satoshi*; Yagi, Juro*; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(12), p.691 - 705, 2012/12
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kanemura, Takuji; Kondo, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Otaka, Masahiko; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(9-11), p.2491 - 2494, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)In IFMIF/EVEDA, tasks for lithium target system are shared to 5 validation tasks (LF1-5) and a design task (LF6). The purpose of LF1 task is to construct and operate the EVEDA lithium test loop, and JAEA has a main responsibility to the performance of the Li test loop. LF2 is a task for the diagnostics of the Li test loop and IFMIF design. Basic research for the diagnostics equipment has been completed, and the construction for the Li test loop will be finished before March in 2011. LF4 is a task for the purification systems with nitrogen and hydrogen. Basic research for the purification equipment has been completed, and the construction of the nitrogen system for the Li test loop will be finished before March in 2011. LF5 is a task for the remote handling system with the target assembly. JAEA has an idea to use the laser beam for cutting and welding of the lip part of the flanges. LF6 is a task for the design of the IFMIF based on the validation experiments of LF1-5.
Ida, Mizuho; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Kondo, Hiroo; Miyashita, Makoto; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugiura, Hirokazu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1294 - 1298, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) was started. As a Japanese activity for the target system, EVEDA Lithium Test Loop simulating hydraulic and impurity conditions of IFMIF is under design and preparation for fabrication. Feasibility of thermo-mechanical structure of the target assembly and the replaceable back-plate made of F82H (a RAFM) and 316L (a stainless steel) is a key issue. Toward final validation on the EVEDA loop, diagnostics applicable to a high-speed free-surface Li flow and hot traps to control nitrogen and hydrogen in Li are under tests. For remote handling of target assemblies and the replaceable back-plates activated up to 50 dpa/y, lip weld on 316L-316L by laser and dissimilar weld on F82H-316L are under investigation. As engineering design of the IFMIF target system, water experiments and hydraulic/thermo-mechanical analyses of the back-plate are going.
Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Asano, Norikazu; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Yanai, Tomohiro; Sato, Shinichi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Oto, Tsutomu; Kimura, Tadashi; Kawamata, Takanori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-030, 165 Pages, 2009/07
The condition of facilities and machinery used continuously were investigated before the renewal work of JMTR on FY 2007. The subjects of investigation were reactor building, primary cooling system tanks, secondary cooling system piping and tower, emergency generator and so on. As the result, it was confirmed that some facilities and machinery were necessary to repair and others were used continuously for long term by maintaining on the long-term maintenance plan. JMTR is planed to renew by the result of this investigation.
Narushima, Takashi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Hinzmann, A*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Physical Review B, 76(10), p.104204_1 - 104204_8, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid Sn was investigated up to 19.4 GPa by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Upon compression up to about 3-6 GPa, the structural features, which reflect the anisotropic local structure become less prominent; i.e., the hump on the high- side of the first peak in the structure factor
side of the first peak in the structure factor 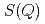 becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in
becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in 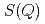 ,
, 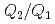 , decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
, decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
Hattori, Takanori; Taga, Naohito*; Takasugi, Yukinobu*; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2005, Part A, p.42 - 43, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 73(5), p.054203_1 - 054203_9, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:68.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid CdTe was investigated at pressures up to 23.5GPa using synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The structure factor, S(Q), and the pair distribution function, g(r), drastically change in two pressure regions, 1.8-3.0 GPa and 7.0-9.0 GPa, accompanied with marked increase in the average coordination number, CN. These findings suggest that there exists at least three stable liquid forms below 23.5GPa. The pressure interval of the structural change is much smaller compared to other liquids of tetrahedrally bonded materials. Comparing the shapes of S(Q) and g(r), and other structural parameters with the respective data for the reference materials reveals that the lowest- and intermediate-pressure forms have the same local structures as the crystalline counterpart (zinc-blende-like local structure and a NaCl-like local structure), while the highest-pressure form has a different local structure from that in the crystalline form.
 NbS
NbS
Guo, F. Z.*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Matsui, Fumihiko*; Kato, Yukako*; Daimon, Hiroshi*; Koyano, Mikio*; Yamamura, Yasuhisa*; Tsuji, Toshihide*; Saito, Yuji
Journal of Applied Physics, 99(2), p.024907_1 - 024907_3, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:30.56(Physics, Applied)Stereoatomscope was used to study the atomic arrangements of intercalation compound Fe NbS
NbS . The three-dimensional atomic arrangements around different kinds of atoms (Nb and Fe) are visualized by taking the photoelectron angular distribution (PEAD) patterns at clockwise and counterclockwise circularly polarized lights. Atomic distances between the emitters and the scatterers are obtained from the PEAD patterns by measuring the rotation angles of the forward focusing peaks. The applications of stereoatomscope to intercalation compound show the possibility to build an ultimate microscope for scientist.
. The three-dimensional atomic arrangements around different kinds of atoms (Nb and Fe) are visualized by taking the photoelectron angular distribution (PEAD) patterns at clockwise and counterclockwise circularly polarized lights. Atomic distances between the emitters and the scatterers are obtained from the PEAD patterns by measuring the rotation angles of the forward focusing peaks. The applications of stereoatomscope to intercalation compound show the possibility to build an ultimate microscope for scientist.
Kikuchi, Makoto*; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*; Ito, Tsutomu*; Sakuma, Takaaki*; Shibata, Taiju; Baba, Shinichi; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Ibaraki Koenkai (2004) Koen Rombunshu (No.040-3), p.57 - 58, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Kondo, Hiroo; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Horiike, Hiroshi; Terai, Takayuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Three and half years has been passed from the start of IFMIF/EVEDA. In IFMIF/EVEDA, tasks for Lithium Target System consists of 5 validation tasks (LF1-5) and a design task (ED3), and are shared by Japan and Europe. Japan is covering the construction and operation of EVEDA Li Test Loop (LF1), diagnostics (LF2), purification system (LF4), remote handling system (LF5) and engineering design (ED3) with the contribution from universities. The present status of these tasks will be reported in the conference.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Ito, Yuzuru*; Hoashi, Eiji*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiated inorganic hydrates
-ray irradiated inorganic hydratesHiraoka, Ryo*; Kawai, Masashi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Ikarugi, Riko; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Kumagai, Jun*
no journal, ,
ESR measurements were conducted on H atoms in gamma-irradiated inorganic hydrates at 77 K. The results showed that a relatively high amount of H atoms was observed in Ba(OH) 8H
8H O at 77 K, although it had a small yield of H
O at 77 K, although it had a small yield of H at room temperature. On the other hand, in Ba(OH)
at room temperature. On the other hand, in Ba(OH) H
H O, no H atoms were observed, and the yield of H
O, no H atoms were observed, and the yield of H at room temperature was large. In CaSO
at room temperature was large. In CaSO 2H
2H O, two types of H atoms with different line widths were observed. The H atom with a larger magnetic interaction with hydrated water decreased first with increasing temperature.
O, two types of H atoms with different line widths were observed. The H atom with a larger magnetic interaction with hydrated water decreased first with increasing temperature.
Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Kondo, Hiroo; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Terai, Takayuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
I will present the outline and the status of the Japanese tasks for the Li Target system, which is ongoing now under the International Fusion Material Irradiation Facility (IFMIF)/Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA). The latest progresses are a completion of the EVEDA Li Loop, a fablication of the remote handling equipment and a repair from the damages caused by the earthquake.
 measurement method for radioactive waste analysis
measurement method for radioactive waste analysisKumagai, Yuta; Kawai, Masashi*; Ikarugi, Riko; Oka, Toshitaka; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Jun*
no journal, ,
We have developed a highly sensitive H analysis method by employing a gas chromatograph with a senser diode, aiming to apply for small amounts of H
analysis method by employing a gas chromatograph with a senser diode, aiming to apply for small amounts of H production from radioactive wastes. The H
production from radioactive wastes. The H analysis method was tested with an X-ray irradiation experiment of Na
analysis method was tested with an X-ray irradiation experiment of Na WO
WO 2H
2H O. Even though the absorbed dose was less than 100 Gy, the H
O. Even though the absorbed dose was less than 100 Gy, the H production from only 1 g of the sample can be analyzed by our method. Based on the experimental results, the lower limit of H
production from only 1 g of the sample can be analyzed by our method. Based on the experimental results, the lower limit of H quantification was evaluated to be 2
quantification was evaluated to be 2  10
10 mol.
mol.
Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Yang, Y.*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Yoshimura, Yoshitaka*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; Tabata, Makoto*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Nakaniwa, Koichi; Ito, Yuzuru; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Ito, Takahiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Ida, Mizuho; Kondo, Hiroo; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Terai, Takayuki*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
IFMIF/EVEDA started at July in 2007. Li Target System consists of five validation tasks (LF1-5) and one design task (LF6). Present status of Li Test Loop Construction and Operation task (LF1) is to complete the fabrication and installation of the almost key components except Target Assembly and Two types of traps for nitrogen and hydrogen, and to continue the connection with the components by the pipes. In the Diagnostics task (LF2), the characterization of the contact probe level meter is on going in Osaka University. In the Purification System task (LF4), the characterization of the Fe-Ti gettering material in Tokyo University and of Y gettering material in Kyushu University is on going. In the Remote Handling task (LF5), the design of the experimental facility has been finished. In the Engineering Design task (LF6), the engineering design for the IFMIF will be completed based on the validation tasks (LF1-5).
Nanayama, Futoshi*; Yamaguchi, Tatsuhiko*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Tsuji, Tomohiro*; Ikeda, Michiharu*; Kondo, Yasuo*; Miwa, Michiko*; Sugiyama, Shinji*; Kimura, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
The characteristics of the post-LGM incised valley fills and the depositional sequence were examined the SKM core collected in the Sukumo coastal lowland, where is expected to huge seismic subsidence due to the Nankai Trough great earthquakes. Our sedimentological, radiocarbon dating and paleoenvironmental results are as bellows. Sediments of the SKM core clearly show a succession influenced by post-glacial sea level change. The Matsuda River incised valley was formed in LGM and filled by fluvial sand and gravels in late Pleistocene. After the postglacial transgression, sea level reached -30 m (a.s.l.) at 9.8 ka and the incised valley changed to an estuary environment. The sea level continued to rise and it became an inner bay mud bottom environment, and reaching a maximum water depth was at 7.5 ka. The 7.3 ka Kikai caldera eruption in southern Kyushu caused heavy K-Ah ash fall in southwestern Shikoku, and then large-scale lahars frequently occurred immediately after the ash fall because of the vicinity of volcanic source. After ash fall, the K-Ah secondary sediments rapidly deposited on the inner bay environment and caused forced regression. After 7.0 ka, the growth of the delta became active ahead of the other regions, which may be due to the large K-Ah ash fall. At 5 ka, the sea level reached + 2.5 m (a.s.l.) estimated by the Sukumo midden and this altitude is recognized as the Holocene marine limit in this area. The information on relative sea level change during the past 10000 years has revealed that the Sukumo Bay area has not subsided due to seismic crustal deformation.
Yamaguchi, Tatsuhiko*; Tsuji, Tomohiro*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Ikeda, Michiharu*; Kondo, Yasuo*; Miwa, Michiko*; Hamada, Yohei*
no journal, ,
Shikoku Island is situated 150 km northwest of the Nankai trough that has developed in response to the convergence of the subducting Philippine Sea Plate and overriding Eurasian Plate. This tectonism causes deformation of the island, megathrust earthquakes, and tsunamis. Shikoku Island experiences coseismic and interseismic deformation. The middle Holocene tectonics of the island are still poorly understood. Relative sea-level (RSL) changes indicated by coastal sediments potentially record seismic uplift and subsidence. To infer RSL changes between 8 and 4 cal. kyr BP, we studied Holocene ostracode assemblages from the SKM drill core in Sukumo, southwest Shikoku Island (Tsuji et al., 2018, JpGU, MIS11-P19), and from six cores in the northern part of the island (Yasuhara et al., 2005, Palaeo3; Yasuhara and Seto, 2006, Paleontol. Res. 10). To estimate paleo-water depth and RSL, we employed the ostracode assemblages and modern analog technique. The SKM core is composed of conglomerate, ash, and mud chiefly. Its geological age was examined, using the  C dating method (Nakanishi et al., 2019, Radiocarbon). The differences in RSL were identified across the island, possibly due to convergence of the Philippine Sea Plate.
C dating method (Nakanishi et al., 2019, Radiocarbon). The differences in RSL were identified across the island, possibly due to convergence of the Philippine Sea Plate.