Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Materials Transactions, 62(6), p.763 - 769, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the iron rust layer formed on the low alloy steel under air-solution alternating conditions was investigated by cross-sectional observation and analysis, and the mechanism of the accelerated corrosion of the steel under alternating conditions was clarified. The observations and analysis showed that the multilayered iron rust layer composed of the red rust layer (FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
Tsukada, Takashi; Soma, Yasutaka
Hozengaku, 19(4), p.37 - 44, 2021/01
Corrosion Cracking phenomena in JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor) the first Japanese Light Water Reactor is reviewed. This review describes two major cracking failure. The first was found during inspection in 1966 as the cracking failure on weld-overlay cladding at the inner wall of the top head. A series of analysis showed that some of the cracks reached the base metal across the weld boundaries and further penetrated into the vessel wall. Significant depletion of ferrite content was detected in manually welded part considered to assisted the cracking. These inspection result in improvement of the welding procedure and no similar failures have been reported in Japanese reactor. This mode of failure gave rise to a new research field studying the corrosion fatigue behavior of low alloy steel because of importance to assess pressure boundary of the reactor. The experiment of JPDR also contributed to the establishment of international cooperation for studying EAC (environmentally assisted cracking). The second failure was found in 1972 near the welded part between stainless piping and safe end. The extensive research concluded that this failure was caused by Stress Corrosion Cracking.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(9), p.246 - 252, 2020/09
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of artificial sea water concentration on the corrosion rate of carbon steel under air/solution alternating condition, and to clarify the corrosion mechanism of carbon steel that changes with artificial seawater concentration. Mass measurements showed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in the alternating condition accelerates with increasing concentration in the concentration region between deionized water to 200 times diluted artificial seawater (ASW), and the corrosion rate decreases with increasing concentration in the concentration region between 20 times diluted ASW to undiluted ASW. It can be considered that the reason why the carbon steel corrosion was suppressed in highly concentrated artificial seawater would Mg ions and Ca ions in the artificial seawater precipitate and cover on the surface due to the increase in pH near the surface by oxygen reduction reaction.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(8), p.205 - 211, 2019/08
In the present study, the iron rust layer formed on the low ally steel in air-solution alternating condition was investigated by cross-sectional observation and analysis, and the mechanism of accelerated corrosion of the steel in the alternating condition was clarified. Observation and analysis showed that the multi-layered iron rust layer composed of red rust layer (FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multi-layered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of the steel in the alternating condition. This acceleration would be the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel in the alternating condition was accelerated.
), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multi-layered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of the steel in the alternating condition. This acceleration would be the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel in the alternating condition was accelerated.
 and Br
and Br and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steel
and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steelHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.304 - 314, 2017/09
A model simulation of  radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br
radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H
played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H O
O , was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl
, was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl +
+  OH
OH  ClOH
ClOH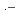 , ClOH
, ClOH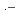
 Cl
Cl +
+  OH, and ClOH
OH, and ClOH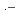 + H
+ H
 Cl
Cl + H
+ H O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl
O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl . An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H
. An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H O
O produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl
produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl and Br
and Br . However, at high pH values (
. However, at high pH values ( 12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H
12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H O
O was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
Fukui, Toshiki*; Maki, Takashi*; Miura, Nobuyuki; Tsukada, Takeshi*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(2), p.169 - 173, 2016/12
The basic research programs for the next generation vitrification technology, which are commissioned project from Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, have been implemented from 2014 until 2018 for developing the advanced vitrification technology of low level wastes and high level liquid wastes.
Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Hanawa, Satoshi; Kasahara, Shigeki; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(8), p.1183 - 1191, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Nuclear Science & Technology) radiolysis of sodium chloride solutions containing a small amount of bromide ion
radiolysis of sodium chloride solutions containing a small amount of bromide ionHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi
Nuclear Technology, 193(3), p.434 - 443, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/05
Effect of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide on corrosion rate of carbon steel in diluted artificial seawater was investigated by electrochemical methods. Diffusion coefficient and thickness of diffusion layer for oxygen and hydrogen peroxide were measured to estimate the diffusion limiting current density. Corrosion tests of carbon steel were also conducted in diluted artificial seawater containing oxygen and/or hydrogen peroxide at 323K. The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen peroxide was about 0.8 times lower than that of oxygen, and the thickness of diffusion layer was almost equivalent between oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Diffusion limiting current density of hydrogen peroxide was estimated to be 0.4 times lower than that of oxygen in the same concentration at 323K. Plot of corrosion rate with the addition of concentration of oxygen and 0.4 times concentration of hydrogen peroxide showed good correlation.
 radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater
radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawaterMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 18, 2015/03
The effect of changes in water by  -ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by
-ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by  irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 22, 2015/03
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants experienced seawater injection into the cores and spent fuel pools as an emergent measure for a short period after the accident. The injected seawater was exposed to radiation, and radiolytic species were produced. Especially, hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is known as an oxidant which affects corrosion of materials. In order to identify the important factor which results in the high concentration of H
) is known as an oxidant which affects corrosion of materials. In order to identify the important factor which results in the high concentration of H O
O in seawater radiolysis, the concentrations of H
in seawater radiolysis, the concentrations of H O
O in
in  -irradiated artificial seawater was measured and compared with the result of radiolysis calculation. Solutions containing some constituents of seawater were also measured to identify which ion affects H
-irradiated artificial seawater was measured and compared with the result of radiolysis calculation. Solutions containing some constituents of seawater were also measured to identify which ion affects H O
O production of seawater radiolysis. The experimental results showed that the H
production of seawater radiolysis. The experimental results showed that the H O
O production from seawater radiolysis is mainly attributed to reactions of Cl
production from seawater radiolysis is mainly attributed to reactions of Cl and Br
and Br in water radiolysis, though many kinds of ions are dissolved in seawater.
in water radiolysis, though many kinds of ions are dissolved in seawater.
Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(3), p.91 - 97, 2015/03
In the boiling water reactors (BWRs), reactor cooling water is maintained in high purity condition by controlling of a deionizing and deaerating apparatus, however H O
O contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H
contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H O
O , the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H
, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H O
O concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4
concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4 10
10 S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288
S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288 C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H
C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H O
O concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H
concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H O
O . The diffusion coefficient of H
. The diffusion coefficient of H O
O at 288
at 288 C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H
C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H O
O concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5
concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5 10
10 cm
cm /s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O
/s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O .
.
 -ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral water
-ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral waterYamamoto, Masahiro; Nakano, Junichi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
Corrosion protection of RPV and PCV is an important issue for the long term maintenance until the end of the decommissioning procedures. One of the uncertain factors for the issue is an effect of radioactivity on corrosion of LAS and CS. Corrosion tests using LAS and CS were conducted in  -rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by
-rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by  -rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with
-rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with  -ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H
-ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H O
O was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in
was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in  -ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
-ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Katayama, Hideki*; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/10
In the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, seawater and natural river water were poured for emergency cooling. Corrosion of materials was worried because of high chloride ion concentration from seawater. The chloride ion concentration was decreased by de-chlorination operation. However, the water was not treated in the viewpoint of microbial breeding, so that many microbes could be alive and microbially induced corrosion (MIC) was worried. So, we attempted to examine the ability of MIC occurrence by using of corrosion potential analysis. Corrosion potentials of samples rose to about 300 mV nobler than the initial values in the NB added solution. The potentials of the welded samples more easily rose than the simple plate. These potential changes are attributed to the biofilms formed on the sample surface. After about 100 days' immersion, evidence of localized corrosion was not observed. More immersion time is needed to clarify the MIC ability.
 -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea saltMotooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), seawater was injected into spent fuel pools in March 2011. Zircaloy-2 is adopted for the fuel cladding at 1F. Zirconium alloys including Zircaloy-2 are susceptible to pitting corrosion in oxidizing chloride solutions. In this study, we investigated the effect of oxide film formed during  -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after  -ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under
-ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under  -ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under
-ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under  -ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
-ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
 atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under
atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under  -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.977 - 986, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Seawater was injected into the reactor cores in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Corrosion of reactor vessel steels is considered to progress. To evaluate durability of the reactor vessel steels, corrosion tests were conducted in diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  -rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N
-rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N H
H were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N
were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N H
H , weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N
, weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N H
H was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N
was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N H
H . When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N
. When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N , weight loss in the vessel steels, and O
, weight loss in the vessel steels, and O and H
and H O
O concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
 radiolysis on pit initiation of zircaloy-2 in water containing sea salt
radiolysis on pit initiation of zircaloy-2 in water containing sea saltMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.987 - 995, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi; Terakawa, Yuto; Ichise, Kenichi; Numata, Masami; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2014-004, 29 Pages, 2014/03
By the effect of the Great East Japan Earthquake, seawater was injected into spent fuel pools in unit 2, 3 and 4 at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant in order to cool spent fuels. It is known that chloride ion contained in seawater could cause pitting corrosion for metallic materials. It was concerned that radioactive products inside of fuel cladding tubes might be escaped through the pits. Therefore we have investigated the pit initiation condition of fuel cladding tubes by measuring pitting potential in order to evaluate stability of the enclosure function of fuel cladding tubes in spent fuel pools containing sea salt. In this report, we describe the development of specimen preparation techniques for pitting measurement of spent fuel cladding tubes having high radioactivity. By accomplishing of the development of the specimen preparation techniques, we could evaluate pit initiation condition of spent fuel cladding tubes in water containing sea salt.
 -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(1), p.1 - 6, 2014/03
The seawater was injected into reactor cores of Units 1, 2 and 3 in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To investigate effects of  rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50
rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N
rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N H
H ) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N
) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N H
H , the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N
, the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N H
H were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N
were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N H
H . When N
. When N was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during
was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during  rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 444(1-3), p.454 - 461, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cracking growth tests were conducted in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H
) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H O
O , the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H
, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H O
O on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.