Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Takashi; Yusa, Yasuhisa; Sasaki, Noriaki; Tsunoda, Naomi; Takano, Hitoshi*
PNC TN8410 89-010, 17 Pages, 1989/02
A considerable range in alteration rates of basaltic glasses in various environments has been reported in previous studies. However, these studies paid only cursory attention to the environmental conditions under which the glass had been altered. In this study, the alteration of basaltic glasses was investigated and the environmental conditions and the alteration rate were discussed. Two sample ages were represented: 280 years and 2800 years. Basaltic glasses and their alteration layers were analyzed by electron probe microanalyzer (EMPA) and the thickness of the alteration layers were measured by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The ground water collected near the sampling point of Zunazawa Scoria (2800 years) and the pore water of both samples were analyzed. The alteration temperature and flow rate of water are estimated to be about 13 C and 0.2 l/m
C and 0.2 l/m /y respectively on the basis of meteorological data. The alteration layers of young aged basaltic glasses in freshwater conditions are similar to those of leached borosilicate glasses. The alteration rates of these basaltic glasses are estimated to be several
/y respectively on the basis of meteorological data. The alteration layers of young aged basaltic glasses in freshwater conditions are similar to those of leached borosilicate glasses. The alteration rates of these basaltic glasses are estimated to be several  m/1000y. The elemental concentrations in the ground water can be roughly explained as the result of leaching of the glasses.
m/1000y. The elemental concentrations in the ground water can be roughly explained as the result of leaching of the glasses.
Miyahara, Kaname; Ashida, Takashi; Sasaki, Noriaki; Yusa, Yasuhisa; Tsunoda, Naomi
PNC TN8410 89-009, 16 Pages, 1989/02
Fully radioactive waste glass of HLLW generated in Tokai Reprocessing Plant was produced by using a small Joule-heated ceramic melter at the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), Tokai Works, PNC, Japan. Static leach tests using the glass were carried out in doubly distilled water for a period of up to three months at 30 C and 90
C and 90 C. Gamma spectrometry was performed to measure
C. Gamma spectrometry was performed to measure  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and
Cs and  Co in the leachates. After the chemical separation of Cs isotopes in the leachates, it was newly possible to measure
Co in the leachates. After the chemical separation of Cs isotopes in the leachates, it was newly possible to measure 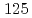 Sb,
Sb,  Ce,
Ce,  Eu and
Eu and  Eu. Alpha spectrometry was performed to measure
Eu. Alpha spectrometry was performed to measure  Pu +
Pu +  Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm in the leachates. Adsorption of the actinides on the wall of the leach vessel was recognized in all cases. Leaching behavior of the measured radionuclides were evaluated by considering mass balance of the radionuclides which were leached.
Cm in the leachates. Adsorption of the actinides on the wall of the leach vessel was recognized in all cases. Leaching behavior of the measured radionuclides were evaluated by considering mass balance of the radionuclides which were leached.
Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko; Yusa, Yasuhisa; Sasaki, Noriaki; Tsunoda, Naomi
PNC TN8410 89-008, 75 Pages, 1989/02
Measurement on plutonium diffusivity in water-saturated compacted bentonite was carried out. Representative specimens of sodium bentonite were taken from Tsukinuno and Kuroishi mines situated in northeast Japan. Tsukinuno bentonite was divided into three types; raw type, purified Na-type, and H-type which was prepared by treating Na-type bentonite with hydrochloric acid. Kuroishi bentonite contained chlorite as impurity. H-type bentonite was used as reference for the convenience of profile measurement in bentonite, since plutonium diffusivity in H-type bentonite was considered to be larger than that in Na-type bentonite because of low pH and low swelling pressure of H-type bentonite. Sampled bentonite was compacted into pellet of 20 mm in diameter and 20 mm in height. Bulk densities of these specimens were 1200 to 1800 kg/m for purified Na-type and H-type bentonite and 1600 kg/m
for purified Na-type and H-type bentonite and 1600 kg/m for raw type bentonite. Plutonium profiles obtained in H-type bentonite can be explained by diffusion equation with constant concentration source. Diffusivity ranges from 10
for raw type bentonite. Plutonium profiles obtained in H-type bentonite can be explained by diffusion equation with constant concentration source. Diffusivity ranges from 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s for H-type and Kuroishi impure sodium bentonite. Diffusivity in both raw type and purified Tsukinuno bentonite was estimated to be less than 10
/s for H-type and Kuroishi impure sodium bentonite. Diffusivity in both raw type and purified Tsukinuno bentonite was estimated to be less than 10 m
m /s. Diffusivity in H-type bentonite showed a tendency to decrease with increasing density. Influence of quartz and hematite contents in bentonite was also studied. Quartz content up to 50% or hematite content up to 1% did not influence diffusivity significantly in H-type bentonite. The chemical species of plutonium in pore water of Na-type and H-type were estimated Pu(OH)
/s. Diffusivity in H-type bentonite showed a tendency to decrease with increasing density. Influence of quartz and hematite contents in bentonite was also studied. Quartz content up to 50% or hematite content up to 1% did not influence diffusivity significantly in H-type bentonite. The chemical species of plutonium in pore water of Na-type and H-type were estimated Pu(OH)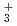 and PuO
and PuO respectively.
respectively.
; Sasaki, Noriaki; ; Tsunoda, Naomi
PNC TN8440 88-016, 18 Pages, 1988/10
The development of the glass melter which will be used in the HLLW vitrification facility has been performed since 1977. The design and operational experiences has been accumulated through the process tests in the cold engineering facilities. The results obtained in these periods have been considered in the design of the Tokai vitrification Facility (TVF), the construction of which has already been started in the spring of 1988. The present PNC melter system includes several features as the result of PNC's own improvements and modifications. The results of the melter development will be described in this paper mainly on the special features which are developed in PNC, such as glass fiber additives, induction-heated bottom drain nozzle and remote handling technique. The mock-up test using the new mock up melter which was constructed following the TVF final design has started to verify the process performance.
Ishiguro, Katsuhiko; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Sonobe, Hitoshi; Nodaka, Masayuki*; Arai, Takashi; Yusa, Yasuhisa; Tsunoda, Naomi
PNC TN8410 87-071, 37 Pages, 1987/08
Experimental studies have been carried out in order to evaluate durability of engineered barriers in geological disposal system. These are as follows; (1) Leaching behavior of waste borosilicate glass. Leaching experiments of simulated waste glass were carried out for more than one year in both scale of laboratory and of engineering. The leachability was suppressed under the condition of high SA/V (the surface area of glass/leachant volume). Saturation of leachant with silicon reduces leaching rates of the other elements. (2) Corrosion behavior of candidate overpack materials. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel and titanium was studied in synthetic groundwater with or without bentonite. No localized corrosion was observed in both the materials. Corrosion rate of carbon steel depends on bentonite/water ratio. Crevice corrosion resistance of titanium and its alloy was also studied. (3) Permeability of compacted bentonite as buffer material. Hydraulic conductivity of saturated compacted bentonite decreases and the swelling pressure increases with the increase of density. Influence of cracks on permeability was also studied, and significant effect was not observed. Infiltration of water into dry compacted bentonite was also studied to evaluate permeability of buffer material at the initial stage of disposal.
Tsunoda, Naomi; Nagaki, Hiroshi; *; Igarashi, Hiroshi; *; Sasaki, Noriaki; *
PNC TN841 85-44, 41 Pages, 1985/10
no abstracts in English
Tsunoda, Naomi; Igarashi, Hiroshi
PNC TN160 82-06, 62 Pages, 1982/07
None
Tsunoda, Naomi; *; *; ; *; *; Kawanishi, N.*; *
PNC TN851 80-01, , 1980/07
no abstracts in English
Tsunoda, Naomi; Sasaki, Noriaki; Nagaki, Hiroshi
PNC TN841 80-22, 104 Pages, 1980/04
no abstracts in English
; Tsunoda, Naomi; Ogino, Naohiko*
PNC TN841 79-56, 16 Pages, 1979/10
Simulated HLLW from reprocessing plant of PNC at Tokai was solidified into sintered ceramics by normal-sintering or hot-pressing with addition of some oxides. Among various ceramic products obtained so far, the most preferable one was Nepheline types intered solids formed with addition of SiO/SUB2 and A1/SUB2/O/SUB3 to the Simulated waste calcine. The solid shows advantageous properties in leach-rate and mechanical strength, which possively comprise the ceramic product be a promising solid waste form. Other type of ceramic solids were prepared with addition of ZrO/SUB2 or MnO/SUB2, and some of them showed preferable characters.
Ogino, Naohiko*; ; Tsunoda, Naomi; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TN841 79-55, 21 Pages, 1979/10
The compositions of glass-ceramics for the solidification of HLLW were studied and the glass-ceramics in the diopside system was concluded to be the most suitable. Compared with the properties of HLW borosilicate glasses, those of diopside glass-ceramic were thought to be almost equal in leach rate and superior in thermal stability and mechanical strength. It was also found out that the glass in this system can be also crytallized simply by pouring it into a thermally insulated canister and then allowing it to cool room temperature.
Nagaki, Hiroshi; Ogino, Naohiko*; Tsunoda, Naomi; Segawa, Takeshi*
PNC TN841 79-54, 18 Pages, 1979/10
Some processes have been investigated to develop the technology of solidification of the high level radio active liquid waste generated from the nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at PNC. This report covers the present state of development of a joule heated ceramic melter and a direct megahertz induction heated furnace. An engineeing scale test has been performed by both of these melters. A joule heated melter could treat 45 kg glass an hour or 16 1/hr. A direct induction furnace was able to melt 5 kg glass per an hour or 1.8 1/hr. Both of the meltes were composed of refractory ceramics and electro-fused cast. Therefore, glass could be melted at above 1200 degrees celsius. At the higher temperature melting, the glass would be the more reliable, in general.
Tsunoda, Naomi; *; *; Nagaki, Hiroshi; *; *; Sasaki, Noriaki
PNC TN841 79-64, 51 Pages, 1979/07
no abstracts in English
Tsunoda, Naomi; *; Sasaki, Noriaki; Nagaki, Hiroshi
PNC TN842 78-02, 113 Pages, 1978/11
None
Tsunoda, Naomi; *; *; ; Tachibana, Toshimichi; Furuya, Hirotaka; Koizumi, Masumichi
PNC TN841 77-64, 48 Pages, 1977/12
no abstracts in English