Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:90.03(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Ikeya, Kosuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
Applied Geochemistry, 76, p.218 - 231, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:66.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Ino, Kohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Tanabe, Akifumi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 8(2), p.285 - 294, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:70.41(Environmental Sciences)To understand the subsurface biosphere, borehole investigation was conducted for 300-m deep granitic rocks at the Mizunami underground research laboratory, Japan. The initial biomass was the highest with the flourish of aerobic H -oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
-oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Hirota, Akinari*; Watanabe, Katsuaki*; Togo, Yoko*; Morikawa, Noritoshi*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Aosai, Daisuke*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(12), p.e113063_1 - e113063_20, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:38.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We present multi-isotopic evidence of microbially mediated sulfate reduction in a granitic aquifer, a representative of the terrestrial crust habitat. Deep groundwater of meteoric origin was collected from underground boreholes drilled into the Cretaceous Toki granite, central Japan. A large sulfur isotopic fractionation of 20-60 permil diagnostic to microbial sulfate reduction is associated with the investigated groundwater containing sulfate below 0.2 mM. In contrast, a small carbon isotopic fractionation ( 30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:36.87(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
Fukuda, Akari*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ioka, Seiichiro*; Amano, Yuki; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Mizuno, Takashi
Microbial Ecology, 60(1), p.214 - 225, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:65.69(Ecology)To better understand the geochemical and microbiological relationships, we characterized granitic groundwater collected from a 1,148 to 1,169 -m deep borehole interval at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory site, Japan, in 2005 and 2008. Geochemical analyses of the groundwater samples indicated that major electron acceptors, such as NO
 and SO
and SO
 , were not abundant, while dissolved organic carbon (not including organic acids), CH
, were not abundant, while dissolved organic carbon (not including organic acids), CH and H
and H were moderately rich. The most common phylotypes were both related to
were moderately rich. The most common phylotypes were both related to 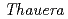 spp., the cultivated members of which can utilize minor electron donors, such as aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Geomicrobiological results suggest that deep granitic groundwater has been stably colonized by
spp., the cultivated members of which can utilize minor electron donors, such as aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Geomicrobiological results suggest that deep granitic groundwater has been stably colonized by 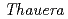 spp. probably owing to the limitation of O
spp. probably owing to the limitation of O , NO
, NO
 and organic acids.
and organic acids.
 reduction at deep granitic aquifer by anaerobic and high pressure culture experiment
reduction at deep granitic aquifer by anaerobic and high pressure culture experimentHirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Komatsu, Daiyu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
Microbial activity in deep groundwater at Mizunami URL was estimated based on isotopic composition. The result shows that sulfate reduction activity is higher at low-H gas condition.
gas condition.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Mizuno, Takashi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Konno, Yuta*; Fukuda, Akari; Kozuka, Mariko*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Aosai, Daisuke; Mizuno, Takashi; Suzuki, Yohei*
no journal, ,
Our knowledge of biogeochemical processes mediated in those associated with freshwater should be integrated. We collected the groundwater samples from 200 m to 1150 m depths below ground level at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory located in central Japan. We measured the concentration and both hydrogen and carbon isotopic compositions of dissolved methane, total inorganic carbon (TIC) and molecular hydrogen. The origin of methane could be speculated to be not biogenic CO reduction or acetate fermentation but thermogenic or abiogenic. In contrast, C1/C2+C3 ratios supported biogenic methane production. The 300 m deep samples were enriched in hydrogen and acetate and depleted in sulfate, which is characteristic of acetogenesis. From these results, it is suggested that the production of acetate rather than methane could be dominant biogeochemical processes in the reducing portions of freshwater aquifers in granitic rocks.
reduction or acetate fermentation but thermogenic or abiogenic. In contrast, C1/C2+C3 ratios supported biogenic methane production. The 300 m deep samples were enriched in hydrogen and acetate and depleted in sulfate, which is characteristic of acetogenesis. From these results, it is suggested that the production of acetate rather than methane could be dominant biogeochemical processes in the reducing portions of freshwater aquifers in granitic rocks.
 reduction continuing for millions years in Neogene mudstone resulting in extreme
reduction continuing for millions years in Neogene mudstone resulting in extreme  C-enrichment
C-enrichmentMiyakawa, Kazuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Mizuno, Takashi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Ikeya, Kosuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Katsuyama, Chie*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Kato, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Akari*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Mizuno, Takashi
no journal, ,
JAEA and AIST have been conducting collaborative work on hydrochemical study at MIU construction site. The aim of this collaborative study is to establish the methodology for investigation, analysis and evaluation of colloid/organics/microbes study. This paper reports the biogeochemical study. As the result, it is suggested that groundwater taken from deeper part (1150m depth) is relatively oxidized.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Fukuda, Akari*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Ishimura, Toyoho*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Mizuno, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Mizuno, Takashi; Ishii, Eiichi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Ikeya, Kosuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 reduction depending on groundwater flow characteristics in deep granitic aquifers
reduction depending on groundwater flow characteristics in deep granitic aquifersKonno, Yuta*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Nishimura, Shusaku*; Fukuda, Akari; Aosai, Daisuke; Mizuno, Takashi; Nagao, Seiya*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Suzuki, Yohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Kenji*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Fukuda, Akari*; Konno, Yuta*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Komatsu, Daiyu*; Nagao, Seiya*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
Isotopic compositions of sulfate, sulfide ions were measured in deep groundwater of Mizunami URL to estimate microbial activity. The results show that relatively large isotopic fractionation between sulfate and sulfide by microbial reduction.