Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Takito, Kiyotaka; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Takada, Tsuyoshi
Transactions of 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Takito, Kiyotaka; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Takada, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
no abstracts in English
 ) cross-sections of a nucleus in the range 0.008
) cross-sections of a nucleus in the range 0.008 
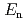
 20 MeV
20 MeVSegawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Fukahori, Tokio; Matsue, Hideaki; Oshima, Masumi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 618(1-3), p.153 - 159, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new measurement system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at 0.008 
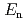
 20 MeV has been installed at the 4 MV Pelletron accelerator laboratory at the facility of radiation standards at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Pulsed neutrons are produced by bombarding a pulsed proton beam on
20 MeV has been installed at the 4 MV Pelletron accelerator laboratory at the facility of radiation standards at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Pulsed neutrons are produced by bombarding a pulsed proton beam on  Li (or
Li (or  H) or a deuteron beam on
H) or a deuteron beam on  H. The performance of the new system was studied by measuring discrete
H. The performance of the new system was studied by measuring discrete  rays from neutron capture by
rays from neutron capture by  Pb and
Pb and  Pb to their low-lying states at several resonances at 10
Pb to their low-lying states at several resonances at 10 
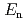
 110 keV using neutrons from
110 keV using neutrons from  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be. The
Be. The  rays were detected with a good signal-to-noise ratio by means of a highly sensitive anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer combined with a time-of-flight method. The present study demonstrated good sensitivity of the new system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at keV neutron energy.
rays were detected with a good signal-to-noise ratio by means of a highly sensitive anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer combined with a time-of-flight method. The present study demonstrated good sensitivity of the new system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at keV neutron energy.
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Sugino, Hideharu*; Onizawa, Kunio; Mori, Kazunari*; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-004, 167 Pages, 2006/03
EBISA (Equipment Base Isolation System Analysis) code evaluates the effectiveness of seismic isolation for the important components in the seismic safety, and consists of the three codes, probabilistic seismic hazard code (SHEAT), seismic dynamic response analysis code (RESP) and seismic failure probability and frequency evaluation code. In these codes, RESP code is used for the calculation of the dynamic response behavior of a nuclear component with seismic isolation devices. This report describes the overall explanation of EBISA, and user's guide of RESP code including the analysis function, input manual and sample problem.
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Ebisawa, Katsumi*; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Fujimoto, Shigeru*
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai JCOSSAR 2003 Rombunshu, p.829 - 836, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Suzuki, Masahide; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Nakajima, Hajime*
JAERI-Tech 2003-073, 125 Pages, 2003/08
Concerning the cracks due to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) observed on the core shrouds of BWRs, a study was conducted on structural integrity evaluation based on crack growth analysis. The cracks investigated were those observed on the regions of lower ring and support ring of the core shroud at Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station (NPS) Unit-3, and that on the middle shell region of the core shroud at Fukushima Daiichi NPS Unit-4 of Tokyo Electric Power Company. It was confirmed through data analysis of past SCC growth rate experiments applicable to the condition of the ring regions that the SCC growth rate prescribed in the JSME rule was conservative. The analysis on the core shroud rigidity with a crack indicated that the rigidity reduction was small enough not to affect the dynamic seismic response for the regions studied. Through the comparison of the required area in a cracked section or the allowable crack length, and crack growth analysis results, it was confirmed that the integrity of the core shrouds would be maintained even 4 effective full power years later.
Yamada, Hiroyuki; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Ebisawa, Katsumi*; Suzuki, Masahide
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-001, 161 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Mori, Kazunari*; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki
JAERI-Tech 2001-037, 85 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Fujimoto, Shigeru*
JAERI-Tech 2001-033, 124 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Ebisawa, Katsumi; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Ando, Kazuhiro*; Baba, Osamu; Suzuki, Hideyuki
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-009, 96 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Mori, Kazunari*; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki
JAERI-Tech 2000-086, 93 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Fujimoto, Shigeru*
Doboku Gakkai Dai-2-Kai Menshin, Seishin Korokiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.75 - 82, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki
JAERI-Tech 2000-045, 107 Pages, 2000/07
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Teragaki, Toshio*; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Shibata, Katsuyuki
Seismic Engineering 2000 (PVP-Vol.402-1), p.141 - 146, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
 3"LaBr
3"LaBr (Ce) detector to high-energy
(Ce) detector to high-energy  -rays
-raysHarada, Hideo; Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki; Kitatani, Fumito; Toh, Yosuke; Oshima, Masumi; Matsue, Hideaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Kowatari, Munehiko; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Energy resolution of a LaBr (Ce) detector has been investigated for a wide
(Ce) detector has been investigated for a wide  -ray energy range. High-energy
-ray energy range. High-energy  -rays have been produced by the (p,
-rays have been produced by the (p, 
 ), (n,
), (n, ) reactions. The superiority of the LaBr
) reactions. The superiority of the LaBr (Ce) detector on the energy resolution has been demonstrated to a NaI(Tl) detector.
(Ce) detector on the energy resolution has been demonstrated to a NaI(Tl) detector.
Kato, Rino*; Hida, Takenori*; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
With the aim of constructing a more realistic earthquake response analysis model of a nuclear facility, we constructed a model using the system identification method developed by the authors making maximum use of the strong motion observation records in the past earthquakes, and discussed its validity.
Takada, Tsuyoshi; Nishida, Akemi; Choi, B.; Takito, Kiyotaka; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Muramatsu, Ken; Kubo, Kotaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takada, Tsuyoshi; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Choi, B.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takada, Tsuyoshi; Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Kawata, Manabu
no journal, ,
The 2006 seismic design review guide requires results of their site-specific probabilistic seismic hazard assessment (PSHA) for setting Design Basis Ground Motions (DBGMs) to verify seismic safety of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs). All electric utilities have submitted their results of their DBGMs to the NRA (Nuclear Regulatory Authority) together with the results of their PSHA. The AEPs (Annual Exceedance Probabilities) of DBGMs reflect not only the site-specific physical earthquake environment but also degree of design conservatisms which each electric utility wants to maintain for their NPPs. The present paper, based on the publicly available documents submitted to NRA, demonstrates the AEPs of the DBGMs of 16 NPPs in Japan and shows the regulatory requirements as well as utilities' decision by statistically analyzing the AEPs, which certainly can lead to risk-informed decision-making activities for nuclear safety assurance in Japan.