Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Ishikawa, Masao; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Yutaka; Masaki, Kei; Naito, Osamu; Kurihara, Kenichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.997 - 1004, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:78.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Ferritic steel plates have been installed to improve the energetic ion confinement through reducing a toroidal magnetic field ripple. Aiming at cost-effective installation, orbit following calculations of energetic ions were performed for a design of ferritic installation on JT-60U by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field Orbit-Following Monte-Carlo (F3D OFMC) code. The installed ferritic steel adds the non-linear magnetic field on magnetic sensors for a plasma control and an equilibrium calculation. The code for a real-time control has been modified to take into account the magnetic field by ferritic steel. The plasma operation was successfully resumed and a real-time plasma control was successfully carried out after usual preparation processes. The heat load measurement indicates the improved confinement of energetic ions. These results are important for practical application of ferritic steel which is a leading candidate of a structural material on a demo reactor.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(7), p.689 - 697, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)After the installation of FSTs in JT-60U, ripple induced fast ion losses have been reduced by 1/2 1/3. The increase in the absorbed power at the same injection power can reduce the required number of NB units to sustain a given
1/3. The increase in the absorbed power at the same injection power can reduce the required number of NB units to sustain a given 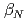 . The smaller recycling level and edge density, which is suitable condition to get higher edge temperature, can be kept longer. The higher edge temperature is essential in keeping the peaked pressure/temperature profile. In addition to this, smaller fast ion losses reduce the effective torque for ctr-rotation and increase in better flexibility of torque input. Then, better quality of
. The smaller recycling level and edge density, which is suitable condition to get higher edge temperature, can be kept longer. The higher edge temperature is essential in keeping the peaked pressure/temperature profile. In addition to this, smaller fast ion losses reduce the effective torque for ctr-rotation and increase in better flexibility of torque input. Then, better quality of  -ITB was obtained in the plasmas with co-rotation. By making use of these advantages to sustain an ITB, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high
-ITB was obtained in the plasmas with co-rotation. By making use of these advantages to sustain an ITB, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high 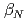 and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (
and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (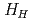 ). High
). High 

 2.3 together with
2.3 together with 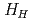
 1 was sustained for 23.1s (
1 was sustained for 23.1s (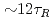 , where
, where 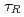 is the current diffusion time.), which also provide high
is the current diffusion time.), which also provide high 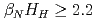 . These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
Ueda, Yoshio*; Fukumoto, Masakatsu*; Nishikawa, Masahiro*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Miya, Naoyuki; Arai, Takashi; Masaki, Kei; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Asakura, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 363-365, p.66 - 71, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
McDonald, D. C.*; Cordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; Stober, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(3), p.147 - 174, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:29.82(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper describes the updates to and analysis of the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) Global H-node Confinement Database version 3 (DB3) over the period 1994-2004. Global data, for the energy confinement time and its controlling parameters, have now been collected from 18 machines of different sizes and shapes: ASDEX, ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod CoMPASS-D, DIII-D, JET, JFT-2M, JT-60U, MAST, NSTX, PBX-M, PDX, START, T-10, TCV, TdeV, TFTR and TUMAN-3M. A wide range of physics studies has been performed on DB3 with particular progress made in the separation of core and edge behavior, dimensionless parameter analyses and the comparison of the database with one-dimensional transport code. A key aim of the database has always been to provide a basis for estimating the energy confinement properties of next step machines such as ITER, and so the impact of the database and its analysis on such machines is also discussed.
Kubo, Hirotaka; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Urano, Hajime; Fujimoto, Kayoko; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Ishikawa, Masao; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Yutaka; Masaki, Kei; Naito, Osamu; Kurihara, Kenichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Ferritic steel plates have been installed to improve the energetic ion confinement through reducing a toroidal magnetic field ripple. Aiming at cost-effective installation, orbit following calculations of energetic ions were performed for a design of ferritic installation on JT-60U by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field Orbit-Following Monte-Carlo (F3D OFMC) code. The installed ferritic steel adds the non-linear magnetic field on magnetic sensors for a plasma control and an equilibrium calculation. The code for a real-time control have been modified to take into account the magnetic field by ferritic steel. The plasma operation was successfully resumed and a real-time plasma control was successfully carried out after usual preparation processes. The heat load measurement indicates the improved confinement of energetic ions. These results are important for practical application of ferritic steel which is a leading candidate of a structural material on a demo reactor.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
After installation of ferritic steel tiles (FSTs) which reduced fast ion losses due to toroidal field ripple, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high normalized beta (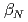 ) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (
) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (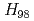 ). High
). High 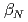
 2.3 together with
2.3 together with 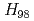
 1 was sustained for 23.1s (
1 was sustained for 23.1s ( 12
12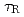 )
) 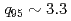 , which also provide high
, which also provide high 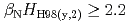 , which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
, which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Ido, Takeshi*; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Oasa, Kazumi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
We report on the potential/density fluctuations in the JFT-2M tokamak. We identified a geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) and its electric field structure. The GAM interacts with the background turbulence in consistent with a drift wave - zonal flow theory. The GAM modulates the turbulence, and the suppression depends on the direction and gradient of the flow velocity in consistent with a theory. During the H-mode, the GAM disappears presumably due to the suppression of the turbulence. We analysed the low frequency potential oscillation during the H-mode. A wavelet analysis showed a low frequency characteristic potential fluctuations (several handred kHz), which disappears in the L-mode and at the occurence of ELM. Observed poloidal flow is about 20 times as large as that of the GAM during the H-mode. If the potential has a spatial inhomogineity, there is a possibility that this low frequency fluctuation comes from the EXB flow or the zonal flow.
Kizu, Kaname; Yagyu, Junichi; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Nakano, Tomohide; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Miya, Naoyuki; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Nishimura, Kiyohiko*; Sagara, Akio*
Annual Report of National Institute for Fusion Science; April 2005 - March 2006, P. 65, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Bakhtiari, M.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kurita, Genichi; Takechi, Manabu; Kasai, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(11), p.966 - 971, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Goto, Yoshitaka*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Masaki, Kei; Arai, Takashi; Kubo, Hirotaka; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Miya, Naoyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 357(1-3), p.138 - 146, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Uehara, Kazuya; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Amemiya, Hiroshi*; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Sadamoto, Yoshiro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 45(24), p.L630 - L633, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.93(Physics, Applied)Data for detecting the magnetic flux surfaces at the edge plasma in tokamak are presented. When the magnetic surfaces are moved by the plasma jog, it is observed that a current increment appears in the two set of double probe whose front surfaces are shifted by a small distance and that the difference of these two currents through the differential amplifier giving a signal of the arrival of the separatrix also appears, where we refer the separatrix point as a typical position of the magnetic flux surfaces. It is confirmed that magnetic flux surfaces are located by a few cm outward from that calculated by the eqfit-code (EQFIT) and the absolute value of its deviation is identified. This identification is supported by the result of observation of the correlation of the floating potential fluctuation between two different points using one probe pin of the same differential double probe. The ion temperature and the space potential are observed by the another use of the differential double probe are modified following the estimated real magnetic surfaces positions.
Kaye, S. M.*; Valovic, M.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Cordey, J. G.*; McDonald, D.*; Meakins, A.*; Thomsen, K.*; Akers, R.*; Bracco, G.*; Brickley, C.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A429 - A438, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:46.03(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effects of aspect ratio and beta on confinement scaling are studied with the use of the H-mode database extended by the low aspect ratio data from NSTX and MAST. Various statistical methods are applied. Development of scalings using engineering parameters as predictor variables results in the inverse-aspect-ratio scaling with the range from 0.38 to 1.29. The transformation of these scalings to physics variables results in an unfavorouble dependence of the normalized energy confinement time on beta. There is a strong correlation between the inverse aspect ratio and beta, and this makes scalings based on physics variables imprecise.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Konoshima, Shigeru; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Ide, Shunsuke; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S39 - S48, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:52.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Higashijima, Satoru; Nishi, Masataka; Kobayashi, Yasunori*; Konishi, Satoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.827 - 832, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Exhaust gas from JT-60U during experimental operation has been measured with Gas Chromatography (GC), and the gas exhaust characteristic from JT-60U on plasma discharge conditions has been investigated during the JT-60U experimental campaign in 2003-2004. During experimental operation of JT-60U, hydrogen isotope concentration strongly depended on the type of discharges such as high performance, long pulse and so on. On the other hand, impurity species, such as helium, hydrocarbon and carbon oxide, were detected during plasma discharges occasionally. During the experimental operation, plasma disruption remarkably tended to produce high concentration impurities. Glow discharge and Taylor discharge for wall conditioning also produced impurities. In the case of normal plasma, impurity was detected and high performance plasma, such as high  plasma, tended to produce high concentration impurities. This result indicated that impurities concentration might be higher in the case of normal plasma in ITER, because of its high performance.
plasma, tended to produce high concentration impurities. This result indicated that impurities concentration might be higher in the case of normal plasma in ITER, because of its high performance.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nishio, Satoshi; Kurita, Genichi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Bakhtiari, M.*; Kawashima, Hisato; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kusama, Yoshinori; Tobita, Kenji
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1589 - 1598, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Blanket-plasma interaction is important for plasma performance enhancement and reliability of first-wall/ blanket. Typical examples are harminization of wall stabilization and reduction of EM force during current quench, error field effect by ferritic steel, neutral-wall interaction under wall saturation, etc. JAERI reactor studies, JT-60U and JFT-2M results on this topics will be described.
Shinohara, Koji; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Isei, Nobuaki; Tani, Takashi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; Shibata, Takatoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.187 - 196, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)In JFT-2M, the toroidal field ripple was reduced by ferritic insert. Two kinds of ripple reduction were carried out. In the first case, ferritic steel was installed between toroidal field coil and vacuum vessel, just under toroidal field coil, outside vacuum vessel. In the second one, ferritic steel was installed inside vacuum vessel covering almost whole inside wall. The ripple was successfully reduced in the both cases. The temperature increment on the first wall measured by infrared TV was also reduced. A new version of OFMC code was also developed to analyze fast ion behavior in the complex structure of the toroidal field. The TF ripple reduction with ferritic insert in JFT-2M is summarized in this article.
Kasai, Satoshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Uehara, Kazuya; Miura, Yukitoshi; Okano, Fuminori; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.225 - 240, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)The diagnostic system of JFT-2M has consisted of about 30 individual diagnostic instruments,which were used to study the plasma production, control, equilibrium, stability, confinement, plasma heating by NBI and/or RF (LH, ICRF, ECH) and current drive by RF. In these instruments, the motional Stark effect (MSE) polarimeter, charge exchanged recombination spectroscopy (CXRS), heavy-ion beam probe (HIBP), time of flight (TOF) neutral particle analyzer, etc. have contributed to make clear the improved mechanism of confinement such as H-mode and High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode, and to search the operational region of these modes.The infrared TV camera system and lost ion probe have played a very important role to investigate the heat load onto the walls due to ripple loss particles and escaping ions from core plasma, respectively.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Kimura, Haruyuki; Okano, Fuminori; Kawashima, Hisato; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shinohara, Koji; JFT-2M Group; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.241 - 248, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)JFT-2M has been modified three times in the Advanced Material Tokamak Experiment (AMTEX) program to investigate compatibility of the low activation ferritic steel F82H with tokamak plasmas as a structural material for future reactors. The ferritic steel plate/wall was installed inside and/or outside of the vacuum vessel to reduce the ripple of toroidal magnetic field step by step through three modifications. This paper focuses on engineering aspects in these modifications; electromagnetic analysis to find a suitable way for fixing these plates, installation procedure to keep small tolerance, a three-dimensional magnetic field measurement device used to obtain information of the actual shape of the vacuum vessel used as a installation standard surface. To keep a good surface condition of the ferritic steel plate/wall that rusts easily, careful treatment was executed before the installation. To reduce oxygen impurities further, a boronization system with tri-methyl boron, which is safe and easy to operate, was developed.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ogawa, Toshihide; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Kasai, Satoshi*; Kashiwa, Yoshitoshi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Miura, Yukitoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.209 - 224, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English