Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Tsuzuki, Takayuki*; Murai, Tetsuro*
JAEA-Technology 2022-023, 128 Pages, 2022/11
In a mercury target of the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), pulsed proton beams repeatedly bombard the flowing mercury which is confined in a stainless-steel vessel (target vessel). Cavitation damage caused by the propagation of the pressure waves is a factor of the life of the target vessel. As a measure to reduce damages, we developed a bubbler to inject the gas microbubbles into the flowing mercury, which can reduce the pressure waves. To operate the mercury target vessel stably with the 1 MW high-intensity proton beams, further reduction of the damage is required. The bubbler setting position should be closer to the beam window to increase the bubble population, which could enhance the reduction effect on the pressure waves and damage. However, the space at the beam window of the target vessel is restricted. The bubbler design and setting position as well as the vane design for the mercury flowing pattern are optimized by means of a machine learning technique to get more suitable bubble distribution, increasing in bubble population and optimizing bubble size nearby the beam window of the target vessel. The results of CFD analyses performed with 1000 cases were used for machine learning. Since the flow rate of mercury affects the temperature of the target vessel, this was used for the constraint condition. As a result, we found a design of mercury target vessel that can increase the bubble population by ca. 20% higher than the current design.
Soejima, Goro; Iwai, Hiroki; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Tsuzuki, Satoshi*; Yasunaga, Kazushi*; Kume, Kyo*
Heisei-29-Nendo Koeki Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta kenkyu Nempo, 20, P. 80, 2018/11
We investigated the behavior of the dust generated by Laser and Plasma-arc cutting underwater and in air aimed at the simulant material of reactor components (SUS304) and the pressure and calandria tube (Zr-2.5%Nb, Zry-2) of the prototype reactor "FUGEN".
Soejima, Goro; Iwai, Hiroki; Kadowaki, Haruhiko; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Tsuzuki, Satoshi*; Yasunaga, Kazushi*; Nakata, Yoshinori*; Kume, Kyo*
Heisei-28-Nendo Koeki Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta kenkyu Nempo, 19, P. 9, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Ido, Takeshi*; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Oasa, Kazumi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
We report on the potential/density fluctuations in the JFT-2M tokamak. We identified a geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) and its electric field structure. The GAM interacts with the background turbulence in consistent with a drift wave - zonal flow theory. The GAM modulates the turbulence, and the suppression depends on the direction and gradient of the flow velocity in consistent with a theory. During the H-mode, the GAM disappears presumably due to the suppression of the turbulence. We analysed the low frequency potential oscillation during the H-mode. A wavelet analysis showed a low frequency characteristic potential fluctuations (several handred kHz), which disappears in the L-mode and at the occurence of ELM. Observed poloidal flow is about 20 times as large as that of the GAM during the H-mode. If the potential has a spatial inhomogineity, there is a possibility that this low frequency fluctuation comes from the EXB flow or the zonal flow.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Bakhtiari, M.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kurita, Genichi; Takechi, Manabu; Kasai, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(11), p.966 - 971, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Higashijima, Satoru; Nishi, Masataka; Kobayashi, Yasunori*; Konishi, Satoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.827 - 832, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Exhaust gas from JT-60U during experimental operation has been measured with Gas Chromatography (GC), and the gas exhaust characteristic from JT-60U on plasma discharge conditions has been investigated during the JT-60U experimental campaign in 2003-2004. During experimental operation of JT-60U, hydrogen isotope concentration strongly depended on the type of discharges such as high performance, long pulse and so on. On the other hand, impurity species, such as helium, hydrocarbon and carbon oxide, were detected during plasma discharges occasionally. During the experimental operation, plasma disruption remarkably tended to produce high concentration impurities. Glow discharge and Taylor discharge for wall conditioning also produced impurities. In the case of normal plasma, impurity was detected and high performance plasma, such as high  plasma, tended to produce high concentration impurities. This result indicated that impurities concentration might be higher in the case of normal plasma in ITER, because of its high performance.
plasma, tended to produce high concentration impurities. This result indicated that impurities concentration might be higher in the case of normal plasma in ITER, because of its high performance.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nishio, Satoshi; Kurita, Genichi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Bakhtiari, M.*; Kawashima, Hisato; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kusama, Yoshinori; Tobita, Kenji
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1589 - 1598, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Blanket-plasma interaction is important for plasma performance enhancement and reliability of first-wall/ blanket. Typical examples are harminization of wall stabilization and reduction of EM force during current quench, error field effect by ferritic steel, neutral-wall interaction under wall saturation, etc. JAERI reactor studies, JT-60U and JFT-2M results on this topics will be described.
Kasai, Satoshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Uehara, Kazuya; Miura, Yukitoshi; Okano, Fuminori; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.225 - 240, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)The diagnostic system of JFT-2M has consisted of about 30 individual diagnostic instruments,which were used to study the plasma production, control, equilibrium, stability, confinement, plasma heating by NBI and/or RF (LH, ICRF, ECH) and current drive by RF. In these instruments, the motional Stark effect (MSE) polarimeter, charge exchanged recombination spectroscopy (CXRS), heavy-ion beam probe (HIBP), time of flight (TOF) neutral particle analyzer, etc. have contributed to make clear the improved mechanism of confinement such as H-mode and High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode, and to search the operational region of these modes.The infrared TV camera system and lost ion probe have played a very important role to investigate the heat load onto the walls due to ripple loss particles and escaping ions from core plasma, respectively.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ogawa, Toshihide; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Kasai, Satoshi*; Kashiwa, Yoshitoshi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Miura, Yukitoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.209 - 224, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Uehara, Kazuya; Kurita, Genichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.197 - 208, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Ido, Takeshi*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Bakhtiari, M.*; Kasai, Satoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(2), p.272 - 276, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An attractive operational regime without any large ELMs, namely High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode, was found on JFT-2M during Y2000 campaign after boronization. Recent experiments have concentrated on the studies of the access conditions for the HRS regime, in terms of the pedestal parameters. The HRS regime was more likely at higher edge density and lower edge temperature, which corresponds to the normalized electron collisionality of 1 in the plasma edge region.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Yamauchi, Yuji*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kasai, Satoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yamaguchi, Kaoru*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.678 - 682, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Shinohara, Koji; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kurita, Genichi; Bakhtiari, M.; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.721 - 725, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; Kawashima, Hisato; Kusama, Yoshinori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A157 - A163, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:56.48(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A new operating regime, High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime, has been discovered on JFT-2M, which is easily reproduced under the wall fueling from the boronized first wall. Accompanying the HRS H-mode transition, the coherent magnetic and floating potential fluctuations are seen on magnetic probes at vessel wall and Langmuir probe in SOL, respectively. These coherent fluctuations have a frequency of the order of 10-100 kHz with significant variation, which is recognized to be important to enhance the particle transport. The HRS can be seen even at 

 3 with
3 with 
 /
/
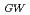
 0.4 for the fixed delta
0.4 for the fixed delta 0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta
0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta 0.75 and
0.75 and 

 2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta
2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta 0.3 with moderate
0.3 with moderate 

 4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of
4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of 
 /
/
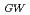
 0.4.
0.4.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ido, Takeshi*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Bakhtiari, M.; Shinohara, Koji; Uehara, Kazuya; Oasa, Kazumi; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.345 - 348, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1288 - 1293, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:74.23(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Masayasu; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Sasao, Hajime; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.586 - 593, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:80.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In JFT-2M, the ferritic steel was installed inside the vacuum vessel as the third step of tne Advanced Material Tokamak Experiment (AMTEX) programme. The magnetic field structure has become the complex ripple strucuture such as non-periodic ripple structure in the toroidal direction and high Fourier-number ripple because of the existence of the port and the limitation of the periodic installation. Under such a complex ripple structure, we have performed the experiment to understand its effect on fast ions. To actively change the ripple structure, we have installed the additional ferritic steel plates (FPs). We also have compared the experiment result with the newly updated OFMC code which does not need the toroidal 16-folded symmetry. The experiment results were almost consistent with the OFMC calcution with the complex magnetic field and the complex first wall.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Kitsunezaki, Akio; Shimizu, Masatsugu; Kuriyama, Masaaki; JT-60 Team; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Isei, Nobuaki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.7 - 31, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:27.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish scientific basis for the sustainment of highly integrated performance required in the advanced steady-state operation, JT-60U has been optimizing the discharge control scenarios of improved confinement plasmas and expanding the operation regions. Promising results toward the steady-state tokamak were obtained. The detail of such results is reported. JFT-2M has performed advanced and basic research for the development of high performance tokamak plasma as well as the structural material for a fusion reactor. The toroidal ripple reduction with ferritic steel plates outside the vacuum vessel was successfully demonstrated. No adverse effects were observed in the pre-testing on compatibility between ferritic steel plates, covering ~20% of the inside wall of the vacuum vessel, and plasma. The results of TRIAM-1M is also reported.
Konishi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Yasunori*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Higashijima, Satoru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasunori*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Higashijima, Satoru; Konishi, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English