Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nguyen, H. H.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 230, p.112171_1 - 112171_13, 2026/06
Times Cited Count:0This study examined the effects of the moderator-to-fuel volume ratio, fuel debris shape, and the number of damaged fuel assemblies on the neutronic characteristics of a partially damaged reactor model, where the fuel assemblies at the core center melt to fuel debris while the fuel assemblies at the outer region remain intact. The investigations were conducted using the Serpent code and the JENDL-5 library. The results show that when fuel debris is surrounded by intact fuel assemblies, the k can be classified into two groups based on the shape of the fuel debris. Conversely, in scenarios where the fuel debris is not fully encircled by intact fuel assemblies, the shape of the fuel debris has a negligible impact on the k
can be classified into two groups based on the shape of the fuel debris. Conversely, in scenarios where the fuel debris is not fully encircled by intact fuel assemblies, the shape of the fuel debris has a negligible impact on the k . Additionally, the relationship between the number of neutrons entering and leaving the fuel debris determines how the shape of the fuel debris affects the k
. Additionally, the relationship between the number of neutrons entering and leaving the fuel debris determines how the shape of the fuel debris affects the k .
.
Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Luu, V. N.; Tasaki, Yudai; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 231, p.112177_1 - 112177_16, 2026/06
Times Cited Count:0Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Tasaki, Yudai; Katsuyama, Jinya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 230, p.112114_1 - 112114_14, 2026/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 148(3), p.031501_1 - 031502_12, 2026/06
Embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steel caused by neutron irradiation has been evaluated using ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) derived from surveillance tests (Charpy impact tests) during plant operation. For reliable structural integrity assessment of the RPV, incorporating adequate safety margins which take into account uncertainties inherent in surveillance Charpy impact tests is needed. In this study, a model to evaluate temperature dependence of Charpy absorbed energy variability using approximately 1,900 datasets of unirradiated and irradiated materials manufactured in Japan and United States was developed. Next, probability distribution of Charpy ductile-to-brittle transition temperature at a 41J energy level (
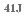 ) was evaluated by estimating the probability distribution of Charpy test data using Monte Carlo sampling and Bayesian inference. From the detailed evaluation of the relationship between the number of specimens and
) was evaluated by estimating the probability distribution of Charpy test data using Monte Carlo sampling and Bayesian inference. From the detailed evaluation of the relationship between the number of specimens and 
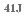 uncertainty, uncertainty of
uncertainty, uncertainty of 
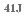 was found to be almost the same in materials manufactured in Japan and U.S., and unchanged with neutron irradiation (no clear change in material inhomogeneity). Regarding product form on the other hand, uncertainty of
was found to be almost the same in materials manufactured in Japan and U.S., and unchanged with neutron irradiation (no clear change in material inhomogeneity). Regarding product form on the other hand, uncertainty of 
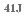 for base metal and weld metal was almost the same, but the heat affected zone was shown to have large uncertainty.
for base metal and weld metal was almost the same, but the heat affected zone was shown to have large uncertainty.
Furuta, Takuya; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1086, p.171320_1 - 171320_8, 2026/06
Times Cited Count:0A new function to incorporate nuclear data libraries with outgoing particles plus residual nuclei in specific excitation states for neutron-induced reactions has been implemented in a Monte Carlo simulation code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). With this function, accurate predictions of outgoing particle spectra and angular distributions according to the nuclear data libraries become possible, while accounting for production of residual nuclei and de-excitation gammas, conserving total energy and momentum in each event. This feature allows users to perform high-precision simulations of detector responses and radiation damage in materials.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Sugita, Moe; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 36(3), p.4900905_1 - 4900905_5, 2026/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Motegi, Kosuke; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Hibiki, Takashi*; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 258, p.128275_1 - 128275_15, 2026/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Kreinder, B.; Cox, I.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; 24 of others*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1085, p.171298_1 - 171298_7, 2026/05
Times Cited Count:0Shiotsu, Hiroyuki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 195, p.106300_1 - 106300_11, 2026/05
Times Cited Count:0Kondo, Masatoshi*; Kitamura, Yoshiki*; Kawarai, Atsushi*; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari
Corrosion Science, 262, p.113646_1 - 113646_14, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0The corrosion resistance of FeCrAl alloy APMT (Fe-21Cr-5Al-3Mo) in flowing lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) was investigated by corrosion tests performed at 723 K using a non-isothermal forced convection loop. The oxygen concentration in flowing LBE was controlled at 1 10
10 wt%. No severe corrosion or erosion was detected on the specimens exposed to flowing LBE for 2000 h and 4000 h. Multiple oxide layers consisting of Fe-rich, Cr-rich and Al-rich sub-layers were formed in situ on the surface of APMT during the corrosion tests, which effectively suppressed corrosion and erosion. The oxide layers were intentionally removed by gentle abrasion prior to re-immersion and the specimens were then re-immersed in flowing LBE for an additional 2000 h. The oxide layers were spontaneously re-formed in situ on the abraded surface. This behavior indicates a self-healing capability. The results of micro-scratch tests indicated that the in-situ formed multiple oxide layers exhibited high adhesion strength in the shear direction after the 2000 h corrosion test.
wt%. No severe corrosion or erosion was detected on the specimens exposed to flowing LBE for 2000 h and 4000 h. Multiple oxide layers consisting of Fe-rich, Cr-rich and Al-rich sub-layers were formed in situ on the surface of APMT during the corrosion tests, which effectively suppressed corrosion and erosion. The oxide layers were intentionally removed by gentle abrasion prior to re-immersion and the specimens were then re-immersed in flowing LBE for an additional 2000 h. The oxide layers were spontaneously re-formed in situ on the abraded surface. This behavior indicates a self-healing capability. The results of micro-scratch tests indicated that the in-situ formed multiple oxide layers exhibited high adhesion strength in the shear direction after the 2000 h corrosion test.
Mohamad, A. B.; Chen, J.*; Ioka, Ikuo*; Suzuki, Eriko; Kondo, Keietsu; Abe, Yosuke; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Okada, Yuji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 625, p.156513_1 - 156513_9, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0Shimodaira, Masaki; Ha, Yoosung; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 148(2), p.021504_1 - 021504_10, 2026/04
In the current structural integrity assessment of the reactor pressure vessel, the accurate reference temperature (T ) based on the Master Curve method is necessary. The T
) based on the Master Curve method is necessary. The T can be estimated by using the Mini-C(T) fracture toughness specimen in accordance with ASTM E1921 and JEAC4216, which prescribe the crack straightness criteria. A requirement in ASTM E1921 has been revised in a decade to increase the accuracy and reasonability, and the applicable crack curvature has been varied by applied codes. The crack curvature of the Mini-C(T) specimen might have an impact on the T
can be estimated by using the Mini-C(T) fracture toughness specimen in accordance with ASTM E1921 and JEAC4216, which prescribe the crack straightness criteria. A requirement in ASTM E1921 has been revised in a decade to increase the accuracy and reasonability, and the applicable crack curvature has been varied by applied codes. The crack curvature of the Mini-C(T) specimen might have an impact on the T because of the variation of the plastic constraint. In this work, the effect of the crack curvature on the fracture toughness (K
because of the variation of the plastic constraint. In this work, the effect of the crack curvature on the fracture toughness (K ) evaluation using the Mini-C(T) specimen was quantitatively evaluated by using the finite element analysis (FEA) including the Weibull stress analysis, to discuss the difference in a requirement of the crack straightness in ASTM E1921 and JEAC4216. FEAs showed a possibility that the upper limit curvature would decrease the plastic constraint, and consequently obtain higher K
) evaluation using the Mini-C(T) specimen was quantitatively evaluated by using the finite element analysis (FEA) including the Weibull stress analysis, to discuss the difference in a requirement of the crack straightness in ASTM E1921 and JEAC4216. FEAs showed a possibility that the upper limit curvature would decrease the plastic constraint, and consequently obtain higher K in the Mini-C(T) specimen. Furthermore, if the upper limit curvature according to the ASTM E1921-21 was allowed, the T
in the Mini-C(T) specimen. Furthermore, if the upper limit curvature according to the ASTM E1921-21 was allowed, the T would be estimated as nonconservative based on the Weibull stress analysis. In contrast, the difference in (T
would be estimated as nonconservative based on the Weibull stress analysis. In contrast, the difference in (T ) between the crack with upper limit curvature according to JEAC4216 and the ideal straight crack was not significant.
) between the crack with upper limit curvature according to JEAC4216 and the ideal straight crack was not significant.
Yamada, Ippei; Kojima, Kunihiro; Chimura, Motoki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1084, p.171261_1 - 171261_12, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Okagaki, Yuria; Hibiki, Takashi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 194, p.106267_1 - 106267_23, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0 :Ce using PHITS track-structure simulations
:Ce using PHITS track-structure simulationsHirata, Yuho; Kai, Takeshi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Kato, Takumi*; Kawaguchi, Noriaki*; Yanagida, Takayuki*
Radiation Measurements, 193, p.107651_1 - 107651_8, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0CaF :Ce has a high potential to be used as a dosimeter due to its high optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) intensity. However, when phosphors such as CaF
:Ce has a high potential to be used as a dosimeter due to its high optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) intensity. However, when phosphors such as CaF :Ce are irradiated with swift ions, the OSL intensity per dose decreases due to quenching effects. Traditionally, quenching effects in phosphors have been evaluated based on energy deposition density, using linear energy transfer (LET) as a metric. However, the relationship between quenching effects and LET varies with ion type, complicating unified evaluations. The track structure in PHITS can precisely simulate the radiation interactions. In this study, we simulated the detector response of CaF
:Ce are irradiated with swift ions, the OSL intensity per dose decreases due to quenching effects. Traditionally, quenching effects in phosphors have been evaluated based on energy deposition density, using linear energy transfer (LET) as a metric. However, the relationship between quenching effects and LET varies with ion type, complicating unified evaluations. The track structure in PHITS can precisely simulate the radiation interactions. In this study, we simulated the detector response of CaF :Ce irradiated with swift-ions and compared these results with experimental data. The comparison suggests that the quantum yield of OSL is a critical parameter influencing the quenching effect in CaF
:Ce irradiated with swift-ions and compared these results with experimental data. The comparison suggests that the quantum yield of OSL is a critical parameter influencing the quenching effect in CaF :Ce. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of improved phosphor detectors.
:Ce. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of improved phosphor detectors.
Tani, Riku; Inoue, Satoshi*; Mizoguchi, Takafumi*; Suda, Shoya; Nakajima, Ryota; Inoue, Hidetaka*; Kurabeishi, Nariaki*; Ouchi, Yasuhiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Shimizu, Osamu
JAEA-Technology 2025-018, 32 Pages, 2026/03
With rising summer temperatures, the number of heatstroke incidents at worksites has been increasing. Even short-term exposure to high-temperature and high-humidity environments can result in serious health hazards. In recent years, measures to prevent heatstroke in the workplace have been legally mandated, requiring employers to manage the work environment and ensure workers' health. At the JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility (JRTF), basic heatstroke prevention measures such as pre-shift health checks and strategic placement of water stations have been implemented. However, due to rising workplace temperatures and longer work durations, these conventional measures alone were considered insufficient to adequately reduce risk. This year, large spot coolers were installed, and cooling vests were introduced to improve both the work environment and individual thermal load. Data on temperature, humidity, and WBGT values were collected before and after the implementation to evaluate the effects on environmental conditions and worker comfort. This report aims to assess the effectiveness of specific countermeasures in reducing the risk of heatstroke during decommissioning work and to inform future improvements to the work environment.
Futemma, Akira; Ochi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Nakama, Shigeo; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Sanada, Yukihisa; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2025-015, 171 Pages, 2026/03
On March 11, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake and tsunami caused the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, releasing radioactive material. Since then, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) with manned helicopters has been used to assess radiation distribution quickly. In FY2024, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under commission from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, conducted ARM around the Shimane Nuclear Power Station, producing background dose rate maps validated against ground and other data. During a nuclear emergency drill, UAV training flights complemented manned monitoring, confirming the effectiveness of real-time communication and rapid mapping. The UAV data system was developed and demonstrated for real-time analysis and multi-platform use. Skill training for multicopters was also conducted to strengthen operational capability. Additionally, joint monitoring with the U.S., France, South Korea, and Canada provided insights into international technologies and practices, emphasizing the value of information sharing. This report summarizes the results and technical challenges from these FY2024 activities, contributing to the advancement of emergency radiation monitoring.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2025-013, 206 Pages, 2026/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances conducted in FY2024. Car-borne and walk surveys, a measurement using survey meters, and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data on land to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of those air dose rates were analyzed. In order to confirm the applicability of unmanned aircraft to monitoring in mountainous areas, a basic performance of unmanned aircraft was investigated in mountainous areas. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. These measurement results were published on the WEB site. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out. Representative life patterns that can be expected after the return to the evacuation-designated restricted area were set, and the cumulative exposure doses were evaluated for the local governments and residents in the area. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the temporal changes in the score were analyzed. A system to report the tritium concentration level in seawater to the Nuclear Regulation Authority was operated, and the variation of tritium concentration before and after the discharge of ALPS treated water to the ocean was analyzed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until FY2024 was analyzed.
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki
JAEA-Review 2025-063, 50 Pages, 2026/03
In the decommissioning of reprocessing facilities, one of the reasons why a safe storage period is usually not set is that Pu-241 decays into Am-241, which accumulates in the process. As eighteen years have passed since the Tokai Reprocessing Plant finished its operation in 2007, it was considered during recent work that the relative proportion of Am-241 has increased compared to earlier measurements. Therefore, this trend was investigated using records of  nuclide analyses conducted during operations. In this investigation, we focused on and discussed the relative proportion of the major nuclide, Cs-137 and Am-241. The survey confirmed that the proportion of Am-241 tended to increase in all process equipment, though the extent of the increase varied depending on the process. In operations related to spent fuel storage systems, decontaminating when moving fuel, and the solubility of Cs-137 have an effect. In recent years, there have even been cases where Am-241 accounted for 80 % to 90 % of the
nuclide analyses conducted during operations. In this investigation, we focused on and discussed the relative proportion of the major nuclide, Cs-137 and Am-241. The survey confirmed that the proportion of Am-241 tended to increase in all process equipment, though the extent of the increase varied depending on the process. In operations related to spent fuel storage systems, decontaminating when moving fuel, and the solubility of Cs-137 have an effect. In recent years, there have even been cases where Am-241 accounted for 80 % to 90 % of the  nuclides detected. In operations related to mechanical processes, including the shearing equipment, the increase appears to correspond to the composition of the spent fuel, and the proportion of Am-241 in all
nuclides detected. In operations related to mechanical processes, including the shearing equipment, the increase appears to correspond to the composition of the spent fuel, and the proportion of Am-241 in all  nuclides can exceed 40 % in some cases. In operations related to vitrification process, while the increase seems to correspond to the composition of the high-level radioactive waste, the proportion of Am-241 among all
nuclides can exceed 40 % in some cases. In operations related to vitrification process, while the increase seems to correspond to the composition of the high-level radioactive waste, the proportion of Am-241 among all  nuclides has not exceeded 10 % in any case. In operations related to radioactive liquid waste processes, the precipitate components at the bottom of storage tanks have an effect and Am-241 tends to be detected at a high proportion. In operations related to incineration processing of radioactive solid waste, the overall trend is thought to correspond to the type of waste handled, but relatively high proportions of Am-241 have been detected on internal walls of incinerators and similar areas.
nuclides has not exceeded 10 % in any case. In operations related to radioactive liquid waste processes, the precipitate components at the bottom of storage tanks have an effect and Am-241 tends to be detected at a high proportion. In operations related to incineration processing of radioactive solid waste, the overall trend is thought to correspond to the type of waste handled, but relatively high proportions of Am-241 have been detected on internal walls of incinerators and similar areas.
Department of Radiation Protection, Nuclear Science Research Institute; Nuclear Facilities Management Section, Aomori Research and Development Center
JAEA-Review 2025-055, 107 Pages, 2026/03
This annual report describes the activities in the 2024 fiscal year of Department of Radiation Protection at Nuclear Science Research Institute, Harima Synchrotron Radiation Radioisotope Laboratory, and Nuclear Facilities Management Section at Aomori Research and Development Center. The activities described in this report are environmental monitoring, radiation protection practices in workplaces, individual monitoring, maintenance of monitoring instruments, and research and development of radiation protection. At these institutes, the occupational exposures did not exceed the dose limits. The radioactive gaseous and liquid discharges from the facilities were well below the prescribed limits. The research and development activities in the field of radiological protection were continued.