Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 (cr) solubility determined by solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe
(cr) solubility determined by solubility experiments of Se co-existing with FeDoi, Reisuke; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1554 - 1562, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)To determine log K for FeSe
for FeSe (cr) dissolution reaction, solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe were performed. Temperature was maintained at 348 K. Se concentration as a function of equilibration periods indicated that Se concentrations were similar at different equilibration periods. Only FeSe
(cr) dissolution reaction, solubility experiments of Se co-existing with Fe were performed. Temperature was maintained at 348 K. Se concentration as a function of equilibration periods indicated that Se concentrations were similar at different equilibration periods. Only FeSe (cr) was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the equilibrated precipitates.
(cr) was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the equilibrated precipitates. 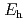 and pH of the equilibrated suspensions ranged from -188.6 to -4.9 mV vs. SHE and 6.00 to 8.76, respectively. Se
and pH of the equilibrated suspensions ranged from -188.6 to -4.9 mV vs. SHE and 6.00 to 8.76, respectively. Se
 and Fe
and Fe are thermodynamically stable in this region. Interpretations using SIT model showed that the relationship between
are thermodynamically stable in this region. Interpretations using SIT model showed that the relationship between 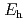 and the measured concentrations could be interpreted well when in the following equation n = 0.50
and the measured concentrations could be interpreted well when in the following equation n = 0.50 0.01 and log K
0.01 and log K  = -17.24
= -17.24 0.31 : 4Fe
0.31 : 4Fe Se(cr) = 4nFe
Se(cr) = 4nFe + Se
+ Se
 + (8n - 2)e
+ (8n - 2)e . The logK
. The logK value calculated from the available thermodynamic data agrees with that determined here.
value calculated from the available thermodynamic data agrees with that determined here.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Hayashi, Masanori*; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.161 - 172, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.07(Chemistry, Physical)The sorption and diffusion behavior of Cs in illite-added compacted montmorillonite was investigated by through-diffusion experiment. The obtained distribution coefficient of Cs for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite was several times larger than that for the montmorillonite without illite, while no increase of effective diffusion coefficient was observed for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite. The dominant sorption site of Cs on illite is considered to be the frayed edge site (FES) considering the Cs concentration in this experiment. Therefore, the surface diffusion of Cs sorbing on the FES on illite surface was considered to be negligible in compacted montmorillonite.
Doi, Reisuke; Uchikoshi, Keiji*
no journal, ,
Solubility experiments of Se in the presence of Fe under reducing conditions were performed from oversaturation direction to determine the solubility limiting solid of Se. In 1 month, Se concentration decreased to about 10  mol/dm
mol/dm  and equilibrium was attained. XRD patterns of the solid obtained after equilibrium showed that the Se solid phase was only FeSe
and equilibrium was attained. XRD patterns of the solid obtained after equilibrium showed that the Se solid phase was only FeSe . The dependencies of Se concentration on Fe concentration and Eh were interpreted as a dissolution reaction of FeSe
. The dependencies of Se concentration on Fe concentration and Eh were interpreted as a dissolution reaction of FeSe . A solubility limiting solid of Se was determined to be FeSe
. A solubility limiting solid of Se was determined to be FeSe .
.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Otsuka, Shunji*; Hayashi, Masanori*; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Doi, Reisuke; Uchikoshi, Keiji*
no journal, ,
Solubility experiments of Se were performed from oversaturation direction in the presence of Fe under reducing conditions to determine the solubility-controlling solid phase of Se. Equilibrium and the steady Se concentrations were reached in  1 month. The Se solid that was detected by XRD analyses of the solid samples from the equilibrated suspensions was only FeSe
1 month. The Se solid that was detected by XRD analyses of the solid samples from the equilibrated suspensions was only FeSe . The thermodynamic interpretations of the solubility data and XRD analyses of the solid samples show FeSe
. The thermodynamic interpretations of the solubility data and XRD analyses of the solid samples show FeSe to be SSP.
to be SSP.
Doi, Reisuke; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
no journal, ,
In order to determine the solubility-controlling solid of Se under reducing conditions, solubility experiments of Se were performed from oversaturation direction in the presence of Fe under reducing conditions. The Se concentration as a function of equilibration periods suggested the attainment of equilibrium in our system within a month. Only FeSe was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the solid samples from the equilibrated suspensions. Interpretations using the specific ion interaction theory model showed that the relationship between Eh and the measured concentrations of Se and Fe could be interpreted well by the dissolution reaction of FeSe
was detected as the Se solid phase by XRD analysis of the solid samples from the equilibrated suspensions. Interpretations using the specific ion interaction theory model showed that the relationship between Eh and the measured concentrations of Se and Fe could be interpreted well by the dissolution reaction of FeSe . Therefore, we conclude that FeSe
. Therefore, we conclude that FeSe is most likely the solubility-controlling solid of Se under these conditions.
is most likely the solubility-controlling solid of Se under these conditions.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Otsuka, Shunji*; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Kamei, Gento; Alexander, W. R.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English