Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 L. irradiated by
L. irradiated by  rays
raysKitano, Sayaka*; Miyagi, Atsuko*; Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Yamaguchi, Masatoshi*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kawai, Maki*
Metabolomics, 11(1), p.134 - 142, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:25.41(Endocrinology & Metabolism) -ray irradiation on oxalate metabolism in
-ray irradiation on oxalate metabolism in  L.
L.Kitano, Sayaka*; Miyagi, Atsuko*; Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kawai, Maki*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 108, 2014/03
 ray irradiation on
ray irradiation on  L.
L.Kitano, Sayaka*; Miyagi, Atsuko*; Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kawai, Maki*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 101, 2013/01

Nakasone, Akari*; Fujiwara, Masayuki*; Fukao, Yoichiro*; Biswas, K.; Rahman, A.*; Yamada, Maki*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Physiology, 160(1), p.93 - 105, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.62(Plant Sciences)
Nakasone, Akari; Kawai, Maki*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 65, 2009/12
 potentially mediates the response to synthetic auxin, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, in
potentially mediates the response to synthetic auxin, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, in 
Nakasone, Akari; Yamada, Maki*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
Journal of Plant Physiology, 166(12), p.1307 - 1313, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:13.07(Plant Sciences) -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid reveals that
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid reveals that 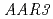 , a gene encoding a DCN1-like protein, regulates responses to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in Arabidopsis roots
, a gene encoding a DCN1-like protein, regulates responses to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in Arabidopsis rootsBiswas, K. K.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Higuchi, Kanako*; Miyazaki, Yuji*; Nguyen, V. V.*; Rahman, A.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*; Koshiba, Tomokazu*; Tanaka, Atsushi; et al.
Plant Physiology, 145(3), p.773 - 785, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:66.14(Plant Sciences)We screened mutants for root growth resistance to a putative antiauxin, PCIB, which inhibits auxin action by interfering the upstream auxin signaling events. Eleven PCIB-resistant mutants were obtained. Genetic mapping indicates that the mutations are located in at least 5 independent loci including two known auxin-related loci,  and
and 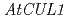 .
. 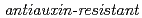 mutants (
mutants (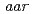 s)
s) 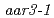 ,
, 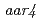 and
and 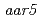 were also resistant to 2,4-D as shown by a root growth assay. Positional cloning of
were also resistant to 2,4-D as shown by a root growth assay. Positional cloning of 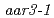 revealed that the
revealed that the 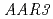 gene encodes a protein with a domain of unknown function (DUF298), which has not previously been implicated in auxin signaling. The protein has a putative nuclear localization signal and shares homology with the DCN-1 protein through the DUF298 domain. The results also indicate that PCIB can facilitate the identification of factors involved in auxin or auxin-related signaling.
gene encodes a protein with a domain of unknown function (DUF298), which has not previously been implicated in auxin signaling. The protein has a putative nuclear localization signal and shares homology with the DCN-1 protein through the DUF298 domain. The results also indicate that PCIB can facilitate the identification of factors involved in auxin or auxin-related signaling.
Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Akari*; Chhun, T.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Biswas, K. K.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Baskin, T. I.*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Journal, 47(5), p.788 - 801, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:59.9(Plant Sciences)2,4-D, a chemical analogue of IAA, is widely used as a growth regulator and exogenous source of auxin. It is believed that they share a common response pathway. Here, we show that a mutant, 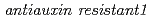 (
(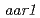 ) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the
) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the 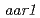 mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the
mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the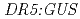 and
and 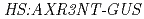 backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of
backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of 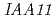 expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a
expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a 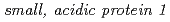 with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
 -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis root
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis rootOno, Yutaka; Oura, Chiharu*; Rahman, A.; Aspuria, E. T.; Hayashi, Kenichiro*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*
Plant Physiology, 133(3), p.1135 - 1147, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:132 Percentile:92.45(Plant Sciences)PCIB ( -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of 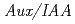 genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in
genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in 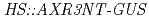 transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.
transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.
Aspuria, E. T.; Oura, Chiharu*; Chen, Q.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Cell Reports, 21(1), p.52 - 57, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:17.54(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English
Ono, Yutaka; Oura, Chiharu*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
Annals of Botany, 89(1), p.77 - 82, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:24.54(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English
Oura, Chiharu*; Aspuria, E. T.; Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
JAERI-Review 2001-039, TIARA Annual Report 2000, p.67 - 69, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
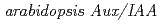 genes
genesLiu, J.; Oura, Chiharu*; Aspuria, E. T.; Ono, Yutaka; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(19), p.1642 - 1645, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:1.82(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kawai, Maki; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Hirata, Aiko*; Ono, Yutaka; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
Plant Biotechnology, 17(4), p.305 - 308, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Kawai, Maki; Pan, L.*; Reed, J. C.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
FEBS Letters, 464(3), p.143 - 147, 1999/12
Times Cited Count:125 Percentile:93.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Kawai, Maki; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ono, Yutaka; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, P. 56, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
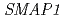 , a gene encoding small acidic protein revealed by mutant screening with antiauxin is involved in 2,4-D sensitivity but not IAA sensitivity in arabidopsis roots
, a gene encoding small acidic protein revealed by mutant screening with antiauxin is involved in 2,4-D sensitivity but not IAA sensitivity in arabidopsis rootsOno, Yutaka; Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Hikari; Chhun, T.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakasone, Akari; Kawai, Maki*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
no journal, ,
The 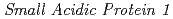 (
(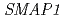 ) gene is recently identified as the factor that mediates the synthetic auxin 2,4-D response in
) gene is recently identified as the factor that mediates the synthetic auxin 2,4-D response in  root. SMAP1 has the conserved phenylalanine and asparagic acid (F/D) domain, which is highly conserved in both plants and animals. Introduction of
root. SMAP1 has the conserved phenylalanine and asparagic acid (F/D) domain, which is highly conserved in both plants and animals. Introduction of 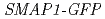 to
to 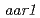 recovered 2,4-D sensitivity of
recovered 2,4-D sensitivity of 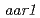 while that of
while that of 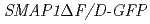 did not. Using anti-GFP-MicroBeads, the proteins that form complexes with SMAP1-GFP but not with SMAP1
did not. Using anti-GFP-MicroBeads, the proteins that form complexes with SMAP1-GFP but not with SMAP1 F/D-GFP were pulled down from the
F/D-GFP were pulled down from the  extract and identified by MS analysis. The identified peptide sequences indicated that SMAP1-GFP binds to COP9 Signalosome (CSN). The results implied that SMAP1 regulates 2,4-D response by interacting to CSN through F/D region.
extract and identified by MS analysis. The identified peptide sequences indicated that SMAP1-GFP binds to COP9 Signalosome (CSN). The results implied that SMAP1 regulates 2,4-D response by interacting to CSN through F/D region.
Nakasone, Akari; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei; Ono, Yutaka; Kawai, Maki*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
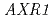 and
and 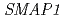 that function in the 2,4-D signal transduction pathway in
that function in the 2,4-D signal transduction pathway in 
Ono, Yutaka; Nakasone, Akari; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
The 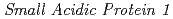 (
(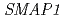 ) gene is responsible for the anti-auxin resistant mutation,
) gene is responsible for the anti-auxin resistant mutation, 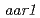 , and encodes a factor that mediates the synthetic auxin 2,4-D response. To gain an insight into the function of SMAP1, the
, and encodes a factor that mediates the synthetic auxin 2,4-D response. To gain an insight into the function of SMAP1, the 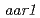 mutant was crossed with known auxin-related mutants. The double mutants,
mutant was crossed with known auxin-related mutants. The double mutants, 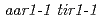 ,
,  , and
, and 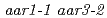 showed more resistant to 2,4-D than the corresponding single mutants in root growth assay. On the other hand, the
showed more resistant to 2,4-D than the corresponding single mutants in root growth assay. On the other hand, the 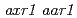 double mutants showed severe morphological defects with a lack of root meristem formation. The overexpression of
double mutants showed severe morphological defects with a lack of root meristem formation. The overexpression of 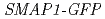 fusion gene under 35S promoter relieved pleiotropic morphological phenotypes of
fusion gene under 35S promoter relieved pleiotropic morphological phenotypes of 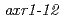 such as dwarf, multiple shoots, altered flower structure, low fertility and reduced auxin response. The results suggested that the function of
such as dwarf, multiple shoots, altered flower structure, low fertility and reduced auxin response. The results suggested that the function of 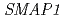 is tightly linked to that of
is tightly linked to that of 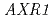 in genetic level.
in genetic level.