Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Udagawa, Makoto; Li, Y.; Nishida, Akemi; Nakamura, Izumi*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 167, p.2 - 10, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.76(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)It is important to assure the structural Integrity of piping systems under severe earthquakes because those systems comprise the pressure boundary for coolant with high pressure and temperature. In this study, we examine the seismic safety capacity of piping systems under severe dynamic seismic loading using a series of dynamic-elastic-plastic analyses focusing on dynamic excitation experiments of 3D piping systems which was tested by NIED. Analytical results were consistent with experimental data in terms of natural frequency, natural vibration mode, response accelerations, elbow opening-closing displacements, strain histories, failure position, and low-cycle fatigue failure lives. Based on these results, we concluded that the analytical model used in the study can be applied to failure behavior evaluation for piping systems under severe dynamic seismic loading.
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio*; Udagawa, Makoto
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 139(2), p.021202_1 - 021202_13, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.57(Engineering, Mechanical)Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Otsu, Takuyo; Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(5), p.051405_1 - 051405_8, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.86(Engineering, Mechanical)We conducted a series of fracture toughness tests based on the Master curve method for several specimen size and shapes, such as 0.16T-CT, pre-cracked Charpy type, 0.4T-CT and 1T-CT specimens, in commercially manufactured 5 kinds of A533B class1 steels with different impurity contents and fracture toughness levels. The reference temperature ( ) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher
) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher  , and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining
, and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining  using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 131, p.85 - 95, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.59(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)A number of cracks due to primary water stress corrosion cracking (PWSCC) in pressurized water reactors and Ni-based alloy stress corrosion cracking (NiSCC) in boiling water reactors have been detected around Ni-based alloy welds. The causes of crack initiation and growth due to stress corrosion cracking include weld residual stress, operating stress, the materials, and the environment. We have developed the analysis code PASCAL-NP for calculating the failure probability and assessment of the structural integrity of cracked components on the basis of probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) considering PWSCC and NiSCC. This PFM analysis code has functions for calculating the incubation time of PWSCC and NiSCC crack initiation, evaluation of crack growth behavior considering certain crack location and orientation patterns, and evaluation of failure behavior near Ni-based alloy welds due to PWSCC and NiSCC in a probabilistic manner. Herein, actual plants affected by PWSCC have been analyzed using PASCAL-NP. Failure probabilities calculated by PASCAL-NP are in reasonable agreement with the detection data. Furthermore, useful knowledge related to leakage due to PWSCC was obtained through parametric studies using this code.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Li, Y.; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
The J-integral solution for cracked pipes is a high important parameter in crack growth calculation and failure evaluation based on the elastic-plastic fracture mechanics. One of the most important crack types in structural integrity assessment for nuclear piping systems is circumferential semi-elliptical surface crack. Although several J-integral solutions have been provided, no solution was developed at both the deepest and the surface points of circumferential semi-elliptical surface cracks. In this study, the J-integral solutions of circumferential semi-elliptical surface cracks were developed by numerical finite element analyses. Moreover, in order to benefit users in practical applications, a pair of convenient J-integral estimation equations were developed. The accuracy and applicability of the convenient equations were confirmed by comparing with the provided stress intensity factor solutions in elastic region and with finite element analysis results in elastic-plastic region.
Tobita, Toru; Udagawa, Makoto; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 452(1-3), p.61 - 68, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To investigate the changes in the mechanical properties of cladding materials irradiated with high neutron fluence, two types of cladding materials were fabricated using the submerged-arc welding and electroslag welding methods. The tensile tests, Charpy impact tests and fracture toughness tests were conducted before and after neutron irradiation with a fluence of 10 n/cm
n/cm at 290
at 290  C. With neutron irradiation, the yield strength and ultimate strength increased, and the total elongation decreased. The Charpy upper-shelf energy was reduced and the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature was increased with neutron irradiation. There was no obvious decrease in the elastic-plastic fracture toughness (J
C. With neutron irradiation, the yield strength and ultimate strength increased, and the total elongation decreased. The Charpy upper-shelf energy was reduced and the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature was increased with neutron irradiation. There was no obvious decrease in the elastic-plastic fracture toughness (J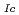 ) of the cladding materials at high neutron fluence. The tearing modulus decreased with neutron irradiation, and considerable low J
) of the cladding materials at high neutron fluence. The tearing modulus decreased with neutron irradiation, and considerable low J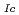 values were observed at high temperatures submerged-arc-welded cladding materials.
values were observed at high temperatures submerged-arc-welded cladding materials.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Udagawa, Makoto; Onizawa, Kunio; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Li, Y.*
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/07
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on the Integrity of Nuclear Components (ASINCO-10), p.219 - 226, 2014/04
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL-NP has been improved continuously with reference to the latest knowledge. This code treats not only primary water stress corrosion cracking (PWSCC) in PWR but also Ni-based alloy stress corrosion cracking (NiSCC) in BWR. This code can also evaluate both leakage and break probabilities due to these types of SCC, considering the scatters of parameters which affect the structural integrity of Ni-based alloy welds. In this paper, failure probability analyses have been performed focusing on vessel head penetrations affected by PWSCC detected at Ohi unit 3 nuclear power plant as well as control rod drive housings affected by NiSCC at Hamaoka unit 1. In order to perform case studies for these actual plants, analytical models of predicting the incubation time to PWSCC and NiSCC initiation were introduced to PASCAL-NP. Failure probabilities calculated by PASCAL-NP reasonably agreed with inspection results in these plants.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-013, 145 Pages, 2013/11
As a part of research on the structural integrity assessment for LWR components considering aging degradation, a PFM analysis code PASCAL-NP has been developed. This code evaluates the failure probabilities on a basis of Monte Carlo method caused by PWSCC / NiSCC at dissimilar metal welds and structurally discontinuous components. This PFM analysis code has functions of crack initiation and crack growth calculations for various patterns of crack locations and orientations in a probabilistic manner such as the scatters of material strength, crack growth rate and residual stress distribution, and so on. This code can also evaluate the failure probabilities such as leakage and/or break probabilities of Ni-based alloy welds due to these types of SCC. This report summarizes the failure examples in actual plants and theoretical backgrounds. This one also represents methods to execute program and the case studies using PASCAL-NP code.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Udagawa, Makoto; Nakamura, Mitsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 135(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_9, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:71.63(Engineering, Mechanical)The residual stresses generated within the weld-overlay cladding and base material of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steel was evaluated for as-welded and post-welded heat-treated conditions using thermo-elastic plastic creep analyses considering phase transformation. By comparing the analytical results with the experimentally determined values, we found a good agreement for the residual stress distribution within the cladding and the base material. It was shown that considering phase transformation during welding was important for improving the accuracy of residual stress analysis. Using the calculated residual stress distribution, we performed fracture mechanics analyses for an RPV during pressurized thermal shock events. We evaluated the effect of the weld residual stress on the structural integrity of an RPV. The results indicated that consideration of residual stress produced by weld-overlay cladding and PWHT is important for assessing the structural integrity of RPV.
Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Otsu, Takuyo; Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Mini-CT (0.16T-CT) specimens up to eight can be taken from broken halves of surveillance Charpy specimens. We conducted a series of fracture toughness tests based on the Master curve method for several specimen size and shapes, such as 0.16T-CT, pre-cracked Charpy type, 0.4T-CT and 1T-CT specimens, in commercially manufactured 5 kinds of A533B class1 steels with different impurity contents and fracture toughness levels. Reference temperature To of 0.16T-CT specimens was approximately equal to those of 1T-CT and other type of specimens for all materials. We also examined a loading rate effect on TO of Mini-CT specimens for some materials within the specified range in the test method. Higher loading rate gave rise to slightly higher TO. The difference in TO between upper and lower loading rate of the standard was approximately 10 C.
C.
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki; Katsuyama, Jinya; Udagawa, Makoto; Nakamura, Mitsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, A, 76(770), p.56 - 64, 2010/10
In order to evaluate residual stress distributions in the vessel wall of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) due to weld-overlay cladding and post-weld heat-treatment (PWHT), thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analysis considering the changes of material properties in heat-affected zone (HAZ) has been performed. Analytical results of stress distributions considered the material property changes in HAZ agreed well with the ones measured experimentally from weld-overlay cladded plates. Applying the analysis method to a RPV model, through-wall residual stress distributions caused by weld-overlay cladding, PWHT, hydrostatic test, operational load and transient loads during pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events have been computed. Effects of the weld-overlay cladding on the stress distributions in the vessel wall of a RPV have been evaluated. Using the stress distributions, stress intensity factors for a postulated crack during PTS events have been studied.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Udagawa, Makoto; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Nakamura, Mitsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 2(2), p.50 - 64, 2010/08
Weld residual stress is the most important factors to assess the structural integrity of RPV since it affects crack initiation and growth behaviors. Inner surface of the RPV is protected against corrosion by cladding. At the J-weld of the vessel head penetrations, Ni-based alloys are used for weld material. After the fabrication process, the residual stress remains in such dissimilar welds after PWHT. The residual stresses were measured using the DHD method. Thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analyses considering phase transformation were also performed. By comparing analytical results with measured ones, it was shown that there was a good agreement of residual stress distribution. It was suggested that taking phase transformation into account was important to improve the accuracy of analysis. Using the residual stress distributions, PWSCC behavior was calculated using PFM analysis code. Effects of the residual stress and scatter of PWSCC growth rate on the crack penetration were evaluated.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2010 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2010) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
A number of cracks due to primary water stress corrosion cracking (PWSCC) in PWR and Ni-based alloys stress corrosion cracking (NiSCC) in BWR have been observed near Ni-based alloy welds. One of the causes of initiation and growth due to the SCC is high tensile residual stress as well as operating stress. In this study, an analysis code, PASCAL-NP, for the PWSCC/NiSCC growth at the dissimilar metal welds based on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) was developed. This PFM analysis code has a function of SCC growth calculation for some patterns of crack locations and orientations in a probabilistic manner. This code can also evaluate the failure probability of Ni-based alloy welds due to PWSCC/NiSCC. Using this code and results from welding simulations, case studies on PWSCC growth were performed focusing on the location and orientation of PWSCC. Effect of the scatter of PWSCC growth rate on the crack penetration, i.e. leakage is shown in comparison with deterministic analyses.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki; Onizawa, Kunio
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 28(3), p.261 - 271, 2010/07
Stainless steel is welded as a cladding on the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) made of low alloy steel. In order to assess the structural integrity of an RPV more precisely, the residual stress distribution caused by weld-overlay cladding and post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) is to be evaluated. Although cladding layer is very thin compared to vessel wall, it is not easy to evaluate steep residual stress distribution which occurs in dissimilar metal weld. In this study, cladded specimens were fabricated using different welding methods. Residual stress measurements using both sectioning and DHD methods were then performed to evaluate the residual stress distributions. It was shown that thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analysis results based on finite element method were agreed with experimental results. It was also clarified that the main cause of residual stress due to welding and PWHT was the difference of thermal expansion between weld and base metals.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 8th International Symposium of the Japan Welding Society on Innovations in Welding and Joining for a New Era in Manufacturing (8WS) (DVD-ROM), P. 319, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki; Katsuyama, Jinya; Udagawa, Makoto; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 8th International Symposium of the Japan Welding Society on Innovations in Welding and Joining for a New Era in Manufacturing (8WS) (DVD-ROM), 83 Pages, 2008/11
Weld-overlay cladding of austenitic stainless steel is applied to the inner surface on ferritic low-alloy steel of RPV for protecting from corrosion. After the manufacturing processes of an RPV including weld-overlay cladding, post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) and pressure test, welding residual stress still remains in such dissimilar metal welds, which could affect the structural integrity of RPV during PTS. In the present study, thermal-elastic-plastic analysis using finite element method has been performed to evaluate residual stress distribution in reactor pressure vessel produced by weld-overlay cladding. Stress intensity factor during PTS has been calculated using PFM analysis code (PASCAL2). The stress intensity factor considering weld-overlay cladding is larger than that of no weld residual stress.
Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2007 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference/8th International Conference on Creep and Fatigue at Elevated Temperatures (PVP 2007/CREEP-8) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/07
In order to assess the structural integrity of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV), it is assumed that a surface crack resides through the cladding at the inner surface of the vessel. It is, therefore, important to precisely evaluate stress intensity factor (SIF) taking the residual stress due to weld overlay cladding and post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) into account. In this study, we performed a numerical simulation based on thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analysis using finite element method to evaluate residual stress distribution near the cladding layer produced by weld overlay cladding and PWHT. The tensile residual stress of about 400 MPa occurs in the cladding at room temperature after the PWHT. The residual stress distributions under the normal operating conditions (pressure and temperature) of RPV were also evaluated. The effect of residual stress and evaluation methods on SIF behavior for various crack size were studied under several PTS conditions such as SBLOCA, MSLB and LBLOCA.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Udagawa, Makoto; Li, Y.*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Toru; Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
For safe operation of light water reactors, the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is confirmed based on the evaluation and prediction of aging degradation such as irradiation embrittlement and stress corrosion cracking. To contribute to this issues, we have performed to study on the improvement of fracture toughness evaluation method and development of probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code for RPVs. It was clarified that temperature dependence of the fracture toughness of RPV steels with different toughness levels can be evaluated with enough accuracy using miniature specimens. In addition, in order to evaluate the failure probability of the RPV head penetration due to the PWSCC at the nickel based dissimilar metal welds, we have developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL-NP. The major findings of these studies are summarized in the poster.