Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Br-
Br- -methyl-phenylalanine for tumor PET imaging
-methyl-phenylalanine for tumor PET imagingHanaoka, Hirofumi*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Suzuki, Yurika*; Yamaguchi, Aiko*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Uehara, Tomoya*; Nagamori, Shushi*; Kanai, Yoshikatsu*; Ishioka, Noriko; Tsushima, Yoshito*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 56(5), p.791 - 797, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.87(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
Dispersion and freezing of molten core material was calculated by the COMPASS code to compare with the experimental data of GEYSER. Molten core material flowed up with freezing on the pipe inner surface. As a molten pool behavior, CABRI-TPA2 experiment was analyzed, where a sphere of solid steel was surrounded by solid fuel. Power was injected to cause melting and boiling of the steel sphere. SCARABEE-BE+3 test was analyzed by COMPASS as a validation of failure of duct walls.
Uehara, Yasushi*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamamoto, Yuichi*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-17) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2009/06
A mesoscopic approach with the COMPASS code is expected to advance the understanding of key phenomena during event progression in core disruptive accidents. In this paper, the overall analysis of SCARABEE-BE+3 test with the SIMMER-III is described as well as the simulation with COMPASS, focusing on the duct wall failure in a small temporal and spatial window cut from the SIMMER-III analysis results.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2009/05
A computer code, named COMPASS, is developed for multi-physics analysis of core disruptive accidents of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). A meshless method, called MPS method, is employed since complex thermal-hydraulics and structural problems with various phase change processes have to be analyzed. Verification for separeted basic processes and validation for practical phenomena are carried out. COMPASS is also expected to investigate molten fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality in large size SFR cores. Both MOX and metal fuels are considered. Eutectic reactions between the metal fuel and the cladding material are investigated by phase diagram calculation, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics. Basic studies relevant to the numerical methods support the code development of COMPASS. Parallel processing is implemented by OpenMP to treat large-scale problems. A visualization tool is also prepared by using AVS.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
A computer code, named COMPASS, is being developed for various complex phenomena of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The COMPASS is designed to analyze multi-physics problems involving thermal hydraulics, structure and phase change, in a unified framework of the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method. The project has been carried out by six organizations for five years from FY2005 to FY2009. In this paper, the outcomes of the project in FY2007 are presented. Three validation calculations were completed by following the validation plan: melt freezing and blockage formation, molten pool boiling, and duct wall failure. The COMPASS code development was supported by basic studies of the numerical method, material science for eutectic reaction of the metal fuel, and SIMMER-III analyses.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of IAEA Topical Meeting on Advanced Safety Assessment Methods for Nuclear Reactors (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2007/10
A computer code, named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis), is being developed for various complex phenomena of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). Theoretical studies are performed about a unified algorithm for compressible and incompressible flows, fluid flow with solid debris, and algorithm improvement for free surface flows. Code verification and validation procedures are established by exploiting the past experiences in those of SIMMER-III code. COMPASS will be used for separated phenomena in CDAs, while the whole core will be analyzed by SIMMER-III. COMPASS is expected to clarify the detailed process in duct wall failure and fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality during CDAs in large size SFRs.
 Re]Organorhenium-labeled antibody fragments with renal enzyme-cleavable linkage for low renal radioactivity levels
Re]Organorhenium-labeled antibody fragments with renal enzyme-cleavable linkage for low renal radioactivity levelsUehara, Tomoya*; Koike, Miho*; Nakata, Hideo*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Iida, Yasuhiko*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Endo, Keigo*; Arano, Yasushi*
Bioconjugate Chemistry, 18(1), p.190 - 198, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:57.65(Biochemical Research Methods)Renal localization of radiolabeled antibody fragments constitutes a problem in targeted imaging and radiotherapy. To estimate the applicability of the molecular design to metallic radionuclides, [ Re]tricarbonyl(cyclopentadienylcarbonate)rhenium ([
Re]tricarbonyl(cyclopentadienylcarbonate)rhenium ([ Re]CpTR-COOH) was conjugated with maleoyl-glycyl-lysine to prepare [
Re]CpTR-COOH) was conjugated with maleoyl-glycyl-lysine to prepare [ Re]CpTR-GK. The cleavage of the glycyl-lysine linkage of the compound generates a glycine conjugate of [
Re]CpTR-GK. The cleavage of the glycyl-lysine linkage of the compound generates a glycine conjugate of [ Re]CpTR-Gly. [
Re]CpTR-Gly. [ Re]CpTR-GK was conjugated to thiolated Fab fragments to prepare [
Re]CpTR-GK was conjugated to thiolated Fab fragments to prepare [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab. The biodistribution of radioactivity after injection of [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab. The biodistribution of radioactivity after injection of [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab was compared with that of [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab was compared with that of [ Re]CpTR-Fab. [
Re]CpTR-Fab. [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab exhibited significantly lower renal radioactivity levels than did [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab exhibited significantly lower renal radioactivity levels than did [ Re]CpTR-Fab. The analysis of urine samples collected for 6 h postinjection of [
Re]CpTR-Fab. The analysis of urine samples collected for 6 h postinjection of [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab showed that [
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab showed that [ Re]CpTR-Gly was the major radiometabolite. In tumor-bearing mice, [
Re]CpTR-Gly was the major radiometabolite. In tumor-bearing mice, [ Re]CpTR-GK-Fab significantly reduced renal radioactivity levels without impairing the radioactivity levels in tumor. These findings indicate that the molecular design of radioparmaceuticals labeled with metallic radionuclides can be useful by using a radiometal chelate of high inertness and by designing a radiometabolite of high urinary excretion when released from antibody fragments following cleavage of a glycyl-lysine linkage. This study also indicates that a change in chemical structure of a radiolabel attached to a glycyl-lysine linkage significantly affected enzymes involved in the hydrolysis reaction.
Re]CpTR-GK-Fab significantly reduced renal radioactivity levels without impairing the radioactivity levels in tumor. These findings indicate that the molecular design of radioparmaceuticals labeled with metallic radionuclides can be useful by using a radiometal chelate of high inertness and by designing a radiometabolite of high urinary excretion when released from antibody fragments following cleavage of a glycyl-lysine linkage. This study also indicates that a change in chemical structure of a radiolabel attached to a glycyl-lysine linkage significantly affected enzymes involved in the hydrolysis reaction.
 Re chelate-conjugated bisphosphonate for the development of new radiopharmaceuticals for bones
Re chelate-conjugated bisphosphonate for the development of new radiopharmaceuticals for bonesUehara, Tomoya*; Jin, Z. L.*; Ogawa, Kazuma*; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nakayama, Morio*; Arano, Yasushi*
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 34(1), p.79 - 87, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:60.21(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)In this study, a key factor affecting the pharmacokinetics of a chelate-conjugated BP was investigated to estimate the validity and the applicability of molecular design. Chemically inert and well-characterized [ Re]CpTR-Gly was conjugated with 3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate and purified by HPLC to prepare [
Re]CpTR-Gly was conjugated with 3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate and purified by HPLC to prepare [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD. Plasma stability, plasma protein binding, hydroxyapatite (HA) binding and the pharmacokinetics of [
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD. Plasma stability, plasma protein binding, hydroxyapatite (HA) binding and the pharmacokinetics of [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD were compared with those of
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD were compared with those of  Re 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP). The HPLC-purified [
Re 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP). The HPLC-purified [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD showed higher plasma stability, higher HA binding, higher bone accumulation and lower plasma protein binding than did
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD showed higher plasma stability, higher HA binding, higher bone accumulation and lower plasma protein binding than did  Re -HEDP. Although
Re -HEDP. Although  Re -HEDP possessed HA binding and bone accumulation similar to those of [
Re -HEDP possessed HA binding and bone accumulation similar to those of [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD, the specific activity of
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD, the specific activity of  Re -labeled BPs was found to play a crucial role in bone accumulation and blood clearance. Thus, the molecular design of chelate-conjugated BP would be useful for the development of bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals with a variety of radionuclides by selecting chelating molecules that provide high specific activities.
Re -labeled BPs was found to play a crucial role in bone accumulation and blood clearance. Thus, the molecular design of chelate-conjugated BP would be useful for the development of bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals with a variety of radionuclides by selecting chelating molecules that provide high specific activities.
Ogawa, Kazuma*; Mukai, Takahiro*; Arano, Yasushi*; Otaka, Akira*; Ueda, Masashi*; Uehara, Tomoya*; Magata, Yasuhiro*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saji, Hideo*
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 33(4), p.513 - 520, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:80.60(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)To develop a radiopharmaceutical for the palliation of painful bone metastases based on the concept of bifunctional radiopharmaceuticals, we synthesized a bisphosphonate derivative labeled with rhenium-186 ( Re) that contains a hydroxyl group at the central carbon of its bisphosphonate structure and attached a stable
Re) that contains a hydroxyl group at the central carbon of its bisphosphonate structure and attached a stable  Re-MAMA chelate to the amino group of a 4-amino-butylidene-bisphosphonate derivative,
Re-MAMA chelate to the amino group of a 4-amino-butylidene-bisphosphonate derivative,  Re-MAMA-HBP, and investigated the effect of a hydroxyl group at the central carbon of its bisphosphonate structure on the affinity for hydroxyapatite and biodistribution by conducting a comparative study with
Re-MAMA-HBP, and investigated the effect of a hydroxyl group at the central carbon of its bisphosphonate structure on the affinity for hydroxyapatite and biodistribution by conducting a comparative study with  Re-MAMA-BP.
Re-MAMA-BP.  Re-MAMA-HBP was prepared by a reaction with
Re-MAMA-HBP was prepared by a reaction with  ReO
ReO
 and SnCl
and SnCl in citrate buffer after the deprotection of trityl groups of Tr-MAMA-HBP. After reversed phase HPLC,
in citrate buffer after the deprotection of trityl groups of Tr-MAMA-HBP. After reversed phase HPLC,  Re-MAMA-HBP had a radiochemical purity of over 95 %. Compared with
Re-MAMA-HBP had a radiochemical purity of over 95 %. Compared with  Re-MAMA-BP,
Re-MAMA-BP,  Re-MAMA-HBP showed a greater affinity for hydroxyapatite beads in vitro and accumulated a significantly higher level in the femur in vivo. Thus, the introduction of a hydroxyl group into
Re-MAMA-HBP showed a greater affinity for hydroxyapatite beads in vitro and accumulated a significantly higher level in the femur in vivo. Thus, the introduction of a hydroxyl group into  Re complex-conjugated bisphosphonates would be effective in enhancing accumulation in bone. These findings provide useful information on the design of bone-seeking therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals.
Re complex-conjugated bisphosphonates would be effective in enhancing accumulation in bone. These findings provide useful information on the design of bone-seeking therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals.
Uehara, Tomoya*; Koike, Miho*; Nakata, Hideo*; Miyamoto, Shigehiko*; Motoishi, Shoji; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Oku, Naoto*; Nakayama, Morio*; Arano, Yasushi*
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 30(3), p.327 - 334, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:49.32(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Kazuma*; Ono, Masahiro*; Fujioka, Yasushi*; Saji, Hideo*; Mukai, Takahiro*; Konishi, Junji*; Uehara, Tomoya*; Arano, Yasushi*; Onoma, Katsuyuki
Kaku Igaku, 37(5), P. 577, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
A computer code is developed based on a particle method technology in order to simulate in detail various phenomana in core disruptive accidents in fast reactors. This report is a summary of progress during FY2006 in a five-year project of the code development.
 Br-labeled antibody fragments for reduction of non-target radioactivity
Br-labeled antibody fragments for reduction of non-target radioactivityHanaoka, Hirofumi*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Uehara, Tomoya*; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Iida, Yasuhiko*; Ishioka, Noriko; Arano, Yasushi*; Endo, Keigo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Tc and
Tc and 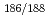 Re
ReKiyota, Sachiko*; Uehara, Tomoya*; Ishii, Daisuke*; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Arano, Yasushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Br-bromo-
Br-bromo- -methyl-L-phenylalanine as a novel
-methyl-L-phenylalanine as a novel  Br-labeled PET tracer
Br-labeled PET tracerOhshima, Yasuhiro; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Yurika*; Yamaguchi, Aiko*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Uehara, Tomoya*; Nagamori, Shushi*; Kanai, Yoshikatsu*; Ishioka, Noriko; Tsushima, Yoshito*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 evaluation of
evaluation of  In labeled hippuric acid derivative with high urinary excretion
In labeled hippuric acid derivative with high urinary excretionSuzuki, Hiroyuki; Kanai, Ayaka*; Uehara, Tomoya*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Arano, Yasushi*
no journal, ,