Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugita, Moe; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Ono, Ayato; Horino, Koki*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Oguri, Hidetomo; Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.519 - 522, 2023/11
In J-PARC RCS, paint bump magnets are used to displace the beam orbit during paint injection, which produces a high intensity beam. A pattern of command current and command voltage can be used to create an output current waveform that varies the beam orbit over time. The accuracy of beam orbit control is determined by the shape difference between the command current and output current waveforms. In the current paint pattern adjustment, a deviation of  1% or less is achieved by manual adjustment after using software that adjusts the pattern according to the response function of the power supply control. However, we would like to reduce the adjustment time. In addition, since the accuracy of paint injection is determined by the adjustment system of the paint magnet power supply, we would like to achieve output current deviation 10 times more precise than before to reduce beam loss. An analytical model of the load-side impedance is necessary to create a high-precision paint pattern, but it is very difficult to construct an analytical model because the load-side impedance changes in a time-varying nonlinear paint pattern. We used machine learning to adjust the output pattern of the paint pattern and achieved a deviation of less than
1% or less is achieved by manual adjustment after using software that adjusts the pattern according to the response function of the power supply control. However, we would like to reduce the adjustment time. In addition, since the accuracy of paint injection is determined by the adjustment system of the paint magnet power supply, we would like to achieve output current deviation 10 times more precise than before to reduce beam loss. An analytical model of the load-side impedance is necessary to create a high-precision paint pattern, but it is very difficult to construct an analytical model because the load-side impedance changes in a time-varying nonlinear paint pattern. We used machine learning to adjust the output pattern of the paint pattern and achieved a deviation of less than  0.5% through repeated learning. This presentation will report on the current status of the system and its prospects.
0.5% through repeated learning. This presentation will report on the current status of the system and its prospects.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayato; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Sugita, Moe; Yamamoto, Kazami; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.242 - 246, 2023/01
At J-PARC, semiconductor short pulse power supplies to replace kicker power supplies and semiconductor long pulse power supplies to replace klystron power supply systems are under construction. We have fabricated a 40kV/2kA/1.2 s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830
s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830 s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.
s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.
 ion source with new parts exposed to plasma
ion source with new parts exposed to plasmaUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2244, p.012029_1 - 012029_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.32(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source is stably suppling about 58 mA beam with a duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 ms
ion source is stably suppling about 58 mA beam with a duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 ms 25 Hz) for the J-PARC LINAC 50 mA operations. For them, only three plasma chambers (PCHs) of #7, #8 and #9PCHs among ten PCHs have been used since the transverse emittances are more superior than others for unknown reasons. However, the emittances were enlarged by 16 % with the #7PCH, in which the plasma electrode (PE) temperature control plate (PETCP) was replaced to brand-new one to solve the air leak at the VCR vacuum fitting. The impurities from the new parts exposed to the plasma seemed to cause the degradation. The beam with almost the best emittances was reproduced by #4PCH with a new PETCP, in which sapphire tubes were used instead of the 99.7 % alumina ceramics tubes, after a new 2-MHz RF power scanning impurities reduction conditioning for 48 hours.
25 Hz) for the J-PARC LINAC 50 mA operations. For them, only three plasma chambers (PCHs) of #7, #8 and #9PCHs among ten PCHs have been used since the transverse emittances are more superior than others for unknown reasons. However, the emittances were enlarged by 16 % with the #7PCH, in which the plasma electrode (PE) temperature control plate (PETCP) was replaced to brand-new one to solve the air leak at the VCR vacuum fitting. The impurities from the new parts exposed to the plasma seemed to cause the degradation. The beam with almost the best emittances was reproduced by #4PCH with a new PETCP, in which sapphire tubes were used instead of the 99.7 % alumina ceramics tubes, after a new 2-MHz RF power scanning impurities reduction conditioning for 48 hours.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2373, p.040002_1 - 040002_8, 2021/07
On 2018, the stable operation of the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source (IS) with a 62 keV 100 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC (RFQ), was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.4 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages were proven. On the other hand, the withstand voltage for the stable operation with an RF plasma production of the present 2 MHz matching circuit and the high voltage power supply was measured as about 66 kV. In the operation with the presently highest beam energy of 65 keV, a 110 mA beam with emittances suitable for the RFQ was stably produced. Since 102.5 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design, the next generation 100 mA LINAC will be possible with the IS.
ion source (IS) with a 62 keV 100 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC (RFQ), was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.4 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages were proven. On the other hand, the withstand voltage for the stable operation with an RF plasma production of the present 2 MHz matching circuit and the high voltage power supply was measured as about 66 kV. In the operation with the presently highest beam energy of 65 keV, a 110 mA beam with emittances suitable for the RFQ was stably produced. Since 102.5 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design, the next generation 100 mA LINAC will be possible with the IS.
 ion source
ion sourceOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011008_1 - 011008_7, 2021/03
A cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was initiated to operate in September, 2014 in response to the need for upgrading J-PARC's linac beam current. The ion source mainly comprises a stainless-steel plasma chamber, a beam extractor and a large vacuum chamber equipped with two turbo molecular pumps, each having the pumping speed of 1500 L/s, for differential pumping. The user operation was started with the beam current of 33 mA from the ion source. We gradually increased both beam current and continuous operation time of the ion source. In July, 2018 (Run#79), approximately 2,200 hours operation was achieved with the typical beam current, pulse length and repetition rate of 47 mA, 300  s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.554 - 557, 2019/07
In September 2014, a cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion (H ) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H
) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H
beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2052, p.050003_1 - 050003_7, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:71.98(Physics, Applied)In order to specify the beam intensity bottlenecks of the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source, the extraction and acceleration voltages (V
ion source, the extraction and acceleration voltages (V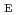 and V
and V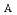 ) higher than the design values of 10 kV and 40 kV were examined. A 100 mA beam, whose about 93 mA has transverse emittances used for a common RFQ design, was stably operated with a duty factor of 5% (1 ms
) higher than the design values of 10 kV and 40 kV were examined. A 100 mA beam, whose about 93 mA has transverse emittances used for a common RFQ design, was stably operated with a duty factor of 5% (1 ms  50 Hz) by using the V
50 Hz) by using the V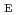 and V
and V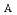 of 12.4 kV and 49.6 kV, respectively. This breakthrough with important information on the space-charge limited bottlenecks in the extraction and acceleration gaps will derive the optimal electrode shapes for the source operated with a beam intensity higher than 100 mA and realize the next generation benchmark H
of 12.4 kV and 49.6 kV, respectively. This breakthrough with important information on the space-charge limited bottlenecks in the extraction and acceleration gaps will derive the optimal electrode shapes for the source operated with a beam intensity higher than 100 mA and realize the next generation benchmark H ion source for high intensity and high energy H
ion source for high intensity and high energy H LINACs.
LINACs.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Namekawa, Yuya*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2052, p.050002_1 - 050002_7, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.93(Physics, Applied)In the 2017/2018 campaign, the J-PARC cesiated rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source producing H
) ion source producing H beam with the beam current of 47 mA accomplished three long-term operations more than 2,000 hours without any serious issues. On the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H
beam with the beam current of 47 mA accomplished three long-term operations more than 2,000 hours without any serious issues. On the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H beam current of 72 mA so that the linac commissioning group could demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. The antenna achieved the operation time approximately 1,400 hours.
beam current of 72 mA so that the linac commissioning group could demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. The antenna achieved the operation time approximately 1,400 hours.
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Namekawa, Yuya*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2011, p.050018_1 - 050018_3, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.15(Physics, Applied) ion source 66 mA operation
ion source 66 mA operationUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2011, p.050002_1 - 050002_5, 2018/09
In order to operate the J-PARC cesiated rf-driven H ion source with a beam intensity of 66 mA stably, the conditions to minimize the extraction electrode current (I
ion source with a beam intensity of 66 mA stably, the conditions to minimize the extraction electrode current (I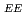 ), whose main component is the electron current co-extracted with the beam, were investigated. The 66 mA H
), whose main component is the electron current co-extracted with the beam, were investigated. The 66 mA H ion beam with a low I
ion beam with a low I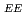 of about 40 mA, which was one-fourth of that in the ordinal operation, were stably extracted by optimizing a rod-filter-field (RFF), a cesium (Cs) density and an axial magnetic field correction (AMFC). Especially, the AMFC of only 40 Gauss had the largest I
of about 40 mA, which was one-fourth of that in the ordinal operation, were stably extracted by optimizing a rod-filter-field (RFF), a cesium (Cs) density and an axial magnetic field correction (AMFC). Especially, the AMFC of only 40 Gauss had the largest I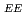 reduction of about one-third. The corresponding 95 % beam transverse normalized rms emittances were degraded about 24 % due to the higher RFF and Cs density. The source will be operated in the conditions to compromise the stability and the beam quality by the investigated results.
reduction of about one-third. The corresponding 95 % beam transverse normalized rms emittances were degraded about 24 % due to the higher RFF and Cs density. The source will be operated in the conditions to compromise the stability and the beam quality by the investigated results.
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira; Namekawa, Yuya*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.889 - 892, 2018/08
In 2017-2018 campaign, three times of long-time operation more than 2,000 hours of the J-PARC rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source producing H
) ion source producing H beam with the beam current of 47 mA were successfully achieved without any serious problems. At the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H
beam with the beam current of 47 mA were successfully achieved without any serious problems. At the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H beam with the current of 72 mA in order to demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. Approximately 1,400-hour operation with the antenna was successfully performed.
beam with the current of 72 mA in order to demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. Approximately 1,400-hour operation with the antenna was successfully performed.
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Takagi, Akira*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.651 - 654, 2017/12
Operation of a cesiated rf-driven negative hydrogen ion source was initiated in September 2014 in response to the requirements of beam current upgrade in J-PARC linac. Delivery of the required beam current from the ion source to the J-PARC accelerators has been successfully performed. In 2016-2017 campaign, continuous operation of the ion source for approximately 1,845 hours (from April to July 2017) was achieved with beam current of 47 mA.
 ion source
ion sourceOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ueno, Akira; Shinto, Katsuhiro
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030053_1 - 030053_7, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.08(Physics, Applied)A cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was started to operate in September, 2014 in response to the need for upgrading J-PARC's linac beam current. The ion source mainly comprises a stainless-steel plasma chamber, a beam extractor, and a large vacuum chamber with two turbo molecular pumps of 1500 L/s for differential pumping. The ion source has been successfully providing the required beam current to the accelerator without any significant issues other than a single-incident antenna failure occurred in October, 2014. Continuous operation for approximately 1,000 h was achieved with a beam current and duty factor of 45 mA and 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz), respectively. In this paper, we will present the some operation parameters and the beam stability through the long-term user operation.
Shibata, Takanori*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Nammo, Kesao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030017_1 - 030017_11, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.09(Physics, Applied)From September 2014, operation of Cs-seeded, multi-cusp, Radio Frequency (RF), hydrogen negative ion source (J-PARC source) has been started. The operation for 1,000 hours of J-PARC source has been achieved with H beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H
beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H
production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H , H
, H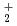 , and Cs
, and Cs ) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H
) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H ) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10
) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10 m
m with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
 ion source to enable 60 mA operation of high-energy and high-intensity LINACs by plasma impurity controls
ion source to enable 60 mA operation of high-energy and high-intensity LINACs by plasma impurity controlsUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030011_1 - 030011_10, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:91.75(Physics, Applied)At the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), the operation of a 400-MeV linear accelerator (LINAC) with an extraction H ion beam intensity of 60 mA is under investigation. This intensity is 20% higher than the 50 mA achieved by the J-PARC LINAC and about 50% higher than those of operating similar LINACs in the world. Recently, the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H
ion beam intensity of 60 mA is under investigation. This intensity is 20% higher than the 50 mA achieved by the J-PARC LINAC and about 50% higher than those of operating similar LINACs in the world. Recently, the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source successfully produces a beam enabling the 60 mA operation. A 66-mA beam with 95%-beam transverse normalized rms emittance of 0.23
ion source successfully produces a beam enabling the 60 mA operation. A 66-mA beam with 95%-beam transverse normalized rms emittance of 0.23  mm
mm mrad is produced by controlling the impurities of argon, nitrogen and water molecules in the hydrogen plasma and tuning rod-filter-field.
mrad is produced by controlling the impurities of argon, nitrogen and water molecules in the hydrogen plasma and tuning rod-filter-field.
Ueno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030052_1 - 030052_7, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.7(Physics, Applied)In order to compare brightnesses of beams produced by different ion sources, a transverse emittance evaluation procedure with consistency and small ambiguity for different background noises is required. The procedure to evaluate emittances of beams produced by the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) cesiated RF-driven H ion source is presented in this paper. The ambiguity in emittance evaluations is eliminated by defining uniquely 100% and 95% beams with a reasonably corrected beam-signal base-level. Two 95%-beam transverse normalized root mean square emittances of beams, which are produced with almost the same 2-MHz RF power and cesiation condition but with different background noise, are estimated as almost the same values by this procedure.
ion source is presented in this paper. The ambiguity in emittance evaluations is eliminated by defining uniquely 100% and 95% beams with a reasonably corrected beam-signal base-level. Two 95%-beam transverse normalized root mean square emittances of beams, which are produced with almost the same 2-MHz RF power and cesiation condition but with different background noise, are estimated as almost the same values by this procedure.
Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ueno, Akira; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.940 - 943, 2016/11
In 2014 October, operation of cesium-seeded Radio Frequency (RF)-driven negative hydrogen ion (H ) source was started in J-PARC LINAC. Due to the skillful RF antenna screening and the proper pre-conditioning process, long term unscheduled beam stop due to the antenna failure did not occur for more than 1 year. The continuous operation of 1,350 hours with a peak beam current of 45 mA was achieved in the recent beam run. Moreover, the fluctuation of beam current in a low energy beam transport (LEBT) is kept within
) source was started in J-PARC LINAC. Due to the skillful RF antenna screening and the proper pre-conditioning process, long term unscheduled beam stop due to the antenna failure did not occur for more than 1 year. The continuous operation of 1,350 hours with a peak beam current of 45 mA was achieved in the recent beam run. Moreover, the fluctuation of beam current in a low energy beam transport (LEBT) is kept within  2% of target value by application of three feedback systems. An ion source test-stand was assembled to investigate the ion source beam characteristic, for example, the emittance at the position of the RFQ entrance. In the presentation, we will report the recent status of the ion source operation and some experimental results obtained at the ion source test-stand.
2% of target value by application of three feedback systems. An ion source test-stand was assembled to investigate the ion source beam characteristic, for example, the emittance at the position of the RFQ entrance. In the presentation, we will report the recent status of the ion source operation and some experimental results obtained at the ion source test-stand.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Oguri, Hidetomo
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B130_1 - 02B130_5, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.03(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) cesiated rf-driven H ion source (IS), whose requirements are a peak beam intensity of 60mA within normalized emittances of 1.5
ion source (IS), whose requirements are a peak beam intensity of 60mA within normalized emittances of 1.5  mm
mm mrad both horizontally and vertically, a flat top beam duty factor of 1.25% (500
mrad both horizontally and vertically, a flat top beam duty factor of 1.25% (500  s
s 25 Hz) and a life-time of longer than 1month, has been successfully operated for about one year. The results of the fine-tuning to minimize the emittances of the J-PARC-IS with plasma chamber #3, which had the largest emittances with initial settings among four plasma chambers, will be presented in this paper. The rod-filter-filed will be finely tuned by selecting magnets with slightly different field strengths and/or changing gap-lengths. The dependence of the beam-hole-diameter on the emittances will be also presented. The tuning procedure to improve the emittances is one of the most important technologies for the IS of the high-energy and high-intensity accelerator.
25 Hz) and a life-time of longer than 1month, has been successfully operated for about one year. The results of the fine-tuning to minimize the emittances of the J-PARC-IS with plasma chamber #3, which had the largest emittances with initial settings among four plasma chambers, will be presented in this paper. The rod-filter-filed will be finely tuned by selecting magnets with slightly different field strengths and/or changing gap-lengths. The dependence of the beam-hole-diameter on the emittances will be also presented. The tuning procedure to improve the emittances is one of the most important technologies for the IS of the high-energy and high-intensity accelerator.
 ion source for J-PARC linac
ion source for J-PARC linacOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ueno, Akira; Shibata, Takanori*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B138_1 - 02B138_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.03(Instruments & Instrumentation)For the upgrade of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac beam current, a cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was installed in 2014 summer shutdown period, and started to operate on September 29, 2014. The ion source has been successfully operated with a beam current and a duty factor of 33 mA and 1.25% (0.5 ms and 25 Hz), respectively. The result of recent beam operation showed that the ion source is capable of continuous operation for approximately 1,100 h. The spark rate at the beam extractor was observed to be less than once a day, which is acceptable level for the user operation. Although the antenna failure occurred during the user operation on October 26, 2014, there were no further serious troubles since then. In this conference, we will present the some operation parameters and the beam stability of the RF-driven ion source through the long-term user operation.
Shibata, Takanori*; Nishida, Kenjiro*; Mochizuki, Shintaro*; Mattei, S.*; Lettry, J.*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B128_1 - 02B128_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)A numerical model of plasma transport and electromagnetic field in the J-PARC RF ion source has been developed to understand relation between antenna coil heat loadings and plasma production/transport processes. From the calculation, the local plasma density increase is observed in the region close to the antenna coil. The magnetic field line with absolute magnetic flux density 30-120 Gauss results in the magnetization of electron which leads to high local ionization rate. The results suggest that modification of magnetic configuration can be made to reduce plasma heat flux onto the antenna.