Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Imai, Yosuke*; Tokiwa, Yuhei*; Ueno, Shusaku*; Tanida, Hajime; Watanabe, Iwao*; Matsubara, Hiroki*; Takiue, Takanori*; Aratono, Makoto*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 91(10), p.1487 - 1494, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.21(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Competitive binding of binary mixed counterions to the headgroups of adsorbed surfactant films has been investigated at solution surfaces by total reflection X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy. The obtained extended XAFS  spectra for bromide counterions are linear combinations of the spectra of fully hydrated bromide ions (free Br) and partially dehydrated bromide ions bound to the headgroups of the surfactant ions (bound Br). From the fraction of bound Br in counterion mixed systems, two series of the relative strengths of counterion binding are proposed for the trimethylammonium (TA
spectra for bromide counterions are linear combinations of the spectra of fully hydrated bromide ions (free Br) and partially dehydrated bromide ions bound to the headgroups of the surfactant ions (bound Br). From the fraction of bound Br in counterion mixed systems, two series of the relative strengths of counterion binding are proposed for the trimethylammonium (TA ) and 3-methylimidazolium (MIM
) and 3-methylimidazolium (MIM ) headgroups: (a) TA-SO
) headgroups: (a) TA-SO
 TA-Cl
TA-Cl  TA-Br
TA-Br  TA-BF
TA-BF and (b) MIM-Br
and (b) MIM-Br  TA-Br
TA-Br  TA-BF
TA-BF
 MIM-BF
MIM-BF . For the TA headgroup, matching the hydration of the headgroups and counterions gives series (a) according to Collins' law, which states that the tendency of contact ion pair formation becomes larger when the absolute values of the hydration enthalpies of the ions match. For the MIM headgroup, the number of binding sites of hydrogen bonds between the MIM headgroup and counterion is essential, which leads to series (b) because of competition between the counterion and water for interaction with the MIM headgroup.
. For the TA headgroup, matching the hydration of the headgroups and counterions gives series (a) according to Collins' law, which states that the tendency of contact ion pair formation becomes larger when the absolute values of the hydration enthalpies of the ions match. For the MIM headgroup, the number of binding sites of hydrogen bonds between the MIM headgroup and counterion is essential, which leads to series (b) because of competition between the counterion and water for interaction with the MIM headgroup.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Uehara, Toshiaki*; Ueno, Shunji*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kumahara, Hajime*; Shibagaki, Taro*; Komanome, Hirohisa*
JAEA-Technology 2017-026, 26 Pages, 2018/02
Under severe accidents, high-integrity transmission techniques are necessary so as to monitor the situation of the nuclear power plant. In this study, effects of gamma irradiation up to 10 Gy on properties of optical devices were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the browning of resin lenses occurred. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the browning of resin window occurred. The dark currents of PDs did not become large enough to adversely affect transmission. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the browning of the resin parts by the irradiation. In addition, basic decrease behaviors of light transmission of several different types of glasses by gamma irradiation were also obtained so as to select the suitable optical windows and filters for the developing radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system.
Gy on properties of optical devices were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the browning of resin lenses occurred. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the browning of resin window occurred. The dark currents of PDs did not become large enough to adversely affect transmission. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the browning of the resin parts by the irradiation. In addition, basic decrease behaviors of light transmission of several different types of glasses by gamma irradiation were also obtained so as to select the suitable optical windows and filters for the developing radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system.
Okabe, Kota; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu*; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Yanagibashi, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.853 - 857, 2017/12
The most important issue is to reduce the uncontrolled beam loss in the high intensity hadron accelerator such as J-PARC proton accelerators. The J-PARC 3 GeV Synchrotron (RCS) has a collimator system which narrows a high intensity beam in the RCS. After startup of RCS in 2007, the collimator system of the RCS worked well. However, in April 2016, vacuum leakage at the collimator system occurred during the maintenance operation. To investigate a cause of the failure, we took apart iron shields of the collimator reducing exposed dose of operators. As a result of inspection, we succeeded to identify the cause of the vacuum leakage failure. In this presentation, we report the failure investigation of the beam collimator system in the RCS.
 irradiation
irradiationTakeuchi, Tomoaki; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Uehara, Toshiaki; Ueno, Shunji; Kumahara, Hajime*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 33, 2015/03
 irradiation effects on LEDs and photo diodes (PDs) were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. The current-voltage characteristics and total luminous flux of the LEDs and the dark current and light sensitivity of the PDs were measured before and after the irradiation. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the resin lenses turned oxblood. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the resin window turned oxblood while the dark currents stayed at most 10 nA. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the coloring of the resin parts by the irradiation.
irradiation effects on LEDs and photo diodes (PDs) were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. The current-voltage characteristics and total luminous flux of the LEDs and the dark current and light sensitivity of the PDs were measured before and after the irradiation. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the resin lenses turned oxblood. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the resin window turned oxblood while the dark currents stayed at most 10 nA. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the coloring of the resin parts by the irradiation.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Bolton, P.; Hori, Toshihiko; Kondo, Kiminori; Saito, Fumihiro; Ueno, Masayuki; Takahashi, Hiroki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.94 - 96, 2010/05
The concept of a compact ion particle accelerator has become attractive in view of recent progress in laser-driven hadrons acceleration. The Photo Medical Research Centre (PMRC) of JAEA was established to address the challenge of laser-driven ion accelerator development for hadrons therapeutic. In the development of the instrument, it is necessary to do the bench-mark of the amount of the different types of radiation by the simulation code for shielding. The Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code (PHITS) was used for bench-mark the dose on laser-shot radiations of short duration. The code predicts reasonably well the observed total dose as measured with a glass dosimeter in the laser-driven radiations.
Hiroki, Seiji; Hayashi, Naoki; Kawase, Masato; Noda, Fumiaki; Saha, P. K.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Hiroki; Ueno, Akira; Arakida, Yoshio*; Lee, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1131 - 1133, 2008/06
A set of six multi-wire profile monitors (MWPMs) has been installed in the injection area of the RCS (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron), and contributed to the initial commissioning for establishing an optimum injection orbit. The Au coated W wires (0.1 mm dia.) for the H beam are fixed to a ceramic wind frame for two directions (horizontal and vertical with 17.7 deg. tilt, typically 51 wires with 2.9 mm or 9.5 mm distance), and the frame can be scanned for horizontal or vertical direction by using a stepping-motor driven actuator. A combination of the 17.7 deg. tilt wires and the precise scan function provides two step measurements, i.e. a rough profile is obtained only at one shot, and a detailed profile is measured for typically 101 shots (10 mm scan at 0.1 mm interval) thereafter. The beam induced charge signals are amplified, integrated and held by using a signal processing circuit. The signals are sequentially retrieved through multiplexers and digitized for obtaining a beam profile.
beam are fixed to a ceramic wind frame for two directions (horizontal and vertical with 17.7 deg. tilt, typically 51 wires with 2.9 mm or 9.5 mm distance), and the frame can be scanned for horizontal or vertical direction by using a stepping-motor driven actuator. A combination of the 17.7 deg. tilt wires and the precise scan function provides two step measurements, i.e. a rough profile is obtained only at one shot, and a detailed profile is measured for typically 101 shots (10 mm scan at 0.1 mm interval) thereafter. The beam induced charge signals are amplified, integrated and held by using a signal processing circuit. The signals are sequentially retrieved through multiplexers and digitized for obtaining a beam profile.
Sato, Susumu; Tomisawa, Tetsuo; Hiroki, Fumio; Lee, S.*; Igarashi, Zenei*; Ikegami, Masanori*; Ueno, Akira; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Toyama, Takeshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 29th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.467 - 469, 2004/08
As a joint project of KEK and JAERI, a MW class of high intensity proton accelerator (J-PARC), consisting of Linac, 3 GeV-RCS, 50 GeV-MR, is under construction. For this accelerator, it is required to minimize the beam loss (typically, lower than0.1 1 W/m at the linac). To achieve the requirement, beam trajectory needs to be controlled with accuracy of some 100
1 W/m at the linac). To achieve the requirement, beam trajectory needs to be controlled with accuracy of some 100  m. The first stage of the acceleration (up to 181 MeV during the first stage of construction) is done by linac. The beam position monitor (BPM) in the linac utilizes 4 stripline pickups (50 ohm) on the beam transportation chamber. In this paper, systematic calibration of the BPM is described.
m. The first stage of the acceleration (up to 181 MeV during the first stage of construction) is done by linac. The beam position monitor (BPM) in the linac utilizes 4 stripline pickups (50 ohm) on the beam transportation chamber. In this paper, systematic calibration of the BPM is described.
Sato, Susumu; Igarashi, Zenei*; Lee, S.*; Tomisawa, Tetsuo; Hiroki, Fumio; Kishiro, Junichi; Ikegami, Masanori*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ueno, Akira; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2004), p.429 - 431, 2004/00
As a joint project of KEK and JAERI, a MW class of high intensity proton accelerator (J-PARC), consisting of Linac, 3 GeV-RCS, 50 GeV-MR, is under construction at Tokai, Japan. For this accelerator, it is required to minimize the beam loss (typically, lower than 0.1 1 W/m at the linac). To achieve the requirement, beam trajectory needs to be controlled with accuracy of some 100 micro-meter. The first stage of the acceleration (up to 181 MeV during the first stage of construction) is done by linac. The beam position monitor (BPM) in the linac utilizes 4 strip-line pickups (50 ohm) on the beam transportation chamber. In this paper, systematic calibration of the BPM is described.
1 W/m at the linac). To achieve the requirement, beam trajectory needs to be controlled with accuracy of some 100 micro-meter. The first stage of the acceleration (up to 181 MeV during the first stage of construction) is done by linac. The beam position monitor (BPM) in the linac utilizes 4 strip-line pickups (50 ohm) on the beam transportation chamber. In this paper, systematic calibration of the BPM is described.
 Br
Br using by neutron quasi-elastic scattering
using by neutron quasi-elastic scatteringShimakura, Hironori; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Ueno, Hiroki; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Shibata, Kaoru; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Chalcogen-halogen systems have low melting point when chalcogen and halogen proportion is 1:1. At this ratio, selenium bromide consists of chain molecule with Br-Se-Se-Br form, where the bond angle and the dihedral angle are about 104 and 83
and 83 respectively. Selenium bromide has strong inter-molecular correlation where each molecule doesn't have enough space to rotate freely due to molecular shape and high density. Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) of liquid Se
respectively. Selenium bromide has strong inter-molecular correlation where each molecule doesn't have enough space to rotate freely due to molecular shape and high density. Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) of liquid Se Br
Br was performed at AMATERAS which installed in MLF/J-PARC. Measured temperatures were 298 K, 373 K and 473 K. It is interesting that S(Q,E) has two components, one is narrow and the other is broad, at specific Q value which represents inter-molecular correlation. We discussed these two components and the other analysis result of QENS spectrum.
was performed at AMATERAS which installed in MLF/J-PARC. Measured temperatures were 298 K, 373 K and 473 K. It is interesting that S(Q,E) has two components, one is narrow and the other is broad, at specific Q value which represents inter-molecular correlation. We discussed these two components and the other analysis result of QENS spectrum.
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shimakura, Hironori; Ueno, Hiroki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Arai, Masatoshi; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
In order to elucidate the dynamical changes caused by differences in the structural phase of AgI which is a typical superionic conducting material, we carried out a detailed examination of the dynamical structure factor S(Q,E) obtained by inelastic neutron scattering measurements. Herein, we show that the intensity in a low-energy region (E  2 meV) at around 2
2 meV) at around 2 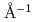 abruptly increases beyond 420 K, and the temperature-dependent behavior of this intensity is remarkably similar to that of dc ionic conductivity over a wide temperature range in the region of 420 K. A unified explanation of the ionic conduction mechanism in superionic materials may be established in terms of their characteristic low-energy excitations.
abruptly increases beyond 420 K, and the temperature-dependent behavior of this intensity is remarkably similar to that of dc ionic conductivity over a wide temperature range in the region of 420 K. A unified explanation of the ionic conduction mechanism in superionic materials may be established in terms of their characteristic low-energy excitations.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Otomo, Toshiya*; Ueno, Hiroki; Tsubota, Masami*; Kumara, L. S. R.*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Suzuya, Kentaro
no journal, ,
Ag (GeSe
(GeSe )
) ternary alloy exhibits an extensive compositional range of bulk glass forming and a rapid enhancement in ionic conductivity from 10
ternary alloy exhibits an extensive compositional range of bulk glass forming and a rapid enhancement in ionic conductivity from 10 to 10
to 10 S/cm of these glasses at Ag concentration of x=0.3 with increasing Ag content. Structural models of this material have already been proposed by reverse Monte Carlo simulation based on experimental structural data of neutron and X-ray diffractions and X-ray absorption fine structure. However, there observed micro-phase separation tendency in these glasses. This tendency might relate to formation of ionic conduction path in supercooled liquid on quenching process. The proposed models will be examined by structure factors over a wide Q range including relatively low momentum-transfer region which have been newly obtained by the total neutron scattering instrument installed at BL21 in MLF, J-PARC. This work was supported by NEDO under "Advanced Fundamental Research Project on Hydrogen Storage Materials".
S/cm of these glasses at Ag concentration of x=0.3 with increasing Ag content. Structural models of this material have already been proposed by reverse Monte Carlo simulation based on experimental structural data of neutron and X-ray diffractions and X-ray absorption fine structure. However, there observed micro-phase separation tendency in these glasses. This tendency might relate to formation of ionic conduction path in supercooled liquid on quenching process. The proposed models will be examined by structure factors over a wide Q range including relatively low momentum-transfer region which have been newly obtained by the total neutron scattering instrument installed at BL21 in MLF, J-PARC. This work was supported by NEDO under "Advanced Fundamental Research Project on Hydrogen Storage Materials".
Ueno, Hiroki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ohara, Koji*; Shimakura, Hironori; Tahara, Shuta*; Kumara, L. S. R.*; Yamaguchi, Hiroshi*; Yasunaga, Akinori*; Wakisaka, Yuiko*; Ito, Masayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Bi-Zn system has a phase diagram with a miscibility gap where critical point is at Bi Zn
Zn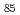 . It is known that concentration fluctuation increases on approaching to the miscibility gap. Earlier studies suggested that the miscibility gap is attributed to difference in atomic size between Bi and Zn. Recent developments of instrument and analysis technique enable us to deduce partial structures and demonstrate atomic configurations in liquid. We performed detailed analysis on medium-range structure in liquid Bi
. It is known that concentration fluctuation increases on approaching to the miscibility gap. Earlier studies suggested that the miscibility gap is attributed to difference in atomic size between Bi and Zn. Recent developments of instrument and analysis technique enable us to deduce partial structures and demonstrate atomic configurations in liquid. We performed detailed analysis on medium-range structure in liquid Bi Zn
Zn by using neutron diffraction data obtained by the two-axis diffractometer, HERMES, installed in JRR-3M, JAEA and, X-ray diffraction at BL08W beamline in SPring-8, Hyogo, Japan. 3D atomic structural model obtained by Revere Monte Carlo technique exhibits temperature evolution of concentration fluctuations in medium-range structure, which suggests that phase separation tendency appears even in the edge of the miscibility gap of liquid Bi-Zn.
by using neutron diffraction data obtained by the two-axis diffractometer, HERMES, installed in JRR-3M, JAEA and, X-ray diffraction at BL08W beamline in SPring-8, Hyogo, Japan. 3D atomic structural model obtained by Revere Monte Carlo technique exhibits temperature evolution of concentration fluctuations in medium-range structure, which suggests that phase separation tendency appears even in the edge of the miscibility gap of liquid Bi-Zn.
Shibata, Kaoru*; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Ueno, Hiroki; Shimakura, Hironori; Nakajima, Kenji; Kambara, Wataru; Inamura, Yasuhiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Br
Br , 2
, 2Shimakura, Hironori; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Ueno, Hiroki; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Shibata, Kaoru*; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueno, Hiroki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ohara, Koji*; Tahara, Shuta*; Kohara, Shinji*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Takeda, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Otomo, Toshiya*; Ueno, Hiroki; Tsubota, Masami*; Kumara, L. S. R.*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Takeda, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
Superionic glasses have attracted widespread interest in relation with their potential application as solid electrolytes in new devices. The interest in Ag (GeSe
(GeSe )
) ternary alloys derives from extensive compositional range of glass forming and rapid increase in conductivity at
ternary alloys derives from extensive compositional range of glass forming and rapid increase in conductivity at 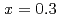 . Neutron diffraction measurements of Ag
. Neutron diffraction measurements of Ag (GeSe
(GeSe )
) glass have been performed over a wide Q range by utilizing the total neutron scattering instrument, NOVA, installed at BL21 in MLF, J-PARC. Since
glass have been performed over a wide Q range by utilizing the total neutron scattering instrument, NOVA, installed at BL21 in MLF, J-PARC. Since  Ag is a good neutron absorber, NOVA instrument and method for data reduction can be examined by this sample. Structural model of this material has already been proposed by reverse Monte Carlo simulation based on experimental structural data. This structure model has been checked in consistency with new data in an extremely wide Q range. This work was supported by NEDO under "Advanced Fundamental Research Project on Hydrogen Storage Materials" (HydroStar).
Ag is a good neutron absorber, NOVA instrument and method for data reduction can be examined by this sample. Structural model of this material has already been proposed by reverse Monte Carlo simulation based on experimental structural data. This structure model has been checked in consistency with new data in an extremely wide Q range. This work was supported by NEDO under "Advanced Fundamental Research Project on Hydrogen Storage Materials" (HydroStar).
Ueno, Hiroki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ohara, Koji*; Tahara, Shuta*; Kohara, Shinji*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Takeda, Shinichi*
no journal, ,