Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The benchmark analyses on the TRIGA reactor of the IEU-COMP-THERM-013 (ICT-013) in the ICSBEP handbook using the MVP version 3 code were carried out with the Japanese, US and European nuclear data libraries, including JENDL-5. The analyses on effective neutron multiplication factors (k 's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k
's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k 's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k
's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k 's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k
's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k 's. Most of the errors involved in k
's. Most of the errors involved in k 's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k
's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k 's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Gunji, Satoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Umeda, Miki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/09
Criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station would be a risk-informed control to mitigate consequences of criticality events, instead of a deterministic control to prevent such events. The Nuclear Regulation Authority of Japan has administrated a research and development program to tackle this challenge since 2014. The Nuclear Safety Research Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, commissioned by the authority, is conducting activities such as computations of criticality characteristics of the fuel debris, development of a criticality analysis code, preparation of criticality experiments, and development of a criticality risk analysis method.
Ozawa, Mayumi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sato, Makoto; Kamohara, Keiko*; Suyama, Kenya; Tonoike, Kotaro; Oki, Keiichi; Umeda, Miki
Proceedings of 53rd Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling Working Group (HOTLAB 2016) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/11
Tonoike, Kotaro; Yamane, Yuichi; Umeda, Miki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Sono, Hiroki
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2015) (DVD-ROM), p.20 - 27, 2015/09
From the viewpoint of safety regulation, criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station would be a risk-informed control to mitigate consequences of criticality events, instead of a deterministic control to prevent such events. The Nuclear Regulation Authority of Japan has set up a research and development program to tackle this challenge. The Nuclear Safety Research Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, commissioned by the authority, has launched activities such as computations of criticality characteristics of the fuel debris, development of criticality risk assessment method, and preparation of criticality experiments to support them.
 9 fuel
9 fuelSuyama, Kenya; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Miki; Yamamoto, Toru*; Suzuki, Motomu*
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.47 - 56, 2015/00
In fission products in used nuclear fuel, there are several stable isotopes which have large neutron absorption effect. It is known that there are several hardly measurable elements in such important fission products. JAEA had been developed the method to assess the amount of fission products which are hardly measurable and have large neutron capture cross section, under the auspices of the JNES. In this development, the measurement method was developed combining a simple and effective chemical separation scheme of fission products from used nuclear fuel and ICP-MS with high-sensitivity and high-precision. This method was applied to the measurement program for used BWR 9 9 fuel assembly. This method is applicable to the required measurement for the countermeasure to the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants of Tokyo Electric Power Company. This presentation describes the measurement method developed in the study as well as the future measurement plan in JAEA.
9 fuel assembly. This method is applicable to the required measurement for the countermeasure to the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants of Tokyo Electric Power Company. This presentation describes the measurement method developed in the study as well as the future measurement plan in JAEA.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Sono, Hiroki; Umeda, Miki; Yamane, Yuichi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.251 - 259, 2015/00
In the Three Mile Island Unit 2 reactor accident, a large amount of fuel debris was formed whose criticality condition is unknown except the possible highest  U/U enrichment. The fuel debris had to be cooled and shielded by water in which the minimum critical mass is much smaller than the total mass of fuel debris. To overcome this uncertain situation, the coolant water was borated with sufficient concentration to secure the subcritical condition. The situation is more severe in the damaged reactors of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, where the coolant water flow is practically "once through". Boron must be endlessly added to the water to secure the subcritical condition of the fuel debris, which is not feasible. The water is not borated relying on the circumstantial evidence that the xenon gas monitoring in the containment vessels does not show a sign of criticality. The criticality condition of fuel debris may worsen due to the gradual drop of its temperature, or the change of its geometry by aftershocks or the retrieval work, that may lead the criticality. To avoid criticality and its severe consequences, a certain principle of criticality control must be established. There may be options, such as prevention of the criticality by coolant water boration or by neutronic monitoring, prevention of the severe consequences by intervention measures against criticality, etc. Every option has merits and demerits that must be adequately evaluated toward selection of the best principle.
U/U enrichment. The fuel debris had to be cooled and shielded by water in which the minimum critical mass is much smaller than the total mass of fuel debris. To overcome this uncertain situation, the coolant water was borated with sufficient concentration to secure the subcritical condition. The situation is more severe in the damaged reactors of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, where the coolant water flow is practically "once through". Boron must be endlessly added to the water to secure the subcritical condition of the fuel debris, which is not feasible. The water is not borated relying on the circumstantial evidence that the xenon gas monitoring in the containment vessels does not show a sign of criticality. The criticality condition of fuel debris may worsen due to the gradual drop of its temperature, or the change of its geometry by aftershocks or the retrieval work, that may lead the criticality. To avoid criticality and its severe consequences, a certain principle of criticality control must be established. There may be options, such as prevention of the criticality by coolant water boration or by neutronic monitoring, prevention of the severe consequences by intervention measures against criticality, etc. Every option has merits and demerits that must be adequately evaluated toward selection of the best principle.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
Kakuhan, Kongo Gijutsu To Toraburu Taisaku, p.341 - 344, 2014/10
The silver mediated electrochemical oxidation (Ag/MEO) process with the ultrasound agitation has been developed for the purpose of the mineralization of organic wastes containing transuranium nuclides at the nuclear fuel reprocessing process. In the Ag/MEO process, organic solvents are decomposed by divalent silver cations under the relatively low temperature and the ambient pressure condition. The ultrasound agitation is effective in mixing the electrolytic solutions and the organic solvents, and is expected to promote the oxidation of the organic solvents. Therefore, the Ag/MEO process with the ultrasound agitation could be a candidate for the treatment of organic solvents. Destruction tests of TBP and dodecane by the Ag/MEO process were conducted to optimize some treatment conditions. Under optimized conditions, the destruction tests of kerosene and TODGA were carried out. It was confirmed that the Ag/MEO process is effective for the mineralization of these organic solvents.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Sono, Hiroki; Umeda, Miki; Yamane, Yuichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 110(1), p.282 - 285, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Suyama, Kenya; Sonoda, Takashi; Okubo, Kiyoshi; Umeda, Miki; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Research 2013-020, 81 Pages, 2013/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency conducted a project "Isotopic Composition measurement of Fission Products in Spent Fuel from FY2008 to FY2011" by the entrustment of Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization. In that project, we measured the isotopic composition of neodymium isotopes which are important to evaluate the burnup value of spent nuclear fuel by using two different methods and obtained different results. So that we carried out the follow-up measurement in order to investigate the reason of the difference between two neodymium measurements. It was found that we needed correction to the measurement results of neodymium for two samples and a part of other fission products for all samples in total five samples. This report summarizes the all works carried out in this follow-up measurement and obtained results.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Sono, Hiroki; Umeda, Miki; Yamane, Yuichi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.729 - 735, 2013/09
JAEA is conducting studies on criticality control of the fuel debris formed in the accident of Fukushima-Daiichi site. A new control principle must be established, referring principles for existing facilities, and based on criticality characteristics of the debris. In accordance with the principle, safe and practical control has to be realized for the debris whose condition is uncertain at present. This report outlines the present condition of debris and Fukushima site, introduces examples of criticality analysis, and discusses control principles. Research subjects are also proposed to realize the control.
Kokusen, Junya; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Umeda, Miki
JAEA-Technology 2012-041, 32 Pages, 2013/02
Uranyl nitrate solution fuel used in the STACY and the TRACY is adjusted in the Fuel Treatment System, in which such parameters are varied as concentration of uranium, free nitric acid, soluble neutron poison, and so on. Operations for concentration and denitration of the solution fuel were carried out with an evaporator from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008 in order to adjust the fuel to the experimental condition of the STACY and the TRACY. In parallel, the solution fuel in which some kinds of soluble neutron poison were doped was also adjusted in JFY 2005 and JFY 2006 for the purpose of the STACY experiments to determine neutron absorption effects brought by fission products, etc. After these experiments in the STACY, a part of the solution fuel including the soluble neutron poison was purified by the solvent extraction method with mixer-settlers in JFY 2006 and JFY 2007. This report summarizes operation data of the Fuel Treatment System from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Tanaka, Yutaka; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.835 - 838, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:75.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutral beam (NB) injectors for JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA) have been designed and developed. Twelve positive-ion-based and one negative-ion-based NB injectors are allocated to inject 30 MW D beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D
beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of
beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of  1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.536 - 544, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:86.55(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Kawai, Mikito*; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Usui, Katsutomi; Sasaki, Shunichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083049_1 - 083049_8, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:88.03(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen negative ion beams of 490 keV, 3 A and 510 keV, 1 A have been successfully produced in the JT-60 negative ion source with three acceleration stages. These successful productions of the high-energy beams at high current have been achieved by overcoming the most critical issue, i.e., a poor voltage holding of the large negative ion sources with the grids of 2 m for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m
for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m ). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
Umeda, Miki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Nagase, Fumihisa; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Ueta, Shohei; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(11), p.991 - 997, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:73.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hanada, Masaya; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Inoue, Takashi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Komata, Masao; Kojima, Atsushi; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.208 - 213, 2010/08
A large negative ion source with an ion extraction area of 110 cm  45 cm has been developed to produce 500 keV, 22 A D
45 cm has been developed to produce 500 keV, 22 A D ion beams required for JT-60 Super Advanced. To realize the JT-60SA negative ion source, the JT-60 negative ion source has been modified and tested on the negative-ion-based neutral beam injector on JT-60U. A 500 keV H
ion beams required for JT-60 Super Advanced. To realize the JT-60SA negative ion source, the JT-60 negative ion source has been modified and tested on the negative-ion-based neutral beam injector on JT-60U. A 500 keV H ion beam has been produced at 3 A without a significant degradation of beam optics. This is the first demonstration of a high energy negative ion acceleration of more than one-ampere to 500 keV in the world. The beam current density of 90 A/m
ion beam has been produced at 3 A without a significant degradation of beam optics. This is the first demonstration of a high energy negative ion acceleration of more than one-ampere to 500 keV in the world. The beam current density of 90 A/m is being increased to meet 130 A/m
is being increased to meet 130 A/m of the design value for JT-60SA by tuning the operation parameters. A long pulse injection of 30 s has been achieved at a injection D
of the design value for JT-60SA by tuning the operation parameters. A long pulse injection of 30 s has been achieved at a injection D power of 3 MW. The injection energy, defined as the product of the injection time and power, reaches 80 MJ by neutralizing a 340 keV, 27 A D
power of 3 MW. The injection energy, defined as the product of the injection time and power, reaches 80 MJ by neutralizing a 340 keV, 27 A D ion beam produced with two negative ion sources.
ion beam produced with two negative ion sources.
Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
At Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility, the cerium mediated electrolytic oxidation method which is a decontamination technique to decrease the radioactivity of TRU wastes to the clearance-level has been developed for the effective reduction of TRU wastes generated from the decommissioning of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility and so on. This method corrodes the oxide layer and the surface of metallic TRU metal wastes by the strong oxidation power of Ce in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce
in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2
initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2 4
4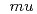 m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3
m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3  m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20
m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20  m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-056, 16 Pages, 2009/11
The silver mediated electrochemical oxidation (Ag/MEO) process with the ultrasound agitation has been developed for the purpose of the mineralization of organic wastes containing transuranium nuclides at the nuclear fuel reprocessing process. In the Ag/MEO process, organic solvents are decomposed by divalent silver cations under the relatively low temperature and the ambient pressure condition. The ultrasound agitation is effective in mixing the electrolytic solutions and the organic solvents, and is expected to promote the oxidation of the organic solvents. Therefore, the Ag/MEO process with the ultrasound agitation could be a candidate for the treatment of organic solvents. Destruction tests of TBP and dodecane by the Ag/MEO process were conducted to optimize some treatment conditions. Under optimized conditions, the destruction tests of kerosene and TODGA were carried out. It was confirmed that the Ag/MEO process is effective for the mineralization of these organic solvents.
Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Umeda, Miki; Udagawa, Yutaka; Sasajima, Hideo; Suzuki, Motoe; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Proceedings of OECD/NEA Workshop on Nuclear Fuel Behaviour during Reactivity Initiated Accidents (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09