Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
浦口 晋平*; 神谷 岳洋*; 坂本 卓也*; 笠井 光治*; 佐藤 豊*; 長村 吉晃*; 石川 覚*; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 藤原 徹*
no journal, ,
Cadmium (Cd) is one of the toxic environmental contaminants known to harm human health. Cd in rice grains is the major source of Cd intake in Japanese people. Precedent studies showed the importance of nodes in xylem to phloem Cd transfer and that of phloem Cd transport in grain Cd accumulation. Identification of Cd transporting molecules in rice will enable to reduce Cd accumulation in grains. However, no Cd transporter responsible for phloem Cd transport has been revealed so far. In the present study, we identified a novel rice transporter OsLCT1. This transporter had a efflux activity of Cd and some other cations. Subcelluler localization analysis suggested that OsLCT1 was localized to plasma membrane. Expression profile analysis demonstrated that OsLCT1 was strongly expressed in leaf blades and nodes at the reproductive stages. We generated the RNAi-mediated OsLCT1 knockdown rice plants and these plants accumulated approximately a half of Cd in the grains compared to control plants. The growth of knock-down plants was comparable to that of control plants. The present study first identified the transporter expressed at nodes responsible for rice grain Cd accumulation.
浦口 晋平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 藤巻 秀; 藤原 徹*
no journal, ,
We have previously reported that 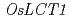 encodes a Cd transporter on plasma membrane and regulates grain Cd accumulation in rice.
encodes a Cd transporter on plasma membrane and regulates grain Cd accumulation in rice. 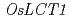 strongly expresses in both leaf blades and nodes during reproductive stages. This raises a possibility that OsLCT1 is involved in Cd translocation from leaf to grains and/or is involved in intervascular Cd transport at nodes. In this study, we clarified the contribution of OsLCT1 in Cd transport into grains by serial isotopic analyses. The experiment using two different stable isotope of Cd showed that knock-down and knock-out of
strongly expresses in both leaf blades and nodes during reproductive stages. This raises a possibility that OsLCT1 is involved in Cd translocation from leaf to grains and/or is involved in intervascular Cd transport at nodes. In this study, we clarified the contribution of OsLCT1 in Cd transport into grains by serial isotopic analyses. The experiment using two different stable isotope of Cd showed that knock-down and knock-out of 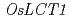 decreased the direct Cd transport from roots to grain through nodes but did not affect Cd translocation from leaf blades. The live-imaging analysis using positron emitting radioisotope
decreased the direct Cd transport from roots to grain through nodes but did not affect Cd translocation from leaf blades. The live-imaging analysis using positron emitting radioisotope  Cd demonstrated that Cd absorbed by roots was preferentially transported to upper nodes rather than to leaf blades and knock-down of
Cd demonstrated that Cd absorbed by roots was preferentially transported to upper nodes rather than to leaf blades and knock-down of 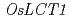 retarded the Cd transport into upper nodes. The improved method for collecting phloem sap using plant brown hopper was established and the Cd level in phloem sap collected from a panicle neck was significantly lower in two different knock-down lines. Immunostaining confirmed the phloem specific expression of OsLCT1 in large vascular bundles and diffuse vascular bundles. These results suggest that OsLCT1 is involved in re-direction of Cd to upper nodes (and a panicle) at nodes probably facilitating Cd loading into sieve element.
retarded the Cd transport into upper nodes. The improved method for collecting phloem sap using plant brown hopper was established and the Cd level in phloem sap collected from a panicle neck was significantly lower in two different knock-down lines. Immunostaining confirmed the phloem specific expression of OsLCT1 in large vascular bundles and diffuse vascular bundles. These results suggest that OsLCT1 is involved in re-direction of Cd to upper nodes (and a panicle) at nodes probably facilitating Cd loading into sieve element.
浦口 晋平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 神谷 岳洋*; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 藤巻 秀; 藤原 徹*
no journal, ,
Reducing cadmium (Cd) contents in cereal grains is significant to prevent a risk of Cd toxicity to human health. In rice, understanding of Cd transport mechanisms has been advanced recently. We have demonstrated that OsLCT1 (low-affinity cation transporter is an efflux Cd-transporter on the plasma membrane and is responsible for Cd transport toward grains in a standard japonica rice (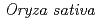 L. cv. Nipponbare). Generally,
L. cv. Nipponbare). Generally, 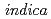 cultivars show higher Cd accumulation in shoot and grains. However, molecular understanding of Cd transporters in indica rice is still insufficient. In this study, we isolated
cultivars show higher Cd accumulation in shoot and grains. However, molecular understanding of Cd transporters in indica rice is still insufficient. In this study, we isolated 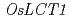 cDNA from cv. Kasalath, a model
cDNA from cv. Kasalath, a model 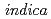 cultivar and characterized the cadmium transport activity of the OsLCT1 allele from Kasalath in the yeast assay system. As a result, the sequence variations found between Nipponbare and Kasalath OsLCT1 do not affect the Cd transport activity mediated by OsLCT1. In the presentation, we will also present the results of Cd dynamics using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system, and discuss physiological roles of OsLCT1 in Cd transport through nodes to grains.
cultivar and characterized the cadmium transport activity of the OsLCT1 allele from Kasalath in the yeast assay system. As a result, the sequence variations found between Nipponbare and Kasalath OsLCT1 do not affect the Cd transport activity mediated by OsLCT1. In the presentation, we will also present the results of Cd dynamics using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system, and discuss physiological roles of OsLCT1 in Cd transport through nodes to grains.