Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 glass up to 10 GPa
glass up to 10 GPaUrakawa, Satoru*; Inoue, Toru*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Kohara, Shinji*; Wakabayashi, Daisuke*; Sato, Tomoko*; Funamori, Nobumasa*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Minerals (Internet), 10(1), p.84_1 - 84_13, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.04(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The structure of hydrous amorphous SiO is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO
is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO glass with 13 wt.% D
glass with 13 wt.% D O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO
O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO rich major phase and a D
rich major phase and a D O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO
O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO glass due to disruption of SiO
glass due to disruption of SiO linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D
linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO
O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO major phase.
major phase.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; Otani, Eiji*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Wang, Y.*; Hernlund, J. W.*; Ballmer, M. D.*
Nature Geoscience, 6(12), p.1041 - 1044, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:96.92(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The bounday between Earth's rigid lighosphere and the underlying, ductile ashenosphere is marked by a distinct siseismic discontinuity. We measure the density, viscosity and structure of basaltic magmas using high-pressure and high-temperature experiments and in situ X-ray analysis under pressure of up to 5.5 GPa. We find that the magmas rapidly become denser with increasing presure and show a viscosity minimum near 4 GPa. Magma mobility determined by the density and viscosity data exhibits a peak at pressures corresponding to depths of 120-150 km, within the asthenosphere. The diminishing mobility of magma in Earth's asthenosphere as the mlets ascend could lead to excessive melt accumulation at depths of 80-100 km, at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. It is concluded that the observed seismic discontinuity at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary records this accumulation of melt.
Nishida, Keisuke*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 96(5-6), p.864 - 868, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:68.19(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of liquid iron sulfide (FeS) was measured up to 3.8 GPa and 1800 K using the X-ray absorption method. The compression curve of the liquid FeS can be fitted using the Vinet equation of state. Isothermal bulk modulus and its temperature and pressure derivatives were determined by a non-linear least squares fit. Liquid FeS is more compressible than Fe-rich Fe-S liquid.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 96(4), p.553 - 557, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.07(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of carbonated peridotite magma was measured up to 3.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. The bulk modulus of carbonated peridotite magma is larger than that of hydrous peridotite magma. The partial molar volume of CO in magma under high pressure and temperature conditions was calculated. Our results show that the partial molar volume of CO
in magma under high pressure and temperature conditions was calculated. Our results show that the partial molar volume of CO is less compressible than that of H
is less compressible than that of H O, suggesting that, on an equal molar basis, CO
O, suggesting that, on an equal molar basis, CO is more effective than H
is more effective than H O in reducing peridotite melt density at high pressure.
O in reducing peridotite melt density at high pressure.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Zhao, D.*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 299(3-4), p.285 - 289, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:60.20(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of the Apollo 14 black glass melt, which has the highest TiO content of pristine mare glasses, was measured to 4.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, its pressure derivative, and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus. Implication for heterogeneities in the lunar mantle is discussed.
content of pristine mare glasses, was measured to 4.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, its pressure derivative, and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus. Implication for heterogeneities in the lunar mantle is discussed.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 95(1), p.144 - 147, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:70.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of a peridotite magma was measured up to 2.5 GPa and 2300 K using an X-ray absorption method. The method allowed measurement of the density of a peridotite melt under seven different conditions and clarified the pressure and temperature dependence of the density. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, 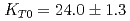 GPa, its pressure derivative,
GPa, its pressure derivative, 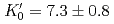 , and the derivative of bulk modulus
, and the derivative of bulk modulus  GPa/K at 2100 K. The large bulk modulus and its pressure derivative of the peridotite melt compared with that of basaltic melt is consistent with previous results from sink-float experiments.
GPa/K at 2100 K. The large bulk modulus and its pressure derivative of the peridotite melt compared with that of basaltic melt is consistent with previous results from sink-float experiments.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 287(3-4), p.293 - 297, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:79.24(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of hydrous peridotite magma containing 5wt.% H O was measured at pressures and temperatures up to 4.3 GPa and 2073 K, respectively, using the X-ray absorption method. A fit of pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnagan equation of state yields isothermal bulk modulus
O was measured at pressures and temperatures up to 4.3 GPa and 2073 K, respectively, using the X-ray absorption method. A fit of pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnagan equation of state yields isothermal bulk modulus 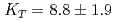 GPa, its pressure derivative
GPa, its pressure derivative 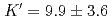 and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus
and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus 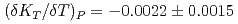 GPa/K at 1773K. The small bulk modulus of the hydrous peridotite magma compared with that of the dry peridotite magma reflects the effect of water, which is more compressible than the silicate melt.
GPa/K at 1773K. The small bulk modulus of the hydrous peridotite magma compared with that of the dry peridotite magma reflects the effect of water, which is more compressible than the silicate melt.
Otani, Eiji*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ando, Ryota*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Advances in High-Pressure Technology for Geophysical Applications, p.195 - 209, 2005/09
This paper summarizes the techniques for the viscosity and density measurements of silicate melt and glasses at high pressure and temperature by using the X-ray radiography and absorption techniques in the third generation synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, Japan. The falling sphere method using in situ X-ray radiography makes it possible to measure the viscosity of silicate melts to the pressures above 6 GPa at high temperature. We summarize the details of the experimental technique of the viscosity measurement, and the results of the measurements of some silicate melts such as the albite and diopside-jadeite systems. X-ray absorption method is applied to measure the density of the silicate glasses such as the basaltic glass and iron sodium disilicate glass up to 5 GPa at high temperature. A diamond capsule, which is not reactive with the glass, is used for the density measurement of the glasses. The present density measurement of the glasses indicates that this method is useful for measurement of the density of silicate melts at high pressure and temperature.
Urakawa, Satoru*; Someya, Keiko*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Yokoshi, Sho*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sueda, Yuichiro*; Irifune, Tetsuo*
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 143-144, p.469 - 479, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:76.63(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
 SiO
SiO determined by high
determined by high 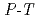 in situ X-ray diffractometry
in situ X-ray diffractometryKatsura, Tomoo*; Yamada, Hitoshi*; Shimmei, Toru*; Kubo, Atsushi*; Ono, Shigeaki*; Kanzaki, Masami*; Yoneda, Akira*; Walter, M. J.*; Ito, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; et al.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 136(1-2), p.11 - 24, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:93.71(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Kiminori*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku
Geophysical Research Letters, 29(8), p.68_1 - 68_3, 2002/05
The in situ viscosity measurements of the pure molten Fe under high pressures were made by falling sphere X-ray radiography method. Viscosity coefficients at about 2000 K were 15-24 mPa s at 2.7-5.0 GPa, and 4-9 mPa s at 5.0-7.0 GPa. Drastic decrease was found at around 5 GPa, at which stable solid phase below the melting temperatures change from delta (bcc) to gamma (fcc) phases. The observation indicates the possibility that the structural change in the molten Fe occurs in a narrow pressure interval (1 GPa) at the similar condition with the phase transformation in the solid.
Urakawa, Satoru*; Hasegawa, Masayuki*; Yamakawa, Junji*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
High Pressure Research, 22(2), p.491 - 494, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 SiO
SiO
Kubo, Tomoaki*; Otani, Eiji*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Kambe, Yuichi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Fujino, Kiyoshi*
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 129(1-2), p.153 - 171, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:66.13(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:69.15(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 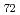 S
S 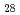 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 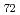 S
S 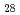 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Yagi, Naoto*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Otaka, Osamu*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Inoue, Toru*; Uchida, Takeyuki*
Ganseki Kobutsu Kagaku, 30(2), p.100 - 101, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
 observation of ilmenite-perovskite phase transition in MgSiO
observation of ilmenite-perovskite phase transition in MgSiO using synchrotron radiation
using synchrotron radiationOno, Shigeaki*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Ito, Eiji*; Kanzaki, Masami*; Yoneda, Akira*; Walter, M.*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Geophysical Research Letters, 28(5), p.835 - 838, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:86.18(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 determined by in situ X-ray observations up to 30GPa and 1400K
determined by in situ X-ray observations up to 30GPa and 1400KOno, Shigeaki*; Ito, Eiji*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Walter, M.*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 27(9), p.618 - 622, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:79.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 SiO
SiO
Kubo, Tomoaki*; Otani, Eiji*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Kambe, Yuichi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Fujino, Kiyoshi*
Geophysical Research Letters, 27(6), p.807 - 810, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:62.72(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Urakawa, Satoru*; Otaka, Osamu*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 42(1), p.24 - 32, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Wataru; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Tamura, Kozaburo*; Inui, Masanori*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Shimomura, Osamu
Hoshako, 12(1), p.17 - 23, 1999/02
no abstracts in English