Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Narita, Ayumi; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Yokoya, Akinari; Noguchi, Miho; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Fujii, Kentaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 166(1-4), p.192 - 196, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.54(Environmental Sciences)For the knowledge about irradiation effects of mammalian cells depending on the cell cycle, most of them had been analyzed by statistical approches. Our purpose is to establish the method for real-time observation of irradiated cells under a microscope. Fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) human cancer (HeLa) cells (red indicates G1; green, S/G2) were exposed to a synchrotron X-ray microbeam. Cells in either G1 or S/G2 were selectively irradiated according to cell color observed in the same microscopic field in a culture dish. Time-lapse micrographs of the irradiated cells were acquired for 24 h after irradiation. The cell cycle was strongly arrested by irradiation at S/G2 and never progressed to G1. In contrast, cells irradiated at G1 progress to S/G2 with a similar time course as non-irradiated control cells. These results show single FUCCI cell exposure and live cell imaging are powerful methods for studying radiation effects on the cell cycle.
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; Konishi, Teruaki*; Usami, Noriko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Azzam, E.*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Suzuki, Masao*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 91(1), p.62 - 70, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:92.21(Biology)Radiation-induced bystander effects have important implications in radiotherapy. Their persistence in normal cells may contribute to risk of health hazards, including cancer. This study investigates the role of radiation quality and gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) in the propagation of harmful effects in progeny of bystander cells. Confluent human skin fibroblasts were exposed to microbeam radiations with different linear energy transfer (LET) by which 0.036 0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.
0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.
Suzuki, Masao*; Autsavapromporn, N.*; Usami, Noriko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Plante, I.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Ikeda, Hiroko; Hattori, Yuya; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(Suppl.1), P. i54, 2014/03
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Suzuki, Masao*; Funayama, Tomoo; Usami, Noriko*; Plante, I.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
Radiation Research, 180(4), p.367 - 375, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:88.83(Biology)We investigated the role of gapjunction intercellular communication (GJIC) in the propagation of stressful effects in confluent normal human fibroblast cultures wherein only 0.036-0.144% of cells in the population were traversed by primary radiation tracks. Confluent cells were exposed to graded doses from X ray, carbon ion, neon ion or argon ion microbeams in the presence or absence of an inhibitor of GJIC. After 4 h incubation, the cells were assayed for micronucleus (MN) formation. Micronuclei were induced in a greater fraction of cells than expected based on the fraction of cells targeted by primary radiation, and the effect occurred in a dose-dependent manner with any of the radiation sources. Interestingly, the inhibition of GJIC depressed the enhancement of MN formation in bystander cells from cultures exposed to high-LET radiation but not low-LET radiation. The results highlight the important role of radiation quality and dose in the observed effects.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Konishi, Teruaki*; Imaseki, Hitoshi*; Yasuda, Keisuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatori, Satoshi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), p.A29 - A47, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:72.31(Biology)Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Ishizaka, Shozo*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 42(3), p.317 - 331, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:27.96(Biology)The characteristics of DNA lesions produced by the phosphorus K-shell absorption in yeast cells were studied using monochromatized soft X-rays tuned to the phosphorus K-edge peak (2153 eV) and below the peak energy (2147 eV). The repaired fractions of DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) were measured relatively by using both a mutant, (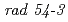 ), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in
), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in 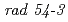 , which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the
, which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the 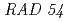 pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.
pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.
Maezawa, Hiroshi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Hieda, Kotaro*; Suzuki, Masao*; Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Mori, Tomoyuki*
Acta Oncologica, 35(7), p.889 - 894, 1997/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.72(Oncology)no abstracts in English
Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Narita, Hirokazu*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Motohashi, Haruhiko; Ono, Hideo; Usami, Noriko*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 1997, P. 81, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Hieda, Kotaro*; Hirono, Taisuki*; Azami, Akira*; Suzuki, Masao*; ; Maesawa, Hiroshi*; Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 70(4), p.437 - 445, 1996/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:95.35(Biology)no abstracts in English
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yokoya, Akinari; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Motohashi, Haruhiko; ; Kashihara, Yasuharu*; ; Harami, Taikan; Sasaki, Teikichi; Maeta, Hiroshi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 372, p.322 - 332, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:97.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari
Journal of Radiation Research, 34(1), 110 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
; Hieda, Kotaro*; Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Radiat. Res., 131(1), p.72 - 80, 1992/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:57.57(Biology)no abstracts in English
Yokoya, Akinari; Usami, Noriko*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Photon Factory News, 10(1), p.13 - 14, 1992/05
no abstracts in English
Yokoya, Akinari; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; ; Hieda, Kotaro*;
Shinku Shigaisen (50nm Ijo) Niyoru Kakusan Sonsho Yuhatsu Kiko No Sogoteki Kenkyu, p.56 - 59, 1992/03
no abstracts in English
Yokoya, Akinari; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*
Photon Factory Activity Report, P. 299, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Noguchi, Miho; Yokoya, Akinari; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Fujii, Kentaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Yokoya, Akinari; Noguchi, Miho; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Fujii, Kentaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaminaga, Kiichi; Kanari, Yukiko; Sakamoto, Yuka; Narita, Ayumi; Usami, Noriko*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Noguchi, Miho; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaminaga, Kiichi; Kanari, Yukiko; Sakamoto, Yuka; Narita, Ayumi; Usami, Noriko*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Noguchi, Miho; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kanari, Yukiko; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Narita, Ayumi; Usami, Noriko*; Suzuki, Keiji*; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English