Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
徐 平光; Zhang, S.-Y.*; Harjo, S.; Vogel, S. C.*; 友田 陽*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.7_1 - 7_13, 2024/01
Comprehensive information about the  microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.
microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.  isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90
isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90 TD
TD  ND (transverse direction
ND (transverse direction  normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
Wallerberger, M.*; Badr, S.*; Hoshino, Shintaro*; Huber, S.*; Kakizawa, Fumiya*; 是常 隆*; 永井 佑紀; Nogaki, Kosuke*; 野本 拓也*; 森 仁志*; et al.
Software X (Internet), 21, p.101266_1 - 101266_7, 2023/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:88.45(Computer Science, Software Engineering)有限温度の多体量子系におけるグリーン関数の情報をスパースモデリング技術を用いて効率的に圧縮するsparse-irというパッケージを開発したことを報告する。このパッケージを用いることで、一粒子グリーン関数であれば数十個の情報でグリーン関数の全領域での松原振動数依存性を計算することが可能となる。発表代表者の永井はこのソフトウェアの応用例を示すために、このパッケージを使うことで超伝導状態のシミュレーションが精度よくできることを示した。今後、このパッケージを使うことで、重元素化合物などの強相関電子系の物性を精度よく計算することが可能となる。
 observation and analysis of solid-state diffusion and liquid migration in a crystal growth system; A Segregation-driven diffusion couple
observation and analysis of solid-state diffusion and liquid migration in a crystal growth system; A Segregation-driven diffusion coupleTremsin, A. S.*; Perrodin, D.*; Losko, A. S.*; Vogel, S. C.*; 篠原 武尚; 及川 健一; Bizarri, G. A.*; Bourret, E. D.*; Peterson, J. H.*; Wang, K. P.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 186, p.434 - 442, 2020/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:37.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Energy-resolved neutron imaging is employed for  measurements of dopant transport in a simple experiment performed before the crystal growth of the scintillator BaBrCl:5%Eu via a vertical gradient freeze technique. During a stabilization period preceding growth, we observed the diffusion of Eu from the solid phase into the melt over a period of approximately 4 h. Comparing the measured centerline concentration profile with a mathematical model for the system, we estimate the solid-state diffusivity of Eu in BaBrCl as
measurements of dopant transport in a simple experiment performed before the crystal growth of the scintillator BaBrCl:5%Eu via a vertical gradient freeze technique. During a stabilization period preceding growth, we observed the diffusion of Eu from the solid phase into the melt over a period of approximately 4 h. Comparing the measured centerline concentration profile with a mathematical model for the system, we estimate the solid-state diffusivity of Eu in BaBrCl as 
 = 1.9
= 1.9  10
10 m
m /s and an upper limit for the liquid-phase diffusivity of Eu in the melt as
/s and an upper limit for the liquid-phase diffusivity of Eu in the melt as 
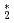 = 2.5
= 2.5  10
10 m
m /s, at temperatures near the melting point. We compare this experiment, where diffusion is driven by a concentration discontinuity arising from segregation, to the classical diffusion couple technique.
/s, at temperatures near the melting point. We compare this experiment, where diffusion is driven by a concentration discontinuity arising from segregation, to the classical diffusion couple technique.
徐 平光; Harjo, S.; 小島 真由美*; 鈴木 裕士; 伊藤 崇芳*; Gong, W.; Vogel, S. C.*; 井上 純哉*; 友田 陽*; 相澤 一也; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.746 - 760, 2018/06
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:90.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Neutron diffraction texture measurements provide bulk textures with excellent grain statistics even for large grained materials, together with the crystallographic parameters and microstructure information such as phase fractions, coherent crystallite size, root mean square microstrain, macroscopic/intergranular stress/strain. The procedure for high stereographic resolution texture and residual stress evaluation was established at the TAKUMI engineering materials diffractometer. The pole figure evaluation of a limestone standard sample with a trigonal crystal structure suggested that the obtained precision for texture measurement is comparable with the oversea well-established neutron beam lines utilized for texture measurements. A high strength martensite-austenite multilayered steel was employed for further verification of the reliability of simultaneous Rietveld analysis of multiphase textures and macro stress tensors. By using a geometric mean micro-mechanical model, the macro stress tensor analysis with a plane stress assumption showed a RD-TD in-plane compressive stress (about -330 MPa) in martensite layers and a RD-TD in-plane tensile stress (about 320 MPa) in austenite layers. The phase stress partitioning was ascribed to the additive effect of volume expansion during martensite transformation and the linear contraction misfit during water quenching.
徐 平光; 友田 陽*; Vogel, S. C.*; 鈴木 徹也*; 米村 雅雄*; 神山 崇*
Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 33(5), p.389 - 395, 2013/08
The ferrite-to-austenite transformation during heating and the austenite-to-ferrite transformation during cooling were  investigated by KEK/SIRIUS and LANSCE/HIPPO neutron diffractometers under the stress-free condition. The deviation of ferrite lattice parameter from the linear thermal expansion and contraction during heating and cooling suggested the compressive strain occurred in ferrite phase. The texture memory effect between the cold compression texture of initial martensite and the final texture of ferrite after
investigated by KEK/SIRIUS and LANSCE/HIPPO neutron diffractometers under the stress-free condition. The deviation of ferrite lattice parameter from the linear thermal expansion and contraction during heating and cooling suggested the compressive strain occurred in ferrite phase. The texture memory effect between the cold compression texture of initial martensite and the final texture of ferrite after  -
- -
- phase transformation was interrupted by the static recrystallization of martensite during step-by-step heating, revealing that the occurrence of texture memory effect was not directly related to the deformation stored energy but related to the transformation strain and the strong variant selection for nucleation.
phase transformation was interrupted by the static recrystallization of martensite during step-by-step heating, revealing that the occurrence of texture memory effect was not directly related to the deformation stored energy but related to the transformation strain and the strong variant selection for nucleation.
徐 平光; 友田 陽*; Vogel, S. C.*
軽金属学会平成24年度第2回加工と熱処理による優先方位制御研究部会公開講演会資料, p.21 - 22, 2012/10
フェライトからオーステナイトを経由して再びフェライトへの低合金鋼拡散変態において、加熱前のフェライト集合組織と冷却終了後のフェライト集合組織の間でよく観察された集合組織の記憶現象はバリアント選択則を用いて検討されてきた。しかし、拡散相変態の中間過程のその場観察例はなく、バリアント選択メカニズムにはまだ不明な点がある。本研究ではSIRIUS中性子回折装置を用い、段階的な加熱と冷却中の低合金マルテンサイト鋼のオーステナイト変態,フェライト変態及び熱膨張過程をその場で観察した。また、HIPPO中性子回折装置を用い、冷間圧縮した低合金鋼の拡散変態中の変態集合組織の変化をその場で測定した。段階的な加熱・冷却中に、低合金マルテンサイト鋼は2相域の格子常数が線形膨張直線より偏倚することから内部応力の存在を確認した。これはフェライトからオーステナイトを経由して再びフェライトへの拡散変態の集合組織記憶効果に関連すると考えられる。
徐 平光; 友田 陽*; Gong, W.*; Vogel, S. C.*; 鈴木 裕士; 鈴木 徹也*
no journal, ,
二相域で大ひずみ圧縮中のフェライト結晶方位密度は小ひずみ加工より著しい変化を示したが、その形成機構はまた不明瞭のため、同じプロセスで熱間圧縮した低合金鋼試料を用い、走査型電子顕微鏡と飛行時間法中性子回折装置でミクロ組織とバルク集合組織を評価した。組織観察によって、大ひずみ圧縮した試料は動的再結晶が生じたことを確認した。その集合組織は強い(001)[uvw]と(111)[uvw]繊維配向が構成され、以前の中性子その場回折実験から予想した結果と一致した。
徐 平光; Vogel, S. C.*; 鈴木 裕士; 目時 直人; 南部 将一*; 井上 純哉*; 秋田 貢一
no journal, ,
中性子回折は金属材料のバルク集合組織を測定できるが、測定精度は中性子回折装置に依存している。本文はJRR-3ガイドホイルにおいてMUSASI-LとRESA-2角度分散法中性子回折とHIPPPO飛行時間法中性子回折を用い、高強度複層鋼板オーステナイトSUS301/マルテンサイトSUS420J2の集合組織を測定し、定量的に比較した。中性子回折装置RESA-2で一次元検出器を用いたプロファイルをガウス積分した回折強度を基づいた結晶方位分布関数(ODF)結果と比較すると、MUSASI-L多目的中性子装置でピック回折強度に基づく集合組織測定結果はよく一致した。HIPPO飛行時間法中性子回折法は短時間で集合組織を測定できるが、角度分解能が低いため、最適化処理しても測定精度はやや低いことを示した。
徐 平光; 友田 陽*; Paradowska, A.*; Vogel, S. C.*
no journal, ,
近年、変形誘発フェライト変態は組織微細化の重要なルートとして重視されてきたが、高加工速度その場実験が困難のため、熱間加工中微細組織の結晶学変化はまだ直接観察されなかった。本研究は飛行時間法中性子回折技術を用いた無加工の静態等温フェライト変態挙動と二つ熱間圧縮速度で熱間加工中の等温変形誘発フェライト変態挙動を比較した。オーステナイト単相域とオーステナイト・フェライト両相域で変形誘発フェライト変態を確認した。
徐 平光; 鈴木 裕士; 目時 直人; 秋田 貢一; Vogel, S. C.*; 南部 将一*; 井上 純哉*
no journal, ,
Compared with the X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction is advantageous to measure complete pole figures of coarse-grained materials, to measure magnetic/residual strain/dislocation density/crystal size pole figures and it is also possible to investigate complex texture evolutions of bulk samples (rather than surfaces) of multiphase materials during heating, cooling and/or straining. Here, the crystallographic textures of high strength austenite-martensite laminated steel were measured with different neutron diffractometers. The comparison of orientation distribution functions showed that the Gaussian integrated intensities obtained from partially overlapping peaks were reliable to calculate the multiphase textures. Collimator optimized neutron beam and careful background correction enabled peak maximum intensities from non-overlapping peaks suitable to evaluate the multiphase textures. The Rietveld texture analysis of time-of-flight neutron diffraction spectra suggested that the spherical harmonic method and the E-WIMV discrete method were convincible up to an expansion series of L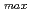 =12 and at a resolution angle of 10 degrees, respectively. In the near future, the development of time-of-flight texture measurement technique at J-PARC will be valuable to carry out the in situ texture evaluation while the introduction of 2-dimensional position-sensitive detector to the angle dispersive diffractometer will reduce the measurement time.
=12 and at a resolution angle of 10 degrees, respectively. In the near future, the development of time-of-flight texture measurement technique at J-PARC will be valuable to carry out the in situ texture evaluation while the introduction of 2-dimensional position-sensitive detector to the angle dispersive diffractometer will reduce the measurement time.
徐 平光; Harjo, S.; Vogel, S. C.*; 伊藤 崇芳*; 友田 陽*
no journal, ,
Ultrafine grained ferrite-austenite duplex steels have better ductility than ultrafine grained ferrite-cementite steels. The static recrystallization of cold rolled martensite steel is easy to get a uniform refined microstructure. The in situ microstructure evaluations from TAKUMI time-of-flight neutron diffraction during the isothermal annealing showed that at 773 K, the austenite precipitation did not initiate before isothermal holding and the austenite transformation rate was slow. On the other hand, the 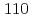 peak did not become shape, the recrystallization behavior was not apparent. At 823 K, the austenite precipitation took place and the
peak did not become shape, the recrystallization behavior was not apparent. At 823 K, the austenite precipitation took place and the 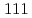 peak became stronger and stronger, revealing that the austenite precipitation was evident. The flatten
peak became stronger and stronger, revealing that the austenite precipitation was evident. The flatten 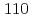 peak became weaker and shaper, revealing that the cold rolled martensite was recrystallized. At 873 K, the austenite transformation was dominated and the transformation rate was much rapid. However, the austenite was meta-stable and some austenite transformed into martensite again during rapid cooling to room temperature. In addition, the in situ texture evolutions during isothermal annealing at above temperatures were investigated by using HIPPO time-of-flight neutron diffraction and the ex situ textures were measured for confirmation by using the MUSASI-L angle dispersive neutron diffraction.
peak became weaker and shaper, revealing that the cold rolled martensite was recrystallized. At 873 K, the austenite transformation was dominated and the transformation rate was much rapid. However, the austenite was meta-stable and some austenite transformed into martensite again during rapid cooling to room temperature. In addition, the in situ texture evolutions during isothermal annealing at above temperatures were investigated by using HIPPO time-of-flight neutron diffraction and the ex situ textures were measured for confirmation by using the MUSASI-L angle dispersive neutron diffraction.
徐 平光; 友田 陽*; Vogel, S. C.*
no journal, ,
Though the phase stress/strain and the texture evolution may provide direct data in modeling the variant selection, no quantitative measurement at high temperature has been reported because these transformations involve evident composition diffusion and the solute concentration change in austenite. Here, the microstructure evolution and the texture evolution in the austenite transformation, the ferrite transformation of low-alloy steel was in situ investigated by neutron diffraction. It is found due to the static recrystallization during heating, the cold compression texture cannot be memorized after the  -
- -
- transformation. The stored energy obtained from cold compression is consumed during the recrystallization, and the diffusional phase transformation is suspected to occur without remarkable influence from the deformation stored energy.
transformation. The stored energy obtained from cold compression is consumed during the recrystallization, and the diffusional phase transformation is suspected to occur without remarkable influence from the deformation stored energy.
徐 平光; 伊藤 崇芳*; Harjo, S.; 秋田 貢一; 相澤 一也; Vogel, S. C.*; Kockelmann, W.*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction may easily obtain the bulk information of various materials from the ex-situ/in-situ stress/strain change, the crystallographic structure evolution to the crystallographic preferred orientation rotation because of high penetrability of neutron beams. Though two angle dispersive diffractometers have been upgraded at JAEA for bulk texture evaluation of coarse-grained materials, structure-anisotropic materials, low symmetric materials as well as various metallic materials, the measurement speed is slow which makes it difficult to carry out in situ texture measurements. In order to improve measurement efficiency and increase the accessibility for general users, the time-of-flight neutron diffraction bulk texture evaluation technique is being developed urgently. Here, our bulk texture measurement research and development activities on TAKUMI will be introduced, including our recent experiment results using overseas time-of-flight neutron diffraction facilities.
徐 平光; 秋田 貢一; 鈴木 裕士; 小島 真由美*; 井上 純哉*; 南部 将一*; Vogel, S. C.*; 小関 敏彦*
no journal, ,
As-quenched martensite is of low ductility and generally not suitable for direct usage as an important sheet structural material. By using the sandwich-type structure alternatively with martensite steel layer and austenite steel layer, the multilayered steel composite after hot rolling, cold rolling and short-time solid solution treatment was reported to possess good strength-ductility balance. In order to evaluate the plastic deformation characteristics of martensite, the neutron diffraction techniques were here employed to investigate the evolution of the residual strain, the bulk texture and the deformation induced martensite transformation after uniaxial tensile deformation of SUS301/420J2 multilayered steel composite at different engineering strains. The neutron diffraction studies finally suggests that the martensite ductility improvement is mostly related to the sandwich-type multiphase layer structure and partially related to the enhancement of work-hardening ability of martensite through the deformation induced martensite transformation from austenite.
徐 平光; 諸岡 聡; 山本 和喜; Vogel, S. C.*; Lutterotti, L.*; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
Because of large spot size and high penetrability, neutron diffraction can acquire the average orientation information of a bulk polycrystalline sample and monitor the microstructure and/or texture evolutions. Though many new neutron facilities with higher thermal beam flux have been established for residual stress and texture measurements, neutron diffraction facilities attached at a conventional research reactor like the Japan Research Reactor No.3 (JRR-3) are still being expected to support broader neutron diffraction application studies not limited by metals, alloys, ceramics, composite materials, and even geological materials. In this oral presentation, the newest experimental results from a round robin texture measurement test of international standard limestone will be formally reported and the related discussion and future prospect will be involved.
徐 平光; Harjo, S.; 小貫 祐介*; 佐藤 成男*; Lutterotti, L.*; Vogel, S. C.*; Liss, K.-D.*; 富田 俊郎*
no journal, ,
For polycrystalline materials, textures as their crystallographic orientation feature have been paid broad attention because of their important effects on mechanical and physical characteristics. Besides metals and ceramics, the widespread applications of textures involving sheet forming simulation, additive manufacturing, minerals, and rocks have also demonstrated this status. Different with the electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD) and the X-ray diffraction (XRD) for surface texture analysis, the neutron diffraction thanks to the excellent penetrability and the coarse beam spot of thermal neutrons can collect high statistical diffraction pattens, valuable for deeply investigating the microstructure change and the characteristic response of polycrystalline materials. Through the Rietveld texture analysis process combined with other profile-analysis-related material parameters (e.g. stress tensor, phase fraction, dislocation density and/or coherent size), the large-scale neutron diffractometers TAKUMI and iMATERIA with good instrumental resolution ( d/d) and high beam flux have higher measurement efficiency, promoting that the precise evaluation of microstructures and related materials parameters of advanced materials. Recently, weak diffraction patterns step-by-step collected in very short time from the RESA angle dispersive neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 have been utilized to realize the precise texture evaluation of various polycrystalline materials. Our international round robin activity for texture analysis confirms that, Rietveld texture analysis using MAUD software may be recommended as a standard bulk texture analysis method, regardless of the neutron source types of steady reactor source or time-pulsed source.
d/d) and high beam flux have higher measurement efficiency, promoting that the precise evaluation of microstructures and related materials parameters of advanced materials. Recently, weak diffraction patterns step-by-step collected in very short time from the RESA angle dispersive neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 have been utilized to realize the precise texture evaluation of various polycrystalline materials. Our international round robin activity for texture analysis confirms that, Rietveld texture analysis using MAUD software may be recommended as a standard bulk texture analysis method, regardless of the neutron source types of steady reactor source or time-pulsed source.