Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Naka, Yasuhito*; Nishijima, Haruyuki*; Imabayashi, Shinichiro*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 51(9), p.726 - 731, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.13(Engineering, Chemical)Thermochemical hydrogen production by the iodine-sulfur process decomposes water into hydrogen and oxygen by combining the chemical reactions of iodine and sulfur. Two types of acids are produced through the Bunsen reaction. To improve the performance of this reaction, ion-exchange membranes for the membrane Bunsen reaction should be developed. In the present study, a cation-exchange membrane was prepared by using a radiation-graft polymerization method. It was found that a divinylbenzene crosslinking procedure was very effective in reducing water permeation through the membrane, and the membrane Bunsen reaction was successfully carried out by using the developed crosslinked membrane. Therefore, the developed crosslinked membrane is a potential candidate for cation-exchange membranes for the membrane Bunsen reaction.
Mochizuki, Izumi; Fukaya, Yuki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yaji, Koichiro*; Harasawa, Ayumi*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Physical Review B, 85(24), p.245438_1 - 245438_6, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.1(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The atomic configuration and electronic band structure of Pt-induced nanowires on a Ge(001) surface are investigated using scanning tunneling microscopy, reflection high-energy positron diffraction, and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. A previously proposed theoretical model, composed of Ge dimers on the top layer and buried Pt arrays in the second and fourth layers, is found to be the fundamental structure of the observed nanowires. At low temperatures (
 80 K), each Ge dimer is alternately tilted in the surface normal direction (asymmetric), causing a p(
80 K), each Ge dimer is alternately tilted in the surface normal direction (asymmetric), causing a p(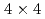 ) periodicity. At high temperatures (
) periodicity. At high temperatures (
 110 K), each Ge dimer is flat with respect to the horizontal axis (symmetric), giving rise to p (
110 K), each Ge dimer is flat with respect to the horizontal axis (symmetric), giving rise to p (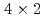 ) periodicity. Upon the above phase transition, the electronic band dispersion related to the Ge dimers in the deeper energy region shifts to the Fermi level.
) periodicity. Upon the above phase transition, the electronic band dispersion related to the Ge dimers in the deeper energy region shifts to the Fermi level.
 He
He ion irradiation
ion irradiationUrushibara, Ayumi*; Shikazono, Naoya; O'Neill, P.*; Fujii, Kentaro; Wada, Seiichi*; Yokoya, Akinari
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 84(1), p.23 - 33, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:91.3(Biology)To characterize the complexity of radiation damage to DNA, fully hydrated plasmid DNA was irradiated with  He
He ions. From quantification of the conformational changes of the irradiated samples, the yields of single-(SSB) and double strand break (DSB) were obtained. Base lesions were visualized as additional strand breaks by treatment with base excision repair enzymes. The yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on LET of the
ions. From quantification of the conformational changes of the irradiated samples, the yields of single-(SSB) and double strand break (DSB) were obtained. Base lesions were visualized as additional strand breaks by treatment with base excision repair enzymes. The yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on LET of the  He
He ions, whereas the yield of prompt DSBs increases with increasing LET. The yields of isolated base lesions, revealed by enzymes as additional SSBs, decrease drastically with increasing LET. The sum of the yields of DSB and additional DSBs revealed by the enzymes increase with increasing LET of the
ions, whereas the yield of prompt DSBs increases with increasing LET. The yields of isolated base lesions, revealed by enzymes as additional SSBs, decrease drastically with increasing LET. The sum of the yields of DSB and additional DSBs revealed by the enzymes increase with increasing LET of the  He
He ions except at the highest LET investigated. These results indicate that the yields of clustered damage, revealed as DSB and non-DSB clustered damage sites, increase with increasing ionization density of radiation.
ions except at the highest LET investigated. These results indicate that the yields of clustered damage, revealed as DSB and non-DSB clustered damage sites, increase with increasing ionization density of radiation.
Mochizuki, Izumi; Fukaya, Yuki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yaji, Koichiro*; Harasawa, Ayumi*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*
no journal, ,
Defect-free quasi-one chain with the single atomic width is reconstructed on the Ge(001) surface by a Pt adsorption of sub-atomic layer. Recently, it has been reported that the atomic chain undergoes the Peierls transition about 80 K. But, the electronic property, the atomic arrangements and displacements in the phase transition are not yet elucidated. Using reflection high-energy positron diffraction (RHEPD), we have reported that the Nano-Wire (NW) model is the fundamental structure of the observed nanowires. In this study, we have tried to determine the atomic arrangement and the transition phenomenon using RHEPD. The rocking curve shows a good agreement with the calculated curve assuming the NW model with the Pt coverage of 0.75 ML. In addition, the change of rocking curves in the phase transition shows that the structural phase transition is caused by the height difference of the topmost Ge dimer atoms.
Mochizuki, Izumi*; Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yaji, Koichiro*; Harasawa, Ayumi*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mochizuki, Izumi*; Yaji, Koichiro*; Fukaya, Yuki; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Harasawa, Ayumi*; Matsuda, Iwao*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sawada, Sumiyuki; Nakayama, Masashi; Tanai, Kenji; Morikawa, Yoshito*; Jo, Mayumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sawada, Sumiyuki; Nakayama, Masashi; Tanai, Kenji; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Masashi; Sawada, Sumiyuki; Tanai, Kenji; Sugita, Yutaka; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji; Jo, Mayumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kodaira, Takahide; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,  , ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting.
, ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting.
Kodaira, Takahide; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,  , ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting. Importantly, controlling the fixed-charge density of the membrane should both lower permeability of SO
, ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting. Importantly, controlling the fixed-charge density of the membrane should both lower permeability of SO and enhance the transport number of H
and enhance the transport number of H .
.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
There has been a strong motivation to develop new cation exchange membranes suitable for the Bunsen reaction in the thermochemical water splitting IS process. We prepared cation exchange membranes by a radiation grafting polymerization method. The grafting reaction into a poly(ethylene- -tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The membrane had an ion exchange capacity of 2.17 mmol g
-tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The membrane had an ion exchange capacity of 2.17 mmol g while Nafion212 possessed 0.90 mmol g
while Nafion212 possessed 0.90 mmol g that is less than half of that for the grafted membrane. Both these membranes exhibited a similar water uptake, but the grafted membrane showed lower water permeation than Nafion212.
that is less than half of that for the grafted membrane. Both these membranes exhibited a similar water uptake, but the grafted membrane showed lower water permeation than Nafion212.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by radiation-induced graft polymerization. The water permeation of the grafted membrane was lower than that of Nafion 212 under the condition of a similar water uptake.
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by radiation-induced graft polymerization. The water permeation of the grafted membrane was lower than that of Nafion 212 under the condition of a similar water uptake.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane. As part of an ongoing JST-ALCA project, therefore, we developed ion exchange membranes for this reaction by radiation-induced graft polymerization, investigating their water permeation properties by the pervaporation method. Our membrane preparation involves the
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane. As part of an ongoing JST-ALCA project, therefore, we developed ion exchange membranes for this reaction by radiation-induced graft polymerization, investigating their water permeation properties by the pervaporation method. Our membrane preparation involves the  -ray-induced grafting of styrene and divinylbenzene into poly(ethylene-
-ray-induced grafting of styrene and divinylbenzene into poly(ethylene- -tetrafluoroethylene) films and the subsequent sulfonation. Water permeate flux values at 25
-tetrafluoroethylene) films and the subsequent sulfonation. Water permeate flux values at 25 C were 7.4 and 19 kg/m
C were 7.4 and 19 kg/m h through the grafted membrane and Nafion 212 at the same water uptake (37%), respectively.
h through the grafted membrane and Nafion 212 at the same water uptake (37%), respectively.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Oura, Kotone*; Ono, Ryuhei*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
There has been a strong motivation to develop new cation exchange membranes suitable for the Bunsen reaction in the thermochemical water splitting IS process. We prepared cation exchange membranes by a radiation grafting polymerization method. The grafting reaction into a poly(ethylene-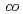 -tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Oura, Kotone*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Ono, Ryuhei*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
Bunsen reactor in the IS process has a potential of the downsizing and the improvement of efficiency by using redox type reactor with an ion exchange membrane. The key to the performance of redox reactor is the development of the high performance ion exchange membrane. In this paper, we investigated the performance (proton transport number (t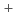 ) and water permeation factor (
) and water permeation factor ( )) of Nafion 212, which is the reference. As a result, t
)) of Nafion 212, which is the reference. As a result, t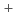 and
and  were 0.63 and 2.82, respectively, indicating that not only H
were 0.63 and 2.82, respectively, indicating that not only H but also I
but also I and water permeate through the membrane. The permeation of these components might cause the precipitation of sulfur and the rising of the voltage. Aftertime, we must new ion exchange membrane which can restrict the permeation of I
and water permeate through the membrane. The permeation of these components might cause the precipitation of sulfur and the rising of the voltage. Aftertime, we must new ion exchange membrane which can restrict the permeation of I and water.
and water.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Wada, Ayumi*; Nobuhara, Fumiyoshi*; Hirao, Yoshihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English