Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.1(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kumada, Takayuki; Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Morooka, Satoshi; Tominaga, Aki; Tanida, Hajime; Shobu, Takahisa; Konno, Azusa; Owada, Kenji*; Ono, Naoko*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 528, p.151890_1 - 151890_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.8(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have developed an anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering (ASAXS) diffractometer in SPring-8 to investigate irradiation-induced nanostructural change in ion-beam irradiated stainless steel. A thermally-aged MA956 stainless steel sample displays power-law scattering that follows the Porod law at the magnitude of scattering vector, Q, below 0.5 nm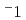 and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm
and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm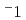 . After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
. After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
 nanocrystals
nanocrystalsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kunisada, Ryoichi*; Chikada, Tsukasa*; Ueno, Shintaro*; Fujii, Ichiro*; Nagata, Hajime*; Ohara, Koji*; Wada, Satoshi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 58(SL), p.SLLA03_1 - SLLA03_7, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.5(Physics, Applied) nanocubes by solvothermal synthesis
nanocubes by solvothermal synthesisYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Nakashima, Koichi*; Nagata, Hajime*; Wada, Satoshi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(10S), p.10NC01_1 - 10NC01_6, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.5(Physics, Applied)The atomic-scale structure of KNbO nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO
nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO
nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
Oikawa, Teruki; Wada, Hajime*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 110(9), p.528 - 535, 2004/09
None
Kubo, Shigenobu; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kawada, Kenichi; Onoda, Yuichi; Sato, Ikkenn; Kamiyama, Kenji; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Fujita, Satoshi; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2004-041, 135 Pages, 2004/07
This report shows the results of the study on countermeasures for the elimination of re-criticality issue for the sodium cooled reactors, which was conducted in 2003 as a part of the feasibility study phase II for the commercialization of fast reactors. A sort of analytical studies related to the in-vessel retention capability under the unprotected loss of flow condition was conducted for the large scale and medium scale sodium cooled reactors, aiming at establishing some promising concepts to resolve the re-criticality issue keeping consistency with the basic concept of the core and plant design. Major conclusions are as follows. ABLE concept, which is proposed as a measure to enhance the fuel discharge capability in the early transition phase, needs much time to initiate fuel discharge than wrapper tube failure. Therefore it is currently concluded that it is difficult to show clear perspective. A modified version of FAIDUS which has less drawbacks on the core and cycle performance and related R&Ds than original FAIDUS was proposed for further study. In-place retention and cooling in the core region is important from view point of reduction of R&D loads conceming post accident material relocation and cooling at the bottom of the reactor vessel. A possibility of which the in-vessel retention can be achieved by quantitatively clarifying the effect of the superior cooling potential of sodium was shown. Based on the currently available information related to FAIDUS and ABLE, possible candidates of experimental studies were shown. An initiating phase analysis for the metallic fuel core with 550 C of core outlet temperature and 8
C of core outlet temperature and 8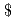 of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
Ishida, Masayoshi; Kawada, Kenichi; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2003-059, 74 Pages, 2003/07
Safety characteristics in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of mid-sized MOX fueled liquid metal reactor core of high converter type have been examined by using the CDA initiating phase analysis code SAS4A. The design concept of high converter type reactor core has been studied as one of options in the category of sodium-cooled reactor in Phase II of Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System.An unprotected loss-of-flow accident (ULOF) has been selected as a representative CDA initiator for this study. A core concept of high converter type, which employed a large diameter fuel pin of 11.1mm with 1.2m core height to get a large fuel volume fraction in the core to achieve high internal conversion ratio was proposed in JFY2001. Each fuel subassembly of the core (abbreviated here as UPL120) was provided with an upper sodium plenum directly above the core to reduce the sodium void reactivity worth. Because of the large fuel pin diameter, average specific fuel power density (31 kW/kg-MOX) of UPL120 is about one half of those of conventional large MOX cores. The reactivity worth of sodium voiding is 6$ in the whole core, and -1$ in the all upper plenums. Initiating phase of ULOF accident in UPL120 under the conditions of nominal design and best estimate analysis resulted in a slightly super-prompt critical power burst. The causes of the super-prompt criticality have been identified twofold: (a) the low specific fuel power density of core reduced the effectiveness of prompt negative reactivity feedback of Doppler and axial fuel expansion effects upon increase in reactor power, and (b) the longer core height compared with conventional 1m cores brought, together with the lower specific power density, a remarkable delay in insertion of negative fuel dispersion reactivity after the onset of fuel disruption in sodium voided subassembly due to the lower linear heat rating in the top portion of the core. During the delay, burst-type fuel failures in sodium un-v
Sawada, Atsushi; Uchida, Masahiro; Shimo, Michito*; Yamamoto, Hajime*; Takahara, H.*; Doe, T. W.*
Engineering Geology, 56(1-2), p.75 - 96, 2002/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:42.55(Engineering, Geological)None
Tobita, Yoshiharu; Morita, Koji; Kawada, Kenichi; Niwa, Hajime; Nonaka, Nobuyuki
PNC TN9410 97-079, 106 Pages, 1997/09
The sequences of ULOF (unprotected loss-of-flow) event in the prototype FBR has been evaluated, as a part of the research and development (R&D) in the reactor safety research, reflecting the latest experimental and analytical knowledge on CDA (core disruptive accident) which has been accumulated at O-arai Engineering Center. In the R&D activity on the FBR reactor safety subject, we have accumulated the experimental knowledge of mitigation mechanism in the energy generating process in CDA, utilizing international in-pile safety experimental programs such as CABRI program, as well as the out-of-pile experiments in Japan and foreign countries. This knowledge has been reflected to the development and validation of the SAS and SIMMER code. The objectives of this study are to apply these new assessment techniques to the prototype FBR and to clarify quantitatively in detail the energy generation process of CDA. In this study, an emphasis is placed on the event sequence of the melt progression phase ("transition phase") which has been recognized as one of the important issues of CDA analysis. The major parameters to be considered in this phase are the change of the mobile molten fuel mass and the history of the fuel motion, and also the relation between these parameters and energy generation mechanism. The following methods and approaches have been taken into account in this evaluation study. (a)The SAS4A code is used for the analysis of the transient behavior in the first Phase driven by core voiding ("initiating phase"), and the SIMMER-III code is used for the latter phases with melt-progression (tansition phase) and also the energy conversion process from the thermal one to the mechanical one. These codes have been developed and validated under the collaboration among PNC, CEA and FZK. (b)The uncertainty band of the void reactivity worth and Doppler coeficient has been reduced through the re-evaluation of the critical experimental data in the neutron physics area. ...
Kumamoto, So*; Shimo, Michito*; Yamamoto, Hajime*; Sawada, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tajiri, Nobuhiro*; Hiroyasu, Tomoyuki*; Wada, Motoi*; Kenmotsu, Takahiro*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Daito, Izuru; Sasao, Hajime*; Suzuki, Masayuki; Okada, Hajime
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Noboru*; Nishikino, Masaharu*; Mikami, Katsuhiro*; Okada, Hajime*; Kondo, Shuji*; Kawachi, Tetsuya*; Shimada, Yoshinori*; Kurahashi, Shinri*; Kitamura, Toshiyuki*; Kotyaev, O.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Owada, Kenji*; Tanida, Hajime; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In steel materials, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method at BL22XU.
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Tanida, Hajime; Owada, Kenji*; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In development of oxide-dispersed ferritic steels, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method using synchrotron radiation.