Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
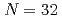 and
and 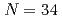 shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRI
shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRIIimura, Shun*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Takamine, Aiko*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Wada, Michiharu*; Chen, S.*; Hou, D. S.*; Xian, W.*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Yan, S.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:88.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Yamada, Ippei; Wada, Motoi*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(4), p.042801_1 - 042801_13, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.33(Physics, Nuclear)A transverse beam profile monitor that visualizes a two-dimensional beam-induced fluorescent image was developed. The monitor employs a sheet-shaped gas flow formed by a technique of rarefied gas dynamics. A simplified analysis method was developed to reconstruct the beam intensity profile from the obtained image. The developed profile monitor and the analysis method were applied to measure the J-PARC 3 MeV H beam profile. The root mean square values of the profiles were consistent with the ones obtained by a wire-scanning-type beam profile monitor. The beam loss due to the gas sheet injection was measured as a beam-current reduction. The amount of the beam current decreased in proportion to the gas sheet flux and the reduction ranged from 0.004 to 2.5%. The assembled system was capable of reconstructing a beam profile from a single shot beam pulse (1.7
beam profile. The root mean square values of the profiles were consistent with the ones obtained by a wire-scanning-type beam profile monitor. The beam loss due to the gas sheet injection was measured as a beam-current reduction. The amount of the beam current decreased in proportion to the gas sheet flux and the reduction ranged from 0.004 to 2.5%. The assembled system was capable of reconstructing a beam profile from a single shot beam pulse (1.7 10
10 protons in 50
protons in 50  s).
s).
Kamiya, Junichiro; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Yamada, Ippei; Ogiwara, Norio*; Hikichi, Yusuke*; Wada, K.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012149_1 - 012149_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:79.08(Physics, Particles & Fields)To obtain a getter effect to titanium vacuum duct surface, the method to remove the oxide on the surface by sputtering with ionized molecules has been developed. In the method, a sheet-shaped gas distribution with a uniform and high density is generated through a narrow slit by a small amount of gas. In this report, the gas density distribution was calculated by the Monte Carlo simulation code. As a result, it was found that a gas injection from both directions was effective to generate uniform density distribution. Furthermore, the gas injection method was applied to a non-destructive beam profile monitor, that detects ions generated by the interaction between gas molecules and beam. In this monitor, dependence of the beam profile on the injected gas amount was measured. A small amount of injected gas was found to be ideal for the beam profile measurements in the unsaturated and a high S/N ratio region.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Finsterle, S.*; Lanyon, B.*;  kesson, M.*; Baxter, S.*; Bergstr
kesson, M.*; Baxter, S.*; Bergstr m, M.*; Bockg
m, M.*; Bockg rd, N.*; Dershowitz, W.*; Dessirier, B.*; Frampton, A.*; Fransson,
rd, N.*; Dershowitz, W.*; Dessirier, B.*; Frampton, A.*; Fransson,  .*; et al.
.*; et al.
Geological Society, London, Special Publications, No.482, p.261 - 283, 2019/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:62.77(Geology)Nuclear waste disposal in geological formations relies on a multi-barrier concept that includes engineered components which in many cases includes a bentonite buffer surrounding waste packages and the host rock. An SKB's (Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.) Modelling Task Force project facilitated to improve the overall understanding of rock - bentonite interactions, as 11 teams used different conceptualisations and modelling tools to analyse the in-situ experiment at the  ps
ps Hard Rock Laboratory. The exercise helped identify conceptual uncertainties that led to different assessments of the relative importance of the engineered and natural barrier subsystems and of aspects that need to be better understood to arrive at reliable predictions of bentonite wetting.
Hard Rock Laboratory. The exercise helped identify conceptual uncertainties that led to different assessments of the relative importance of the engineered and natural barrier subsystems and of aspects that need to be better understood to arrive at reliable predictions of bentonite wetting.
Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Nuryanthi, N.*; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Tautmann, C.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 435, p.162 - 168, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)We used individual single-ion tracks in fluoropolymers with diameters of tens to hundreds of nanometers; chemical etching and ion-track grafting enabled us to develop ion-track and proton-conductive membranes, respectively. In the ion-track membranes of PVDF, strongly-LET-dependent etching was found, so the pore shape as well as the size was exclusively controlled by the track structures. We performed the ion-track grafting of styrene into ETFE to develop nanostructure-controlled proton exchange membranes (PEMs) for applications in PEM fuel cells. Our ion beam technology to develop fluoropolymer-based nanostructures has the potential to apply in the field of filtration processes and fuel cell devices. This would make it possible to provide new microfiltration technology for water treatment, sterilization, petroleum refining and dairy processing.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.77 - 81, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion-track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), a type of fluoropolymer, could find wide applications due to its superior chemical and mechanical properties. In order to produce track-etched pores in PVDF films, we have independently employed much milder etching conditions without any oxidant additives in the alkaline etching solution. The goal of this work is to pursue the possibility of varying beam parameters and applying the effect of the etching pretreatment to control the pore size and shape. Ongoing in-situ/on-line analyses at the M-branch of the UNILAC would shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only ion-induced degradation but also the post-irradiation reactivity.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(2), p.223 - 226, 2012/06
The aim of this study is to investigate the formation of the poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) track membranes in detail by electrolytic conductometry. A PVDF film was irradiated with a 450 MeV  Xe or 2.2 GeV
Xe or 2.2 GeV  Au ion beam, and then the latent tracks were etched in a 9 mol dm
Au ion beam, and then the latent tracks were etched in a 9 mol dm aqueous KOH solution at 80
aqueous KOH solution at 80 C that had been poured into a conductometric cell. At the same time, the evolution of cylindrical nanopores was monitored by measuring the conductance through the membrane. The etching kinetics significantly depended on the deposited energy within each track, which is represented by the LET. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the cell promoted track etching up to the breakthrough probably because the electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
C that had been poured into a conductometric cell. At the same time, the evolution of cylindrical nanopores was monitored by measuring the conductance through the membrane. The etching kinetics significantly depended on the deposited energy within each track, which is represented by the LET. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the cell promoted track etching up to the breakthrough probably because the electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 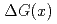 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
ECS Transactions, 35(24), p.1 - 12, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:93.15(Electrochemistry)Our focus has been placed on ion track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), a type of fluoropolymer, because of their superior chemical, mechanical and ferro-electric properties. The aim of this study is to investigate the formation of the PVDF track membranes in more detail by electrolytic conductometry. Interestingly, application of a higher voltage to the conductometry cell as well as irradiation with a higher-LET beam promoted track etching up to breakthrough probably because electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 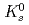 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Sawada, Shinichi; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 78(2), p.146 - 149, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:15.28(Electrochemistry)Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes with conical and cylindrical nanopores were prepared in a controlled manner by the ion-track technique, which involved heavy ion beam irradiation and the subsequent alkaline etching. Etching behavior mainly depended on energy deposition of ion beams, and thus its depth distribution, estimated by theoretical simulation, was successfully applied to control the shapes and diameters of the etched pores. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrolytic conductometry then gave an insight into critical experimental parameters. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the conductometry cell promoted track etching up to breakthrough probably because electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
Kikuchi, Masahiro; Gunawardane, C. R.; Alam, M. K.; Mohd Dzomir, A. Z.; Pitipanaarachchi, R. C.; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Sato, Katsuya; et al.
Radioisotopes, 56(9), p.509 - 517, 2007/09
Since ionizing radiation is used for sterilizing or lowering the microbial content of foods, the development of versatile detection methods of irradiated foods is necessary for appropriate management. In an effort to distinguish between irradiated and non-irradiated food, a method based on the detection of oxidative DNA base damage using the chemiluminescence enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with anti-8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine antibody was developed. It was shown that this chemiluminescence ELISA method could be applied to chicken, beef and pork that were irradiated with over 3 kGy. Twenty milligrams of a loaf of meat was sufficient to distinguish between irradiated and non-irradiated meat by this method.
Nakayama, Takeshi*; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Abe, Mitsushi*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Otsuka, Michio*; Akiyama, Takashi*; Sato, K.*; Kikuchi, Kazuo; Wada, Y.*; Koike, Tsuneyuki; et al.
Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE '99), p.227 - 230, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Sawada, Shinichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*
no journal, ,
We investigated the track-structure-dependent pore formation by scanning electron microscopy and conductometry to control the pore size and shape by direct use of the irradiation effect. PVDF films of 25 and 100  m thicknesses were bombarded with heavy ions in the energy range between a few hundred MeV and GeV, and then etched in a 9 M KOH aqueous solution at 80
m thicknesses were bombarded with heavy ions in the energy range between a few hundred MeV and GeV, and then etched in a 9 M KOH aqueous solution at 80 C. A very low bulk-etch rate was seen because of the mild etching conditions and high chemical stability of pristine PVDF. This finding suggests that the differences in the track structure, mainly depending on the LET, would be the most crucial factor of the resulting pore size. The depth distribution of the LET was applied to control the pore shape, in other words, to prepare nanopores with a conical as well as cylindrical shape. Importantly, direct use of the ion-beam irradiation effect without any concern for etching conditions provided this controllability.
C. A very low bulk-etch rate was seen because of the mild etching conditions and high chemical stability of pristine PVDF. This finding suggests that the differences in the track structure, mainly depending on the LET, would be the most crucial factor of the resulting pore size. The depth distribution of the LET was applied to control the pore shape, in other words, to prepare nanopores with a conical as well as cylindrical shape. Importantly, direct use of the ion-beam irradiation effect without any concern for etching conditions provided this controllability.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The possibility of varying the beam parameters and applying the effect of a pre-etching treatment for poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ion-track membranes was investigated with the goal of achieving enhanced track etching for effective control of the pore size and shape. Commercially available 25  m-thick PVDF films were irradiated at room temperature with swift heavy ions. Irradiation with a higher-LET beam gave faster track etching and larger pores, suggesting that the LET could be the most crucial factor determining the pore size. In-situ infra-red absorption and residual gas analyses shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only the ion-induced degradation, but also post-irradiation reactions. The pre-etching treatment effect involved oxidation of the unsaturated bonds within the latent track, which accelerated the chemical dissolution for efficient pore evolution. In other words, exposure to a gaseous oxidant, i.e., ozone, shortened the breakthrough time.
m-thick PVDF films were irradiated at room temperature with swift heavy ions. Irradiation with a higher-LET beam gave faster track etching and larger pores, suggesting that the LET could be the most crucial factor determining the pore size. In-situ infra-red absorption and residual gas analyses shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only the ion-induced degradation, but also post-irradiation reactions. The pre-etching treatment effect involved oxidation of the unsaturated bonds within the latent track, which accelerated the chemical dissolution for efficient pore evolution. In other words, exposure to a gaseous oxidant, i.e., ozone, shortened the breakthrough time.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
no journal, ,
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes with cylindrical nanopores were prepared in a controlled manner by the ion-track technique, which involved ion-beam irradiation and the subsequent alkaline etching. As is well-known, etching behavior appeared to depend on energy deposition of ion beams, i.e., linear energy transfer (LET) and radial dose distribution in a latent track. Electrolytic conductometry then gave an insight into critical experimental parameters. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the conductometry cell promoted track etching up to breakthrough probably because electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.