Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chiba, Satoshi*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Terashima, Atsunori*; Okumura, Shin*; Yoshida, Tadashi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.13961_1 - 13961_10, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:96.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs:  Se,
Se,  Zr,
Zr,  Tc,
Tc,  Pd,
Pd,  I, and
I, and  Cs) into short-lived or non-radioactive nuclides by fast neutron spectrum reactors without isotope separation has been proposed as a solution to the problem of radioactive wastes disposal. Despite investigation of many methods, such transmutation remains technologically difficult. To establish an effective and efficient transmutation system, we propose a novel neutron moderator material, yttrium deuteride (YD
Cs) into short-lived or non-radioactive nuclides by fast neutron spectrum reactors without isotope separation has been proposed as a solution to the problem of radioactive wastes disposal. Despite investigation of many methods, such transmutation remains technologically difficult. To establish an effective and efficient transmutation system, we propose a novel neutron moderator material, yttrium deuteride (YD ), to soften the neutron spectrum leaking from the reactor core. Neutron energy spectra and effective half-lives of LLFPs, transmutation rates, and support ratios were evaluated with the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP-II/MVP-BURN and the JENDL-4.0 cross section library. With the YD
), to soften the neutron spectrum leaking from the reactor core. Neutron energy spectra and effective half-lives of LLFPs, transmutation rates, and support ratios were evaluated with the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP-II/MVP-BURN and the JENDL-4.0 cross section library. With the YD moderator in the radial blanket and shield regions, effective half-lives drastically decreased from 10
moderator in the radial blanket and shield regions, effective half-lives drastically decreased from 10 to 10
to 10 years and the support ratios reached 1.0 for all six LLFPs. This successful development and implementation of a transmutation system for LLFPs without isotope separation contribute to developing a self-consuming cycle of LLFPs using fast spectrum reactors to reduce radioactive waste.
years and the support ratios reached 1.0 for all six LLFPs. This successful development and implementation of a transmutation system for LLFPs without isotope separation contribute to developing a self-consuming cycle of LLFPs using fast spectrum reactors to reduce radioactive waste.
Kudo, Junichi*; Sakaba, Nariaki; Takahashi, Makoto*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 9(4), p.360 - 367, 2010/12
The HTTR-IS system is one of the plants producing hydrogen with nuclear power. Such a system has high safety requirements. One of the safety studies to be conducted is the probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) study for concerned hydrogen explosion, which was not studied previously. Therefore, this study is conducted for the preliminary PSA of flammable gas leakage in the HTTR-IS system. First, a master logic diagram (MLD) was developed to identify initiating events. After identifying initiating events, event tree analysis (ETA) and fault tree analysis (FTA) were performed to quantify the average frequency of an accident. The initial result of the PSA shows that the nominal frequency of explosion is 2.5 10
10 1/y. This frequency is higher than the criterion defined in this paper and unacceptable. Installments of additional components are investigated in order to reduce frequency. As a result, the average frequency of explosion is decreased to 7.9
1/y. This frequency is higher than the criterion defined in this paper and unacceptable. Installments of additional components are investigated in order to reduce frequency. As a result, the average frequency of explosion is decreased to 7.9 10
10 1/y.
1/y.
Tachi, Yoshiaki; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 103(1), p.268 - 269, 2010/11
It is very attractive technique to transmute long-lived fission products such as iodine-129 included in spent fuel by using Fast Reactors (FRs) to minimize environmental burden and toxic risk due to high level waste disposal. Iodine has low melting point (386K) and low boiling points (457K) compared with FR core temperature. Furthermore, it is corrosive against iron based materials. Then, it is the most important issue to search suitable chemical forms for FR core conditions, having high stability at elevated temperature and good compatibility with cladding material. From the viewpoint of melting point, nuclides generation by neutron irradiation, reactivity with stainless steel, easy fabrication method and recyclability, 5 kinds of iodides of CuI, MgI , YI
, YI , RbI and YI
, RbI and YI were selected as the candidate chemical form of iodine for transmutation in FR. In order to evaluate stability of the candidate iodides at elevated temperature, TG-DTA of CuI, RbI, BaI
were selected as the candidate chemical form of iodine for transmutation in FR. In order to evaluate stability of the candidate iodides at elevated temperature, TG-DTA of CuI, RbI, BaI and YI
and YI were performed. According to TG-DTA results, no significant mass change showed in BaI
were performed. According to TG-DTA results, no significant mass change showed in BaI beyond those temperatures. Mass of CuI, RbI and YI
beyond those temperatures. Mass of CuI, RbI and YI started to be lost severely at the lower temperature than their melting points. Compatibility test between iodides and cladding materials were conducted. Cladding materials in contact with iodides were heated in a capsule filled with pure Ar gas at 873K for 5000h maximum. Results of cross-section observation showed that MgI
started to be lost severely at the lower temperature than their melting points. Compatibility test between iodides and cladding materials were conducted. Cladding materials in contact with iodides were heated in a capsule filled with pure Ar gas at 873K for 5000h maximum. Results of cross-section observation showed that MgI and YI
and YI made pit corrosion on SUS316 and ODS. It appeared that the upper part of the inner surface test capsules with RbI, YI
made pit corrosion on SUS316 and ODS. It appeared that the upper part of the inner surface test capsules with RbI, YI were degraded severely. Based on the experimental results, the most applicable iodide for transmutation by FR is BaI
were degraded severely. Based on the experimental results, the most applicable iodide for transmutation by FR is BaI from the viewpoints of stability at elevated temperature and compatibility with cladding material.
from the viewpoints of stability at elevated temperature and compatibility with cladding material.
 Np Fission Cross Section at YAYOI
Np Fission Cross Section at YAYOIOki, Shigeo; Takashima, Hideki; Wakabayashi, Toshio; Yamaguchi, Kenji*; Yamawaki, Michio*
JNC TY9400 2004-005, 36 Pages, 2004/05
In the framework of the study on transmutation of minor actinide (MA) nuclides with fast reactors, the fission cross section ratio of 237Np relative to 235U has been measured by using a back-to-back (BTB) fission chamber at YAYOI fast neutron source reactor. The compact BTB fission chamber was prepared for the measurements in the experimental holes called Glory hole and Grazing hole passing though the core center and the side blanket of YAYOI, respectively. Dependence of fission cross section ratios on neutron spectrum was investigated by changing the measurement position in these experimental holes.The measured values of fission cross section ratios were compared with those calculated with the following nuclear data libraries: JENDL-3.2, ENDF/B-VI, JEF-2.2, and JENDL-2. It was found that the calculated values in the center of the core systematically overestimated the measurements by about 30%. Dispersion of the calculated values among the nuclear data libraries was smaller than the above difference from the measured value. We also see the dependence of C/E value on the measurement position. It is hardly said that uncertainty of nuclear data brings about the above overestimation of 30%.The present result remained some issues in terms of the measurement accuracy. If we can get rid of those causes, for example, by means of the unfolding technique on pulse height distribution, the result could be utilized as expletive information in nuclear data validation not only for 237Np, but also for 235U and 238U which characterize the neutron spectrum.
 Am,
Am,  Am Fission Cross Sections at YAYOI
Am Fission Cross Sections at YAYOIOkawachi, Yasushi; Oki, Shigeo; Wakabayashi, Toshio; Yamaguchi, Kenji*; Yamawaki, Michio*
JNC TY9400 2004-004, 37 Pages, 2004/05
In the framework of the study on transmutation of minor actinide (MA) nuclides with fast reactors, the fission cross section ratios of MA (241Am, 243Am) relative to 235U have been measured by using a back-to-back (BTB) fission chamber at YAYOI fast neutron source reactor. The compact BTB fission chamber was prepared for the measurements in the main experimental hole (Glory hole) passing though the core of YAYOI. Dependence of fission cross section ratios on neutron spectrum was investigated by changing the measurement position in Glory hole from core center to depleted uranium blanket.The measured values of fission cross section ratios were compared with those calculated with the following nuclear data libraries: JENDL-3.2, ENDF/B-VI, and JEF-2.2. It was found that the calculated values for both 241Am and 243Am in the center of the core systematically underestimated the measurements by 10 to 20%. Dispersion of the calculated values among the nuclear data libraries was smaller than the above difference from the measured value. We also see the dependence of C/E value on the measurement position.The present result remained some issues in terms of the measurement accuracy. If we can get rid of those causes, for example, by means of the unfolding technique on pulse height distribution, the result could be utilized as expletive information in nuclear data validation not only for 241Am and 243Am but also for 235U and 238U which characterize the neutron spectrum.
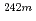 Am from 0.003eV to 10keV using lead slowing-down spectrometer, thermal neutron facility and time-of-flight method
Am from 0.003eV to 10keV using lead slowing-down spectrometer, thermal neutron facility and time-of-flight methodKai, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; Yamamoto, Shuji*; Cho, H.*; Fujita, Yoshiaki*; Kimura, Itsuro*; Okawachi, Yasushi*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 28(8), p.723 - 739, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Mukaiyama, Takehiko; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(6), p.713 - 714, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
R.P.Rulko*; Takano, Hideki; C.Broeders*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; Sasa, Toshinobu; *; D.Lutz*; Mukaiyama, Takehiko; C.Nordborg*
Proc. of Int. Conf. on the Phys. of Nucl. Sci. and Technol., 2, p.1462 - 1469, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Higano, Naomi; Wakabayashi, Toshio
PNC TN9410 96-248, 69 Pages, 1996/11
In spent fuel there are many kinds of long-lived fission products.  Tc and
Tc and  I are contained as fission products in HLW: they have comparatively long half lives and their toxicity remains for more than 1000 years, when the efficacy of the engineered barrier is uncertain. Fortunately, these two nuclides have large capture cross-sections in the thermal-resonance neutron energy region, so they have a good potential to be changed to stable nuclides in such a neutron flux. We tried to reduce the amount of these nuclides using a fast reactor. The neutron spectrum of a FR is too hard for effective transmutation of these nuclides, but the flux of a FR is much higher than in other commercial reactors, and the hard spectrum of a FR can be changed locally into a moderated spectrum by the addition of some moderator materials. We tried to make a good neutron flux for transmutation of these long lived fission products and to get high transmutation rates. In this survey, 60 moderated target subassemblies were modeled on the core periphery of a 600MWe fast reactor. Using a continuous energy Monte-Carlo code (MVP), some parametric surveys have been done, examining the effects on transmutation performances of : moderator fraction ; pin and subassembly arrangements ; moderating materials. The code system allowed us to investigate the effects of self-shielding. For
I are contained as fission products in HLW: they have comparatively long half lives and their toxicity remains for more than 1000 years, when the efficacy of the engineered barrier is uncertain. Fortunately, these two nuclides have large capture cross-sections in the thermal-resonance neutron energy region, so they have a good potential to be changed to stable nuclides in such a neutron flux. We tried to reduce the amount of these nuclides using a fast reactor. The neutron spectrum of a FR is too hard for effective transmutation of these nuclides, but the flux of a FR is much higher than in other commercial reactors, and the hard spectrum of a FR can be changed locally into a moderated spectrum by the addition of some moderator materials. We tried to make a good neutron flux for transmutation of these long lived fission products and to get high transmutation rates. In this survey, 60 moderated target subassemblies were modeled on the core periphery of a 600MWe fast reactor. Using a continuous energy Monte-Carlo code (MVP), some parametric surveys have been done, examining the effects on transmutation performances of : moderator fraction ; pin and subassembly arrangements ; moderating materials. The code system allowed us to investigate the effects of self-shielding. For  Tc, the best transmutation rate is about 10%/y in the case of Duplex pin -the FP region is surrounded by moderator material-. With the best arrangement to maximize the amount transmuted, we can transmute 40kg
Tc, the best transmutation rate is about 10%/y in the case of Duplex pin -the FP region is surrounded by moderator material-. With the best arrangement to maximize the amount transmuted, we can transmute 40kg  Tc in a year. With the present case, the transmutation rate and transmuted amount of
Tc in a year. With the present case, the transmutation rate and transmuted amount of  I are inferior to those of
I are inferior to those of  Tc. In the most effective case, the
Tc. In the most effective case, the  I transmutation rate is 5.2% and the transmuted amount is 18kg in a year. But the produced amount of
I transmutation rate is 5.2% and the transmuted amount is 18kg in a year. But the produced amount of  I from a PWR is small - about 5kg from a 100MWe PWR in a year-, so the transmuted amount of
I from a PWR is small - about 5kg from a 100MWe PWR in a year-, so the transmuted amount of  I is ...
I is ...
Hirano, Masashi; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; *
Genshiryoku Kogyo, 42(10), p.1 - 5, 1996/10
no abstracts in English
Mukaiyama, Takehiko; Kubota, Masumitsu; Ogawa, Toru; Fujine, Sachio; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; Ozawa, Masaki*; *
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 38(7), p.591 - 593, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Wakabayashi, Toshio; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 154(3), p.239 - 250, 1995/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki; Ishikawa, Makoto; Hayashi, Hideyuki; Wakabayashi, Toshio
PNC TN9410 91-365, 368 Pages, 1991/11
A study was performed on TRU transmutation by LMFBRs. This report describes the results of the items shown below. (1) Study on a super long life core loaded with TRU. A feasibility study was performed on a super long life core loaded with TRU fuel which operates without fuel exchange during 30 years. Its advantage is that it can transmute TRU with storing it in the core during plant life time. I It was found that reactivity change and power variation due to burnup can be reduced remarkably by optimizing TRU loading amount and region. Also, it was found that a 1000 MWe core can transmute TRU of 10 ton which comes from 13 LWRs. (2) Study on a heterogeneous core loaded with TRU. The radial hderogeneous core is one of the candidate concepts for TRU transmutation because the internal blanket may be loaded with larger amount of TRU than the core fuel. It was found that the core loaded with large amount of TRU in the internal blanket can transmute TRU several times more than the homogeneous core with no significant in fluence on core characteristics. (3) Study on a method for TRU loading in a subassembly. A TRU loading method was studied where both TRU loaded fuel pins and the MOX fuel pins are arranged in a subassembly aiming at reducing the number of TRU loaded fuel pins. Results are shown with a focus on power distribution in a subassembly.
Kudo, Junichi*; Sakaba, Nariaki; Takahashi, Makoto*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Dai*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; Takahashi, Makoto*; Yokoyama, Tsugio*; Tachi, Yoshiaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Junichi*; Sakaba, Nariaki; Takahashi, Makoto*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Junichi*; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sakaba, Nariaki; Takahashi, Makoto*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing a nuclear hydrogen production system using the high temperature gas cooled reactor to contribute low carbon society. The High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) will be coupled with the hydrogen production plant using the thermochemical IS process, named HTTR-IS plant. The object of this study is to confirm the safety of the HTTR-IS plant using probabilistic safety assessment for toxic material release. The results on the selection of initiating event by using master logic diagram and on the frequency of toxic material release evaluated by the fault tree analysis will be presented.
Tachi, Yoshiaki; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
no journal, ,
For reducing the environmental burden and toxic risk of high-level radioactive wastes, it is one of the effective techniques to transmute iodine-129 by fast reactors. Since iodine has corrosive properties, the chemical form of the iodine-bearing transmutation target material loaded into the FR is one of the important issues. In this study, from the viewpoints of melting point and neutron irradiation properties, the following five iodides were selected as the candidate materials from all binary iodides: CuI, MgI , YI
, YI , RbI and BaI
, RbI and BaI . In order to clarify their applicability as a transmutation target, TG-DTA (Thermogravimetry - Differential Thermal Analysis) of the iodides and compatibility of the iodides with the stainless-steel cladding materials were tested. From the results of them, BaI
. In order to clarify their applicability as a transmutation target, TG-DTA (Thermogravimetry - Differential Thermal Analysis) of the iodides and compatibility of the iodides with the stainless-steel cladding materials were tested. From the results of them, BaI is preferable as a transmutation target material.
is preferable as a transmutation target material.
Tachi, Yoshiaki; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Iida, Takumi*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English