Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuru, Tomohito; Wakeda, Masato*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ogata, Shigenobu*
Journal of Applied Physics, 127(2), p.025101_1 - 025101_9, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.01(Physics, Applied)We explored softening/strengthening behavior in various solute in W matrix by density functional theory (DFT) calculations combined with solid solution model. As a result of DFT calculations for various solute, a clear trend was observed in the interaction energy between a solute and a screw dislocation, which has predominant influence on solid solution behavior. The predictions based on the solid solution model with DFT can reasonably reproduce the complicated softening/strengthening as a function of temperature and solute concentration. We conclude that this specific balance is the origin of macroscopic solid solution softening.
Wakeda, Masato*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Koyama, Masanori*; Ozaki, Taisuke*; Sawada, Hideaki*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ogata, Shigenobu*
Acta Materialia, 131, p.445 - 456, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:79.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Most of the solute species show a significant interaction with the dislocation core, while only several solute species among them, such as Si, P, and Cu, significantly lower the Peierls potential of the screw dislocation motion. A first-principles interaction energy with the "Easy-core" structure excellently correlates with the change in the  -surface caused by solute atoms (i.e., chemical misfit). We show the availability of the interaction energy to predict the effect of each species on macroscopic critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) of the dilute Fe alloy. The CRSS at low and high temperature for various alloys basically agree with experiment CRSS. These results provide a novel understanding of the interaction between a screw dislocation and solute species from the first-principles.
-surface caused by solute atoms (i.e., chemical misfit). We show the availability of the interaction energy to predict the effect of each species on macroscopic critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) of the dilute Fe alloy. The CRSS at low and high temperature for various alloys basically agree with experiment CRSS. These results provide a novel understanding of the interaction between a screw dislocation and solute species from the first-principles.
Ogata, Shigenobu*; Shimizu, Futoshi; Li, J.*; Wakeda, Masato*; Shibutani, Yoji*
Intermetallics, 14(8-9), p.1033 - 1037, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:118 Percentile:97.06(Chemistry, Physical)Shear deformations of Cu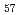 Zr
Zr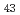 bulk metallic glass (BMG) model systems are performed using molecular dynamics simulation. The results suggest that both the hydrostatic stress and the stress normal to the shear plane should affect the shear response. We see shear localization and shear band nucleation in both a small system of 2,000 atoms, and large systems of 524,288 atoms, and analyze local atomic structure evolution.
bulk metallic glass (BMG) model systems are performed using molecular dynamics simulation. The results suggest that both the hydrostatic stress and the stress normal to the shear plane should affect the shear response. We see shear localization and shear band nucleation in both a small system of 2,000 atoms, and large systems of 524,288 atoms, and analyze local atomic structure evolution.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Daryl, C.*
no journal, ,
Tungsten (W) is a potential candidate for plasma-facing materials in fusion reactors due to its high melting point and high thermal conductivity. Neutron irradiation transmutes W into other 5d metals such as rhenium (Re) and osmium (Os). We have so far carried out first-principles and kinetic Monte Carlo calculations to investigate the formation of radiation defects such as voids and radiation-induced precipitates in W alloys. In the present study, we investigate in detail the effects of Re and other 5d solutes on the interaction energy with a screw dislocation and the energy barrier for the dislocation motion through DFT calculations. Finally, solution hardening/softening behavior is reproduced by combining the DFT results with a theoretical model.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Daryl, C.*
no journal, ,
Tungsten (W) is a potential candidate for plasma-facing materials in fusion reactors due to its high melting point and high thermal conductivity. Neutron irradiation transmutes W into other 5d metals such as rhenium (Re) and osmium (Os). We have so far carried out first-principles and kinetic Monte Carlo calculations to investigate the formation of radiation defects such as voids and radiation-induced precipitates in W alloys. In the present study, we investigate in detail the effects of Re and other 5d solutes on the interaction energy with a screw dislocation and the energy barrier for the dislocation motion through DFT calculations. Finally, solution hardening/softening behavior is reproduced by combining the DFT results with a theoretical model.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*
no journal, ,
We investigated the effect of alloying elements on mechanical properties in dilute BCC alloys via first-principles calculations. Although the approach for dilute alloys is not applicable to high entropy alloys (HEA), we constructed five-element HEA model using SQS and investigate dislocation core.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Chrzan, D.*
no journal, ,
Solutes in bcc and hcp metals induce more unique effects on softening and dramatic change in plastic deformation. In the present study, the sequence of first-principles calculations of dislocation models for various crystallographic structures were implemented. For bcc metals, solid-solution model was established based on the thermally-activated process of kink pair nucleation and kink migration related to Orowan's relation. For hcp metals, while the Burgers vector of the primary slip system in hcp metals is generally 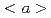 dislocation, the slip plane differs depending on the material types, which mainly belongs to basal and prismatic plane according to the its stacking fault energy. Solute atoms have a large variety of the influence on dislocation motion resulting in dramatic change in plastic deformation.
dislocation, the slip plane differs depending on the material types, which mainly belongs to basal and prismatic plane according to the its stacking fault energy. Solute atoms have a large variety of the influence on dislocation motion resulting in dramatic change in plastic deformation.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Chrzan, D.*
no journal, ,
Unlike fcc metals, where dislocation motion associated with solutes is reproduced by the effect of solute on the stacking fault energy and conventional hardening law, solutes in bcc and hcp metals induce more unique effects such as softening and dramatic change in plastic deformation. Recently, modeling of dislocations based on first-principles calculations was developed, and the modeling for various crystallographic structure were systemized. Especially for BCC metals, solid-solution model was established based on the thermally-activated process of double-kink nucleation and kink migration related to Orowan's relation. While the Burgers vector of the primary slip system in HCP metals is generally 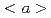 dislocation, the slip plane differs depending on the material, which mainly belongs to basal and prismatic plane according to the its stacking fault energy. Solute atoms have a large variety of the influence on dislocation motion resulting in dramatic change in plastic deformation.
dislocation, the slip plane differs depending on the material, which mainly belongs to basal and prismatic plane according to the its stacking fault energy. Solute atoms have a large variety of the influence on dislocation motion resulting in dramatic change in plastic deformation.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Wakeda, Masato*; Ogata, Shigenobu*
no journal, ,
Effect of transmutation products such as Re and Os is one of the central issues on change in mechanical properties under neutron irradiation in fusion reactors. Especially, Re solutes in W affect not only hardening via radiation-induced precipitation but also significant softening effect. We explored softening/strengthening behavior in various solutes in W matrix by density functional theory (DFT) calculations combined with a solid solution model. In addition, we proposed a method for the dynamics motion of a screw dislocation based on kink nucleation and kink migration, in which Hamiltonian of a dislocation is described by line tension model. As a result of DFT calculations for various solutes, a clear trend was observed in the interaction energy between a solute and a screw dislocation, which has predominant influence on solid solution behavior.