Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Thwe Thwe, A.; Kadowaki, Satoshi; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.731 - 742, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we performed numerical calculations of unsteady reaction flow considering detailed chemical reactions, investigated the unstable behavior of hydrogen-air dilute premixed flame due to intrinsic instability, and clarified the effects of unburned gas temperature and pressure. I made it. The unstable behavior of the flame in a wide space was simulated, and the burning rate of the cellular flame was obtained. Then, the effects of heat loss and flame scale on flame unstable behavior were investigated. The burning velocity of a planar flame increases as the unburned-gas temperature increases and it decreases as the unburned-gas pressure and heat loss increase. The normalized burning velocity increases when the pressure increases and heat loss becomes large, and it decreases when the temperature increases. This is because the high unburned-gas pressure and heat loss promote the unstable behavior and instability of flame.
Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Thwe Thwe, A.; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Visualization, 25(5), p.1075 - 1083, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.12(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Lean combustion and inert-gas addition are useful to control the burning velocity of hydrogen premixed flames, and it is well known that the cellular structure forms on the front of lean hydrogen flames owing to intrinsic instability. However, the influences of inert-gas addition on the instability phenomena of lean hydrogen premixed flames are not understood fully, and then it is needed to be investigated the flame instability experimentally. In the experiments, the cellular structure and fluctuation of H /O
/O /inert gases (Ar, N
/inert gases (Ar, N ,CO
,CO ) premixed flames on a flat burner were obtained using direct observation, laser diagnostics and light emission intensity to elucidate the characteristics of instability phenomena. As the results, the correlation of inert-gas addition, equivalence ratio and total flow rate with the characteristics of cellular flames was revealed, and the influences of these parameters on flame instability were discussed.
) premixed flames on a flat burner were obtained using direct observation, laser diagnostics and light emission intensity to elucidate the characteristics of instability phenomena. As the results, the correlation of inert-gas addition, equivalence ratio and total flow rate with the characteristics of cellular flames was revealed, and the influences of these parameters on flame instability were discussed.
Thwe Thwe, A.; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.573 - 579, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The simulations of the combustion of self-propagating hydrogen-air premixed flame are performed by an open-source CFD code. The flame propagation behavior, flame radius, temperature and pressure are analyzed by varying the initial laminar flame speed and grid size. When the initial laminar speed increases, the thermal expansion effects become strong which leads the increase of flame radius along with the increase of flame surface area, flame temperature and pressure. A new laminar flame speed model derived previously from the results of experiment is also introduced to the code and the obtained flame radii are compared with those from the experiments. The formation of cellular flame fronts is captured by simulation and the cell separation on the flame surface vividly appears when the gird resolution becomes sufficiently higher. The propagation behavior of cellular flame front and the flame radius obtained from the simulations have the reasonable agreement with the previous experiments.
Furuyama, Taisei*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Kobayashi, Hideaki*; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 87(898), p.21-00107_1 - 21-00107_12, 2021/06
The effects of steam addition on the unstable behavior of hydrogen-air lean premixed flames under adiabatic and non-adiabatic conditions were investigated by numerical calculations. Adopting a detailed chemical reaction mechanism of hydrogen-oxyfuel combustion modeled by 17 reversible reactions of 8 active species and diluents, a two-dimensional unsteady reaction flow was treated based on the compressible Navier-Stokes equation. As the steam addition and heat loss increased, the burning velocity of a planar flame decreased and the normalized burning velocity increased. The addition of water vapor promotes the unstable behavior of the hydrogen-air lean premixed flame. This is because the thermal diffusivity of the gas decreases and the diffusion-thermal instability increases. The effect of adding water vapor on the instability of hydrogen premixed flames is a new finding, and it is expected to connect with hydrogen explosion-prevention measures as in NPP.
Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Yamawaki, Hiroshi*; Goto, Yoshito*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(5), p.3065 - 3073, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.31(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)X-ray and neutron diffraction analyses of ammonia borane were conducted at ambient and high pressures. The H-H distance in dihydrogen bonds was shorter than twice the van der Waals radius (2.4  ). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4
). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4  again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of
again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of 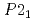 (Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65
(Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65  . The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
. The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
Kadowaki, Satoshi; Thwe Thwe, A.; Furuyama, Taisei*; Kawata, Kazumasa*; Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Kobayashi, Hideaki*
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.20-00491_1 - 20-00491_12, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.03(Thermodynamics)Effects of pressure and heat loss on the unstable motion of cellular-flame fronts in hydrogen-air lean premixed flames were numerically investigated. The reaction mechanism for hydrogen-oxygen combustion was modeled with seventeen reversible reactions of eight reactive species and a diluent. Two-dimensional unsteady reactive flow was treated, and the compressibility, viscosity, heat conduction, molecular diffusion and heat loss were taken into account. As the pressure became higher, the maximum growth rate increased and the unstable range widened. These were due mainly to the decrease of flame thickness. The burning velocity of a cellular flame normalized by that of a planar flame increased as the pressure became higher and the heat loss became larger. This indicated that the pressure and heat loss affected strongly the unstable motion of cellular-flame fronts. In addition, the fractal dimension became larger, which denoted that the flame shape became more complicated.
Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Yasuhito*; Nakagawa, Ryo*; Yazawa, Shinya*; Kumada, Masashi*; Sato, Daisuke*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Chaumeix, N.*; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.21-00044_1 - 21-00044_13, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.40(Thermodynamics)The effects of addition of CO and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO
and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co
addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co or H
or H O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
Kadowaki, Satoshi; Nogami, Masato*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Katsumi, Toshiyuki*; Yamazaki, Wataru*; Kobayashi, Hideaki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 85(879), p.19-00274_1 - 19-00274_13, 2019/11
We dealt with three-dimensional cellular premixed flames generated by hydrodynamic and diffusive-thermal instabilities to elucidate the effects of unburned-gas temperature and heat loss by adopting the three-dimensional compressible Navier-Stokes equation. As the unburned-gas temperature became lower and the heat loss became larger, the growth rate decreased and the unstable range narrowed. With a decrease of unburned-gas temperature, the normalized growth rate increased and the normalized unstable range widened, which was because the temperature ratio of burned and unburned gases became larger. The obtained hexagonal cellular fronts were qualitatively consistent with the experimental results. As the heat loss became larger, the burning velocity of a cellular flame normalized by that of a planar flame increased. This was because diffusive-thermal effects became stronger owing to the increase of apparent Zeldovich number caused by the decrease of flame temperature.
Thwe Thwe, A.; Kadowaki, Satoshi; Hino, Ryutaro
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 13(2), p.18-00457_1 - 18-00457_12, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Two dimensional unsteady calculations of reactive flows were performed in large domain to investigate the unstable behaviors of cellular premixed flames at low Lewis numbers based on the diffusive-thermal (D-T) model and compressible Navier-Stokes (N-S) equations. The growth rates obtained by the compressible N-S equations were large and the unstable ranges were wide compared with those obtained by the D-T model equations. When the length of computational domain increased, the number of small cells separated from large cells of the cellular flame increased drastically. The stronger unstable behaviors and the larger average burning velocities were observed especially in the numerical results based on the compressible N-S equations. In addition, the fractal dimension obtained by the compressible N-S equations was larger than that by the D-T model equations. Moreover, we confirmed that the radiative heat loss promoted the instability of premixed flames at low Lewis numbers.
Soejima, Goro; Iwai, Hiroki; Kadowaki, Haruhiko; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Tsuzuki, Satoshi*; Yasunaga, Kazushi*; Nakata, Yoshinori*; Kume, Kyo*
Heisei-28-Nendo Koeki Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta kenkyu Nempo, 19, P. 9, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Yokoyama, Akihito; Usui, Aya; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.302 - 304, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.703 - 705, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.706 - 708, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology (HIAT 2015) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2015/09
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology (HIAT 2015) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(7), p.073311_1 - 073311_8, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:50.34(Instruments & Instrumentation)The single-pulse formation technique using a beam chopping system consisting of two types of high-voltage beam kickers was modified to improve the quality and intensity of the single-pulse beam with pulse intervals over 1  s at TIARA cyclotron facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Reduction of the multi-turn extraction number for suppressing the neighboring beam bunch contamination was achieved by restriction of a beam phase width and precise optimization of a particle acceleration phase. In addition, the single-pulse beam intensity was increased by a factor of two or more by a combination of two types of beam bunchers using sinusoidal and saw-tooth voltage waveforms. As a result, a contamination rate of neighboring beam bunches in the single-pulse beam was reduced to less than 0.1 %. Long-term purification of the single pulse beam was guaranteed by the well-controlled magnetic field stabilization system for the TIARA cyclotron magnet. Provision of the high quality intense single-pulse beam contributes to improve the accuracy of experiments for investigation of scintillation light time-profile and for neutron energy measurement by a time-of-flight method.
s at TIARA cyclotron facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Reduction of the multi-turn extraction number for suppressing the neighboring beam bunch contamination was achieved by restriction of a beam phase width and precise optimization of a particle acceleration phase. In addition, the single-pulse beam intensity was increased by a factor of two or more by a combination of two types of beam bunchers using sinusoidal and saw-tooth voltage waveforms. As a result, a contamination rate of neighboring beam bunches in the single-pulse beam was reduced to less than 0.1 %. Long-term purification of the single pulse beam was guaranteed by the well-controlled magnetic field stabilization system for the TIARA cyclotron magnet. Provision of the high quality intense single-pulse beam contributes to improve the accuracy of experiments for investigation of scintillation light time-profile and for neutron energy measurement by a time-of-flight method.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Matsumoto, Masaaki*; Sugiyama, Hitoshi*; Kamiji, Yu; Kadowaki, Satoshi*; Hino, Ryutaro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
In the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (NPS) accident, hydrogen was generated by oxidation reaction of the cladding and water etc, then leaked into the NPS building, and finally led to occurrence of hydrogen explosion in the building. This resulted in serious damage to the environment. To improve the safety performance of the NPS, especially on the hydrogen safety under severe accident conditions, a simulation code system has been developed to analyze hydrogen behaviors including diffusion, combustion, explosion and structural integrity evaluation. This developing system consists of CFD and FEM tools in order to support various hydrogen user groups of students, researchers and engineers. Preliminary calculated results obtained with above mentioned tools, damage of piping induced by hydrogen combustion, agreed well with existing test data.
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.372 - 378, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1186 - 1188, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1179 - 1181, 2014/10
no abstracts in English