Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs in a river-sea system boundary area after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
Cs in a river-sea system boundary area after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident高田 兵衛*; 脇山 義史*; 和田 敏裕*; 平尾 茂一*; 青野 辰雄*; 中西 貴宏; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 青山 道夫*
Marine Chemistry, 262, p.104384_1 - 104384_6, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:39.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The radiocesium ( Cs) distribution between dissolved and particulate phases was examined in river water and coastal seawater as a function of the
Cs) distribution between dissolved and particulate phases was examined in river water and coastal seawater as a function of the  Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles. Dissolved
Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles. Dissolved  Cs activity concentrations in the Tomioka River (salinity
Cs activity concentrations in the Tomioka River (salinity  0.1) and in coastal seawater at Tomioka fishery port (salinity
0.1) and in coastal seawater at Tomioka fishery port (salinity  30), Fukushima Prefecture, from June 2019 to October 2021 were 3.6-20 Bq/m
30), Fukushima Prefecture, from June 2019 to October 2021 were 3.6-20 Bq/m (geometric mean 11 Bq/m
(geometric mean 11 Bq/m ) and 2.4-86 Bq/m
) and 2.4-86 Bq/m (13 Bq/m
(13 Bq/m ), respectively. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river (0.2-44 mg/L; geometric mean 2 mg/L) than in seawater (0.8-24 mg/L; 6.4 mg/L), the mean
), respectively. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river (0.2-44 mg/L; geometric mean 2 mg/L) than in seawater (0.8-24 mg/L; 6.4 mg/L), the mean  Cs activity on suspended particles was 11,000 Bq/kg-dry in the river versus 3,200 Bq/kg-dry in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of
Cs activity on suspended particles was 11,000 Bq/kg-dry in the river versus 3,200 Bq/kg-dry in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of  Cs on suspended particles were determined by sequential extraction. The ion-exchangeable fraction accounted for 0.3-2.0% (mean 1.2%) and 0.4-1.3% (0.8%) at the river and port sites, respectively. The organically bound fraction accounted for 0.3-4.8% (1.8%) and 0.1-5.5% (2.1%) at the river and port sites, respectively. In both areas, the refractory fraction accounted for
Cs on suspended particles were determined by sequential extraction. The ion-exchangeable fraction accounted for 0.3-2.0% (mean 1.2%) and 0.4-1.3% (0.8%) at the river and port sites, respectively. The organically bound fraction accounted for 0.3-4.8% (1.8%) and 0.1-5.5% (2.1%) at the river and port sites, respectively. In both areas, the refractory fraction accounted for  90% of
90% of  Cs. Unexpectedly, the ion-exchangeable fraction did not differ between the river and port sites, and the percentage at the river site did not vary during the sampling period. Therefore, the ion-exchangeable fraction in the river's lower reach was originally low or had decreased before the particles arrived there. The small labile
Cs. Unexpectedly, the ion-exchangeable fraction did not differ between the river and port sites, and the percentage at the river site did not vary during the sampling period. Therefore, the ion-exchangeable fraction in the river's lower reach was originally low or had decreased before the particles arrived there. The small labile  Cs fraction on suspended particles indicates that the mobility of radiocesium to marine biota in this coastal region is low.
Cs fraction on suspended particles indicates that the mobility of radiocesium to marine biota in this coastal region is low.
 Cs washoff from bare land in Fukushima
Cs washoff from bare land in Fukushima五十嵐 康記*; 恩田 裕一*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也; 加藤 弘亮*; 小塚 翔平*; 馬目 凌*
Science of the Total Environment, 769, p.144706_1 - 144706_9, 2021/05
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:16.79(Environmental Sciences)The impact of freeze-thaw processes and subsequent runoff affecting the Cs-137 ( Cs) flux and concentration in sediment discharge were revealed in bareland erosion plot following the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident by detailed monitoring and laser scanner measurement on the soil surface. We found that surface topographic changes due to the frost-heaving during the winter- spring period, and rill formation during the summer. We also found the evident seasonal changes in
Cs) flux and concentration in sediment discharge were revealed in bareland erosion plot following the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident by detailed monitoring and laser scanner measurement on the soil surface. We found that surface topographic changes due to the frost-heaving during the winter- spring period, and rill formation during the summer. We also found the evident seasonal changes in  Cs concentration; high during the early spring and gradually decreased thereafter, then surface runoff from the plot frequently occurred during spring and autumn when rainfall was high and reached a maximum in summer.
Cs concentration; high during the early spring and gradually decreased thereafter, then surface runoff from the plot frequently occurred during spring and autumn when rainfall was high and reached a maximum in summer.
恩田 裕一*; 谷口 圭輔*; 吉村 和也; 加藤 弘亮*; 高橋 純子*; 脇山 義史*; Coppin, F.*; Smith, H.*
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (Internet), 1(12), p.644 - 660, 2020/12
被引用回数:142 パーセンタイル:90.10(Environmental Sciences)This review, concerning on findings obtained by detailed field monitoring after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, covers the initial fallout and vertical movement of radionuclide in the land and forest, and subsequent transport and redistribution through hydrological and geomorphological processes in cropland, urban area, paddy field, and forested area. We discuss the finding of the transport of radionuclides through rivers and new discoveries for hydrological and sediment transport environmental impact in monsoonal regions.
恩田 裕一*; 谷口 圭輔*; 吉村 和也; 加藤 弘亮*; 高橋 純子*; 脇山 義史*; Coppin, F.*; Smith, H.*
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (Internet), 1(12), P. 694_1, 2020/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The values along the mass depth axes in Figure 4a and 4b were slightly misaligned, and the relaxation mass depth markers shown in Figure 4b and 4c incorrectly located.
 Cs, and their time dependence
Cs, and their time dependence脇山 義史*; 恩田 裕一*; 吉村 和也; 五十嵐 康記*; 加藤 弘亮*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105990_1 - 105990_12, 2019/12
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:60.05(Environmental Sciences)This study provides the results of observations of plot-scale  Cs wash-off from various land uses (two uncultivated farmlands, two cultivated farmlands, three grasslands and one forest) from 2011 to 2014. Annual
Cs wash-off from various land uses (two uncultivated farmlands, two cultivated farmlands, three grasslands and one forest) from 2011 to 2014. Annual  Cs wash-off rate ranged from 0.0026 to 7.5% per year, and more vegetation cover resulted in lower sediment discharge.
Cs wash-off rate ranged from 0.0026 to 7.5% per year, and more vegetation cover resulted in lower sediment discharge.  Cs concentration observed in uncultivated farmland plot decreased with time and the rate was lower than those of riverine, suggesting that contributions of
Cs concentration observed in uncultivated farmland plot decreased with time and the rate was lower than those of riverine, suggesting that contributions of  Cs from the upslope area may be insignificant to that in riverine. A negative relationship between
Cs from the upslope area may be insignificant to that in riverine. A negative relationship between  Cs concentration normalized by initial deposition amount and sediment concentration in runoff water was found. Cultivation appeared to cause enhanced soil erosion and resulted in constant relatively low
Cs concentration normalized by initial deposition amount and sediment concentration in runoff water was found. Cultivation appeared to cause enhanced soil erosion and resulted in constant relatively low  Cs concentration. A contribution of coarse organic matter to
Cs concentration. A contribution of coarse organic matter to  Cs wash-off was suggested in the forest, which had relatively high
Cs wash-off was suggested in the forest, which had relatively high  Cs concentration and low sediment discharge.
Cs concentration and low sediment discharge.
Yang, B.*; 恩田 裕一*; 大森 良弘*; 関本 均*; 藤原 徹*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也; 高橋 純子*; Sun, X.*
Science of the Total Environment, 603-604, p.49 - 56, 2017/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:6.05(Environmental Sciences)In this study, the effect of topsoil removal measure and fertilizer application on radiocesium uptake by rice plants was investigated over a four-year period. The results indicate that the effect of topsoil removal measure on the accumulation of radiocesium in rice plants was effective. We summarized four year's data to further confirm that potassium and nitrogen fertilizers had an opposite effect on the accumulation of radiocesium in rice plants. Increasing potassium and reducing nitrogen fertilizer conditions tended to inhibit the radiocesium uptake by rice plants.
Yang, B.*; 恩田 裕一*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也; 関本 均*; Ha, Y.*
Environmental Pollution, 208(Part B), p.562 - 570, 2016/01
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:45.67(Environmental Sciences)In this study, we investigated the temporal changes of radiocesium in soil, irrigation water, and rice plant in two adjacent rice paddies, with and without surface-soil-removal practice, in Fukushima Prefecture for over three years (2012 to 2014). Our results showed that radiocesium migrated into 24-28 cm soil layers and that the concentration and inventory of radiocesium in paddy soils generally decreased. The newly added radiocesium to paddies through irrigation water contributed only the maximum values of 0.15% and 0.75% of the total amount present in normal and decontaminated paddies, respectively, throughout the study period. The change trend of radiocesium concentration in suspended sediment in irrigation water exponentially decreased. Radiocesium accumulation in rice plant also decreased with time in both paddies. However, the transfer factor of radiocesium for rice plant in the decontaminated paddy increased compared with normal paddy.
Konoplev, A.*; Golosov, V.*; Laptev, G.*; 難波 謙二*; 恩田 裕一*; 高瀬 つぎ子*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 151(Part 3), p.568 - 578, 2016/01
被引用回数:87 パーセンタイル:91.41(Environmental Sciences)Comparative analysis is provided for radiocesium wash-off parameters and Kd between suspended matter and water in rivers and surface runoff on Fukushima and Chernobyl contaminated areas for the first years after the accidents. It was found that radiocesium distribution coefficient in Fukushima rivers is essentially higher than those in Chernobyl. This can be associated with two factors: a higher RIP of samples in Fukushima and the presence of water insoluble glassy particles. It was found also that dissolved wash-off coefficients for Fukushima catchments are lower than those in Chernobyl. Particulate wash-off coefficients are comparable for Fukushima and Chernobyl. The radiocesium migration in undisturbed forest and grassland soils at Fukushima has been shown to be faster than those in Chernobyl. Investigation and analysis of radiocesium distribution in soils of Niida river catchment revealed accumulation of contaminated sediments on its floodplain.
脇山 義史*; 馬目 凌*; 恩田 裕一*; 吉村 和也
no journal, ,
This study presents a three years' Cs-137 wash-off observation and morphological surveys on a soil erosion in area affected by the accident of Fukushima nuclear power plant to describe detailed processes of Cs-137 wash-off. Cs-137 concentration varied enormously and it appeared to decrease gradually from spring to autumn and increased again after winter. Based on the photos and scan data of soil surface, the expansions of a rill from spring to summer and elevations of soil surface from winter to spring were found. Our analysis suggests that freezing and thawing cycles resulted in high Cs-137 concentration of sediments during winter, whereas expansion of rill makes decrease in Cs-137 concentration in warm seasons.
吉村 和也; 脇山 義史*; 恩田 裕一*; 高瀬 つぎ子*
no journal, ,
This study presents Cs-137 wash-off observations on various land uses including decontaminated lands in Fukushima. We established rectangle soil erosion plots on six landscape; uncultivated farmland (UFL), cultivated farmland (CFL), grassland (GL), forest (F), uncultivated and cultivated farmlands on a decontaminated land (D-UFL and D-CFL). The D-UFL and DCFL were established after the decontamination of erosion plots. Mean Cs-137 concentrations on decontaminated lands decreased down to approx. 10 to 40 % of values observed before decontamination. No significant difference in amount of eroded sediment was found between contaminated and decontaminated lands, suggesting that decontamination works decrease total Cs-137 wash-off.
Zheleznyak, M.*; Pylypenko, O.*; Kivva, S.*; 佐久間 一幸; 五十嵐 康記*; 脇山 義史*; Konoplev, A.*; 難波 謙二*
no journal, ,
物理モデルベースの水、土砂輸送を考慮した流域モデルを開発し、福島県内の試験プロットで懸濁態 Cs流出について試計算を実施した。また、GISベースで経験的な流出率を用いる流域モデルを開発した。開発したモデルを用いて福島県阿武隈川で
Cs流出について試計算を実施した。また、GISベースで経験的な流出率を用いる流域モデルを開発した。開発したモデルを用いて福島県阿武隈川で Csについて試計算を実施し、ウクライナのPripyat川とDnieper川を対象に、放射性核種輸送について妥当性を検証した。
Csについて試計算を実施し、ウクライナのPripyat川とDnieper川を対象に、放射性核種輸送について妥当性を検証した。
脇山 義史*; 恩田 裕一*; 吉村 和也; 加藤 弘亮*
no journal, ,
This study presents two-year observation of soil erosion and radiocesium wash-off to quantify differences in radiocesium behavior in various land uses. High erodibilities and relatively low values of radiocesium wash-off in cultivated farmlands can be attributed to the mixing of surface soil by ploughing. It was found that the total solid wash-off coefficient of radiocesium from farmlands is high and for 2 years period of time after the accident reaches 10%. Generally high precipitation in the region and steep slopes promote higher wash-off of radiocesium as compared to the Chernobyl case. Also, normalized wash-off coefficients exhibited relatively less volatility than erodibilities in thelandscapes. These results suggest that soil erosion management is crucial for mitigating risks of radiocesium.
脇山 義史*; 馬目 凌*; 恩田 裕一*; 吉村 和也
no journal, ,
本研究では、斜面スケールでの土砂移動に伴う放射性セシウムの移動プロセスを明らかにすることを目的として、福島原発により放射性セシウムが沈着した地点に土壌侵食プロットを設置して土砂およびCs-137流出量の観測を行うとともにレーザープロファイラによる地表面の地形変化を追跡し、土砂移動に伴うCs-137流出の時間変化および季節性について考察を行った。本研究結果は、放射性セシウムの移行には季節性があることを示しており、将来予測の精度向上のためには斜面スケールにおけるCs-137移動プロセスについての複数年の観測が有用であることが示唆された。
Chaboche, P.-A.*; 脇山 義史*; 高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; Evrard, O.*; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 舟木 泰智
no journal, ,
The Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident trigged by the Great East Japan Earthquake and subsequent tsunami in March 2011 released large quantities of radionuclides in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although radiocaesium activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high levels of  Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coast of the Prefecture. Accordingly, identifying the sources of sediment is required to elucidate the links between terrestrial and marine radiocaesium dynamics and to anticipate the fate of these persistent radionuclides in the environment.
Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coast of the Prefecture. Accordingly, identifying the sources of sediment is required to elucidate the links between terrestrial and marine radiocaesium dynamics and to anticipate the fate of these persistent radionuclides in the environment.
 Cs in a river-sea system boundary area
Cs in a river-sea system boundary area高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; 脇山 義史*; 平尾 茂一*; 佐藤 俊*; 青野 辰雄*; 中西 貴宏; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦
no journal, ,
The  Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles was studied in river and coastal seawater, Fukushima Prefecture from June 2019 to October 2021. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river than in seawater, the
Cs sorption behavior on suspended particles was studied in river and coastal seawater, Fukushima Prefecture from June 2019 to October 2021. Although the suspended particle concentration was lower in the river than in seawater, the  Cs activity on suspended particles in the river lager than that in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of
Cs activity on suspended particles in the river lager than that in seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of  Cs on suspended particles were also determined by conducting sequential extraction method. The ion-exchangeable fraction was less than 1% at both areas. The organically bound fraction was a few %, resulting in that the refractory fraction accounted for
Cs on suspended particles were also determined by conducting sequential extraction method. The ion-exchangeable fraction was less than 1% at both areas. The organically bound fraction was a few %, resulting in that the refractory fraction accounted for  90%. Thus, it is indicated that the mobility of
90%. Thus, it is indicated that the mobility of  Cs to marine biota is low in the studied areas.
Cs to marine biota is low in the studied areas.
 Cs in a river-sea system boundary
Cs in a river-sea system boundary高田 兵衛*; 脇山 義史*; 和田 敏裕*; 平尾 茂一*; 青野 辰雄*; 中西 貴宏; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦*; 青山 道夫*
no journal, ,
The aim of this study was to measure the sorption behavior of  Cs in suspended particles in Tomioka River and its coastal seawater near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and then, by comparing the sorbed fractions between river water and seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of
Cs in suspended particles in Tomioka River and its coastal seawater near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and then, by comparing the sorbed fractions between river water and seawater. Proportions of ion-exchangeable, organically bound, and refractory fractions of  Cs on suspended particles were determined by sequential extraction. The ion-exchangeable fraction accounted for less than 2% at those two sites. The organically bound fraction accounted for only a few %, suggesting that in both areas, the refractory fraction accounted for
Cs on suspended particles were determined by sequential extraction. The ion-exchangeable fraction accounted for less than 2% at those two sites. The organically bound fraction accounted for only a few %, suggesting that in both areas, the refractory fraction accounted for  90% of
90% of  Cs.
Cs.
恩田 裕一*; 谷口 圭輔*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也; Smith, H.*; Blake, W.*; 岩上 翔*; 加藤 弘亮*
no journal, ,
An intensive field monitoring campaign has been started, immediately after the Fukushima NPP accident including detailed monitoring site in upstream (Yamakiya site), and 30 monitoring sites in downstream river sites. In this presentation, I will present the summary of four years environmental transfer studies after the Fukushima NPP accident. The detailed monitoring of activity concentration of radiocesium and their flux, which can be applicable for the fate and flux of the radionuclide transfer in humid temperate environment. We also found that land use controls most of the transport and then fate of Cs-137 in terrestrial environment.
 Cs wash-off from bareland in Fukushima
Cs wash-off from bareland in Fukushima五十嵐 康記*; 恩田 裕一*; 脇山 義史*; 吉村 和也; 加藤 弘亮*; 小塚 翔平*; 馬目 凌*
no journal, ,
The impact of freeze-thaw processes and subsequent runoff affecting the  Cs flux and concentration in sediment discharge were revealed in bareland erosion plot following the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident by detailed monitoring and laser scanner measurement on the soil surface. We found that surface topographic changes due to the frost-heaving during the winter-spring period, and rill formation during the summer. We also found the evident seasonal changes in
Cs flux and concentration in sediment discharge were revealed in bareland erosion plot following the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident by detailed monitoring and laser scanner measurement on the soil surface. We found that surface topographic changes due to the frost-heaving during the winter-spring period, and rill formation during the summer. We also found the evident seasonal changes in  Cs concentration; high during the early spring and gradually decreased thereafter, then surface runoff from the plot frequently occurred during spring and autumn when rainfall was high and reached a maximum in summer. From these results, the higher
Cs concentration; high during the early spring and gradually decreased thereafter, then surface runoff from the plot frequently occurred during spring and autumn when rainfall was high and reached a maximum in summer. From these results, the higher  Cs concentration in spring was caused by a mixture of unstable surface sediment following freeze- thaw processes and then transported in the early spring, but erosion amount is not significant because of the less rainfall event. The sediment with a lower
Cs concentration in spring was caused by a mixture of unstable surface sediment following freeze- thaw processes and then transported in the early spring, but erosion amount is not significant because of the less rainfall event. The sediment with a lower  Cs concentration, which was supplied from the rill erosion and its expansion, was wash-offed during the summer, contributing most of the flux from erosion in bareland in Fukushima region.
Cs concentration, which was supplied from the rill erosion and its expansion, was wash-offed during the summer, contributing most of the flux from erosion in bareland in Fukushima region.
恩田 裕一*; 谷口 圭輔*; 吉村 和也; 脇山 義史*
no journal, ,
The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident released the largest quantity of radiocaesium into the terrestrial environment since the Chernobyl nuclear accident. The surrounding land received 2.7 PBq of radiocaesium to forests, agricultural lands, grasslands, and urban areas, from which the radionuclides migrated through soil and waterways. In this presentation, the deposition and distribution of radionuclides, especially radiocaesium, in the terrestrial environment as a result of the FDNPP accident are discussed based on the past 10 years' intensive dataset. Anthropogenic activities such as rice and vegetable cultivation and residential activities in the upstream area have led to a rapid decline in the activity concertation of  Cs of suspended sediment (SS) transport in the river network, and these declines directly control the dissolved
Cs of suspended sediment (SS) transport in the river network, and these declines directly control the dissolved  Cs concentration in the river water. We outline the environmental and anthropogenic factors that in uenced the subsequent transport and impacts of radionuclides through the environment. The environmental aftermath of the accident at Fukushima is compared to Chernobyl, and the relatively rapid remediation of the Fukushima region relative to the region surrounding Chernobyl will be explained.
Cs concentration in the river water. We outline the environmental and anthropogenic factors that in uenced the subsequent transport and impacts of radionuclides through the environment. The environmental aftermath of the accident at Fukushima is compared to Chernobyl, and the relatively rapid remediation of the Fukushima region relative to the region surrounding Chernobyl will be explained.
Chaboche, P.-A.*; 脇山 義史*; 高田 兵衛*; 和田 敏裕*; Evrard, O.*; 御園生 敏治; 尻引 武彦; 舟木 泰智
no journal, ,
Following the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in March 2011, large quantities of radionuclides in general, and radiocaesium (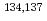 Cs) in particular, were emitted in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although
Cs) in particular, were emitted in terrestrial and marine environments of Fukushima Prefecture. Although  Cs activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high level of
Cs activity in these environments has decreased since the accident, the secondary inputs via the rivers draining and eroding the main terrestrial radioactive plume were shown to sustain high level of  Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coasts of the Prefecture. Accordingly, quantifying the riverine sources of sediment deposited along the coast and characterizing its spatial and depth distribution, as well as its physico-chemical properties, is of the utmost importance to ensure the safety of fishery products and anticipate the environmental fate of radiocaesium. To conduct this project, coastal sediment cores (n=6) from 26 to 60cm depth were collected during cruise campaigns between July and September 2022 at the Ota, Niida and Ukedo river mouths. In this presentation, we report preliminary results regarding the spatial and depth distribution of radiocaesium activities in these sediment cores. Finally, we will discuss the main challenges identified so far to design and implement a sediment tracing method along the coast of the Fukushima Prefecture.
Cs in riverine and coastal sediments, which are likely deposited off the coasts of the Prefecture. Accordingly, quantifying the riverine sources of sediment deposited along the coast and characterizing its spatial and depth distribution, as well as its physico-chemical properties, is of the utmost importance to ensure the safety of fishery products and anticipate the environmental fate of radiocaesium. To conduct this project, coastal sediment cores (n=6) from 26 to 60cm depth were collected during cruise campaigns between July and September 2022 at the Ota, Niida and Ukedo river mouths. In this presentation, we report preliminary results regarding the spatial and depth distribution of radiocaesium activities in these sediment cores. Finally, we will discuss the main challenges identified so far to design and implement a sediment tracing method along the coast of the Fukushima Prefecture.