Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Che, G.*; Tang, X.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Fei, Y.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(39), p.14467 - 14472, 2025/09
Mechanochemical radical polymerization has unique advantages in the synthesis of polymer due to its reduced solvent consumption and adaptability of insoluble monomers. However, it suffers from the uncontrollable degradation of the formed polymers during reaction and new synthetic strategy with precise controllability needs to be developed. Here, by employing high static pressure up to 30 GPa, we found 1,3,5-trifluorobenzene undergoes radical polymerization by breaking the conjugated  -bonds, and forms a carbon nanothread with high selectivity (Polymer-I polymorph). Based on the crystal structure at the threshold pressure and the calculated energy barriers for the bonding pathway, we concluded that the benzene-rings react via a 1-2 radical polymerization pathway. Our work highlights high pressure is a robust method to initiate the solid-state radical polymerization, even for very stable aromatics, and offers fresh insights for the synthesis of polymeric carbon-based materials with high selectivity.
-bonds, and forms a carbon nanothread with high selectivity (Polymer-I polymorph). Based on the crystal structure at the threshold pressure and the calculated energy barriers for the bonding pathway, we concluded that the benzene-rings react via a 1-2 radical polymerization pathway. Our work highlights high pressure is a robust method to initiate the solid-state radical polymerization, even for very stable aromatics, and offers fresh insights for the synthesis of polymeric carbon-based materials with high selectivity.
Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Wang, J.*; Li, L.*; Jia, Y.*; Li, W.*; Xue, J.*; Fan, X.*; Song, R.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.7713_1 - 7713_8, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00Caloric effects usually occur in the vicinity of solid-state phase transitions with a limited refrigeration temperature span. Here, we introduce and realize an unprecedented concept -all temperature barocaloric effect, i.e., a remarkable barocaloric effect in KPF across an exceptionally wide temperature span, from 77.5 to 300 K and potentially down to 4 K, covering typical room temperature, liquid nitrogen, liquid hydrogen, and liquid helium refrigeration regions. The directly measured barocaloric adiabatic temperature change reaches 12 K at room temperature and 2.5 K at 77.5 K upon the release of a 250 MPa pressure. This effect is attributed to a persistent phase transition to a rhombohedral high pressure phases. We depict the thermodynamic energy landscape to account for the structural instability. This unique all-temperature barocaloric effect presents a novel approach to highly applicable solid-state refrigeration technology, transcending the conventional multi-stage scenario.
across an exceptionally wide temperature span, from 77.5 to 300 K and potentially down to 4 K, covering typical room temperature, liquid nitrogen, liquid hydrogen, and liquid helium refrigeration regions. The directly measured barocaloric adiabatic temperature change reaches 12 K at room temperature and 2.5 K at 77.5 K upon the release of a 250 MPa pressure. This effect is attributed to a persistent phase transition to a rhombohedral high pressure phases. We depict the thermodynamic energy landscape to account for the structural instability. This unique all-temperature barocaloric effect presents a novel approach to highly applicable solid-state refrigeration technology, transcending the conventional multi-stage scenario.
 ders band-assisted high uniform ductility in ultrastrong ferrous medium-entropy alloy via hierarchical microstructure
ders band-assisted high uniform ductility in ultrastrong ferrous medium-entropy alloy via hierarchical microstructureKwon, H.*; Lee, J. H.*; Zargaran, A.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, J.*; Gu, G. H.*; Lee, B.-J.*; Bae, J. W.*; Kim, H. S.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 190, p.104378_1 - 104378_18, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 16(10), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:69.06(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.96(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:82.57(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.51(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H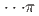 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H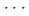 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:91.80(Multidisciplinary Sciences) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 6 of others*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:61.30(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:70.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zr +
Zr +  at 27 MeV/nucleon
at 27 MeV/nucleonHwang, J.*; Chillery, T.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 49 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.093D03_1 - 093D03_12, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear transmutation emerges as a promising approach for reprocessing high-level waste, specifically treating long-lived nuclides like  Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on
Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on  Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes,
Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes, 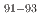 Nb,
Nb, 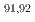 Zr, and
Zr, and 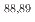 Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for
Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for  Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:97.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:91.92(Physics, Applied)Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H.; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)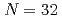
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:71.61(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hwang, Y.*; Puebla, J.*; Kondo, Kota*; Gonzalez-Ballestero, C.*; Isshiki, Hironari*; S nchez Mu
nchez Mu oz, C.*; Liao, L.*; Chen, F.*; Luo, W.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; et al.
oz, C.*; Liao, L.*; Chen, F.*; Luo, W.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 132(5), p.056704_1 - 056704_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:97.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:85.61(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:83.20(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zr + d reaction cross sections measured at 28 MeV/nucleon
Zr + d reaction cross sections measured at 28 MeV/nucleonChillery, T.*; Hwang, J.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 49 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2023(12), p.121D01_1 - 121D01_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:59.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The deuteron is a loosely bound system which can easily break up into its constituent proton and neutron whilst in the presence of Coulomb and nuclear fields. Previous experimental studies have shown that this breakup process has a significant impact on residual nucleus production from deuteron bombardment in the high energy range of 50 - 210 MeV/nucleon. However, there remains a lack of cross-section data at energies below 50 MeV/nucleon. The current study determined  Zr + d reaction cross sections under inverse kinematics at approximately 28 MeV/nucleon using the BigRIPS separator, OEDO beamline, and SHARAQ spectrometer. Cross sections from this research were compared with previous measurements and theoretical calculations. The experimental results show a large enhancement of the production cross sections of residual nuclei, especially those produced from a small number of particle emissions, compared to the proton-induced reaction data at similar bombarding energy. The DEURACS calculation, which quantitatively takes deuteron-breakup effects into account, reproduces the data well. As a long-lived fission product,
Zr + d reaction cross sections under inverse kinematics at approximately 28 MeV/nucleon using the BigRIPS separator, OEDO beamline, and SHARAQ spectrometer. Cross sections from this research were compared with previous measurements and theoretical calculations. The experimental results show a large enhancement of the production cross sections of residual nuclei, especially those produced from a small number of particle emissions, compared to the proton-induced reaction data at similar bombarding energy. The DEURACS calculation, which quantitatively takes deuteron-breakup effects into account, reproduces the data well. As a long-lived fission product,  Zr remains a challenge for nuclear waste disposal and treatment. This study's low-energy data may assist future consideration of nuclear-waste treatment facilities, where
Zr remains a challenge for nuclear waste disposal and treatment. This study's low-energy data may assist future consideration of nuclear-waste treatment facilities, where  Zr + d may feasibly transmute the waste into short-lived/stable nuclei.
Zr + d may feasibly transmute the waste into short-lived/stable nuclei.