Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Futagawa, Kazuo; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-078, 164 Pages, 2023/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2021 to March 2022. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakada, Akira; Nakano, Masanao; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Futagawa, Kazuo; Yamada, Ryohei; Uchiyama, Rei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-062, 163 Pages, 2022/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2020 to March 2021. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042002_1 - 042002_7, 2021/10
For the application in the measurement of the high dose rate hot spots inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) buildings, we propose a novel one-dimensional radiation distribution sensing method using an optical fiber sensor based on wavelength spectrum unfolding. The proposed method estimates the incident position of radiation to the fiber by the unfolding of the wavelength spectrum output from the fiber edge using the fact that the attenuation length of light along the fiber depends on the wavelength. Because this method measures the integrated light intensity, this method can avoid the problem of counting loss and signal pile-up, which occurs in the radiation detector with pulse counting mode under high dose rate field. Through basic experiments using the ultraviolet light source and  Sr/
Sr/ Y radioactive point source, basic properties of source position detection were confirmed.
Y radioactive point source, basic properties of source position detection were confirmed.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Matsubara, Natsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-069, 163 Pages, 2021/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2019 to March 2020. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Wakaida, Ikuo
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Arai, Takehiko*; Arai, Tomoko*; Hirata, Naru*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Honda, Chikatoshi*; Imae, Naoya*; et al.
Space Science Reviews, 208(1-4), p.317 - 337, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:71.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer is installed on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to observe the target C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu at near infrared wavelengths of 1.8 to 3.2 micrometer. It aims to obtain reflectance spectra in order to detect absorption bands of hydrated and hydroxide minerals in the 3 micrometer-band. We adopted a linear-image sensor with indium arsenide (InAs) photo diodes and a cooling system with a passive radiator to achieve an optics temperature of 188 K, which enables to retaining sufficient sensitivity and noise level in the 3 micrometer wavelength region. We conducted ground performance tests for the NIRS3 flight model (FM) to confirm its baseline specifications. The results imply that the properties such as the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conform to scientific requirements to determine the degree of aqueous alteration, such as CM or CI chondrite, and the stage of thermal metamorphism on the asteroid surface.
Sano, Mutsumi*; Takahashi, Sunao*; Watanabe, Atsuo*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.2, p.609 - 614, 2017/00
Dislocation densities of GlidCop with compressive strain applied at high temperature were examined by X-ray line profile analyses with synchrotron radiation. In order to evaluate the dislocation density, we applied the modified Williamson-Hall and modified Warren-Averbach method. The dislocation densities of GlidCop with compressive strain from 0.011-0.04 were in the range of 5.7-8.0 10
10 m
m .
.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Sato, Yoshiharu; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Ishibashi, Satoshi*; Watanabe, Masahisa; Torii, Tatsuo
JAEA-Research 2016-011, 52 Pages, 2016/09
In the Tokyo Electric Power Co.,Inc. the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station, management of the contaminated water becomes the social problem, and the situation that severe correspondence is necessary continues to prevent an outflow to the ocean. Plastic scintillation fiber (PSF) can apply as technique to direct measure the concentration of radioactive material in the water at a tank and drainage. In this paper, the results of fundamental test was summarized to apply for monitoring of leakage to the tank and monitoring of drainage in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Kojima, Atsushi; Umeda, Naotaka; Hanada, Masaya; Yoshida, Masafumi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Akino, Noboru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063006_1 - 063006_9, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:89.45(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Significant progresses in the extension of pulse durations of powerful negative ion beams have been made to realize the neutral beam injectors for JT-60SA and ITER. In order to overcome common issues of the long pulse production/acceleration of negative ion beams in JT-60SA and ITER, the new technologies have been developed in the JT-60SA ion source and the MeV accelerator in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. As for the long pulse production of high-current negative ions for JT-60SA ion source, the pulse durations have been successfully increased from 30 s at 13 A on JT-60U to 100 s at 15 A by modifying the JT-60SA ion source, which satisfies the required pulse duration of 100 s and 70% of the rated beam current for JT-60SA. This progress was based on the R&D efforts for the temperature control of the plasma grid and uniform negative ion productions with the modified tent-shaped filter field configuration. Moreover, the each parameter of the required beam energy, current and pulse has been achieved individually by these R&D efforts. The developed techniques are useful to design the ITER ion source because the sustainment of the cesium coverage in large extraction area is one of the common issues between JT-60SA and ITER. As for the long pulse acceleration of high power density beams in the MeV accelerator for ITER, the pulse duration of MeV-class negative ion beams has been extended by more than 2 orders of magnitude by modifying the extraction grid with a high cooling capability and a high-transmission of negative ions. A long pulse acceleration of 60 s has been achieved at 70 MW/m (683 keV, 100 A/m
(683 keV, 100 A/m ) which has reached to the power density of JT-60SA level of 65 MW/m
) which has reached to the power density of JT-60SA level of 65 MW/m .
.
 Si
Si
Tonegawa, Sho*; Kasahara, Shigeru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Sugimoto, Kunihisa*; Yasuda, Nobuhiro*; Tsuruhara, Yugo*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Mizukami, Yuta*; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.4188_1 - 4188_7, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:89.07(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sano, Mutsumi*; Takahashi, Sunao*; Watanabe, Atsuo*; Shiro, Ayumi; Shobu, Takahisa
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.255 - 259, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sonoda, Tetsu*; Wada, Michiharu*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sakamoto, Chika*; Takatsuka, Takaaki*; Furukawa, Takeshi*; Iimura, Hideki; Ito, Yuta*; Kubo, Toshiyuki*; Matsuo, Yukari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 295, p.1 - 10, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 -rays in
-rays in 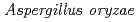
Toyoshima, Yoshiyuki*; Takahashi, Akemi*; Tanaka, Hisaki*; Watanabe, Jun*; Mogi, Yoshinobu*; Yamazaki, Tatsuo*; Hamada, Ryoko*; Iwashita, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 740(1-2), p.43 - 49, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:49.23(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)

 flows in helical plasmas
flows in helical plasmasWatanabe, Tomohiko*; Nunami, Masanori*; Sugama, Hideo*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Maeyama, Shinya; Tanaka, Kenji*
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Torii, Tatsuo; Sugita, Takeshi; Kamogawa, Masashi*; Watanabe, Yasuyuki*; Kusunoki, Kenichi*
Geophysical Research Letters, 38(24), p.L24801_1 - L24801_5, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:83.61(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We identify a migrating source of high energy radiation, lasting for several minutes, attributed to thunderstorm activities through the observations of radiation, atmospheric electric field, and meteorological radar echoes at several points. Our findings indicate that the energetic radiation is emitted continuously from a downward hemispherical surface without lightning, the bottom of which is about 300 m above sea level, and this source of radiation moves from north to south above the observation site at a speed of about 7 m/s. The radiation source probably moves along with the negatively charged region of the cloud at the height of around 1 km, because the estimated migration of the radiation source is consistent with the observed movement of atmospheric electric field variation between ground-based observation sites and with the wind speed and direction at about 1 km altitude. This movement implies that the intensive electric field produced by the charged region in the thundercloud generates a radiation source. In addition, our results suggest that the low altitude of radiation source is related to no lightning activity during the energetic radiation emission.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Tanaka, Yutaka; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.835 - 838, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutral beam (NB) injectors for JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA) have been designed and developed. Twelve positive-ion-based and one negative-ion-based NB injectors are allocated to inject 30 MW D beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D
beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of
beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of  1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.536 - 544, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:84.66(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English