Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics) He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Nemoto, Takahiro; Arakawa, Ryoki; Kawakami, Satoru; Nagasumi, Satoru; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Furusawa, Takayuki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-005, 33 Pages, 2023/05
During shut down of the HTTR (High Temperature engineering Test Reactor) RS-14 cycle, an increasing trend of filter differential pressure for the helium gas circulator was observed. In order to investigate this phenomenon, the blower of the primary helium purification system was disassembled and inspected. As a result, it is clear that the silicon oil mist entered into the primary coolant due to the deterioration of the charcoal filter performance. The replacement and further investigation of the filter are planning to prevent the reoccurrence of the same phenomenon in the future.
Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.603 - 613, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology) , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.52(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
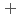 U
U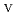
 Fe
Fe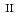
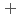 U
U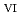 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
 , Zr, and stainless-steel
, Zr, and stainless-steelKirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 567, p.153842_1 - 153842_15, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the chemical structure and stability of nuclear fuel debris consisting of UO , Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO
, Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO -SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600
-SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600 C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O
C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O ) atmospheres.
) atmospheres.  Np and
Np and  Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M
Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO
ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO  -SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U
-SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U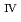 O
O (s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO
(s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO -SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
-SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
 O
O solution
solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.961 - 971, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)We investigated potential degradation of fuel debris caused by H O
O , which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H
, which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H O
O solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H
solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H O
O . Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H
. Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H O
O reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO
reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO improves the stability of fuel debris against H
improves the stability of fuel debris against H O
O reaction.
reaction.
 O
O -induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debris
-induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debrisKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (113), p.61 - 64, 2022/04
The severe accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station resulted in generation of fuel debris. The fuel debris is in contact with water and the radiolysis of water can accelerate degradation of the debris. The analysis of particles sampled from inside or near the damaged reactors indicates the complicated compositions of the fuel debris. It is challenging to estimate the effect of water radiolysis on such a complicated material. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the potential degradation process by leaching experiments of simulated fuel debris in aqueous H O
O solution. The results show that the reaction of H
solution. The results show that the reaction of H O
O induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H
induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H O
O . These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
. These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Sekita, Kenji; Watanabe, Shuji; Furusawa, Takayuki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 388, p.111642_1 - 111642_11, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency adapted High-Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to meet the new regulatory requirements that began in December 2013. The safety and seismic classifications of the existing structures, systems, and components were discussed to reflect insights regarding High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) that were acquired through various HTTR safety tests. Structures, systems, and components that are subject to protection have been defined, and countermeasures to manage internal and external hazards that affect safety functions have been strengthened. Additionally, measures are in place to control accidents that may cause large amounts of radioactive material to be released, as a beyond design based accident. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission rigorously and appropriately reviewed this approach for compliance with the new regulatory requirements. After nine amendments, the application to modify the HTTR's installation license that was submitted in November 2014 was approved in June 2020. This response shows that facilities can reasonably be designed to meet the enhanced regulatory requirements, if they reflect the characteristics of HTGRs. We believe that we have established a reference for future development of HTGR.
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takeda, Shino*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*
The Chemistry of Thorium, Plutonium and MA, 254 Pages, 2022/03
The chemistry of nuclear materials such as Thorium (Part 1) and Plutonium (Part 2) was described in relation from the fundamentals on solid chemistry and solution chemistry to the practicals on the experiment and evaluation method in detail. Minor actinides such as Neptunium, Americium, Curium and Protoactinium, was introduced the basics on the solid and solution chemistry.
 and SrLaCuNbO
and SrLaCuNbO ; Spin-
; Spin- quasi-square-lattice
quasi-square-lattice 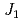 -
-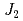 Heisenberg antiferromagnets
Heisenberg antiferromagnetsWatanabe, Masari*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Ueno, Wataru*; Matsui, Kazuki*; Goto, Takayuki*; Hagihara, Masato
Physical Review B, 105(5), p.054414_1 - 054414_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:59.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Watanabe, Masashi; Seki, Takayuki*
Materials Science & Engineering B, 272, p.115369_1 - 115369_6, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of oxygen non-stoichiometry on the initial sintering behavior of CeO was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
 O
O ; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compound
; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compoundKusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Yomogida, Takumi; Takano, Masahide; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(6), p.629 - 634, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takeda, Shino*
Uran No Kagaku (II); Hoho To Jissen, 143 Pages, 2021/03
This book describes necessary facts when readers would have an opportunity to treat Uranium for experiments. In the content, the method section shows experimental facilities and equipment including method, and the practical section mentions solution and solid state experiments using Uranium and/or radioisotopes.
Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uchita, Masato*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Eto, Masao*; Suzuno, Tetsuji*; Matoba, Ichiyo*; Endo, Junji*; Watanabe, Osamu*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00489_1 - 19-00489_16, 2020/06
The authors are developing the design concept of pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) that addresses Japan's specific siting conditions such as earthquakes and meets safety design criteria (SDC) and safety design guidelines (SDGs) for Generation IV SFRs. The development of this concept will broaden not only options for reactor types in Japan but also the range and depth of international cooperation. A design concept of 1,500 MWt (650 MWe) class pool-type SFR was thought up by applying design technology obtained from the design of advanced loop-type SFR, named JSFR, equipped with safety measures that reflect results from the feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems and fast reactor cycle technology development, improved maintainability and repairability, and lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants accident.