Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Ogi, Hiromichi*; Osugi, Takeshi; Taniguchi, Takumi; Sato, Junya; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Kajinami, Akihiko*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 585, p.154610_1 - 154610_6, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Watanabe, Masao; Kihara, Takumi*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.1_1 - 1_10, 2023/03
A pulsed magnet system has been developed as a new user-friendly sample environment equipment at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. It comprises a vacuum chamber, a 4 K closed-cycle refrigerator for samples, and a nitrogen bath made of a stainless-steel tube with a miniature solenoidal coil. The coil is cooled by liquid nitrogen supplied by an automatic liquid nitrogen supply system, and the sample is cooled by a refrigerator. This combination facilitates the automatic high magnetic field diffraction measurement for the user's operation. A relatively large scattering angle is up to 42 degrees, which is significantly wider than the previous setup. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on a multiferroic TbMnO and the field dependence of the diffraction peaks was clearly observed. The new pulsed magnet system was established for a practical high magnetic field diffraction for the user program.
and the field dependence of the diffraction peaks was clearly observed. The new pulsed magnet system was established for a practical high magnetic field diffraction for the user program.
Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) O
O ; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compound
; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compoundKusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Yomogida, Takumi; Takano, Masahide; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(6), p.629 - 634, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Masao; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kihara, Takumi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Sahara, Takuro*; Soda, Minoru*; Takahashi, Ryuta
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 25, p.011024_1 - 011024_5, 2019/03
Recently, neutron scattering experiments have been rapidly progressed under high magnetic field. In the J-PARC, proto-type compact pulse magnet system with the power supply, the coil and the sample stick has been developed. Basic specifications of the power supply are as follows; maximum charged voltage with capacitor is 2 kV, maximum current is 8 kA, repetition rate is a pulse per several minutes and pulse duration is several msec. Maximum magnetic field in the coil is more than 30 Tesla. The sample stick is designed for Orange-Cryostat. In this presentation, We report the details of the pulsed magnet system and the performance of it on neutron scattering experiments at MLF beam line (HRC).
Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Gulden, W.*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2028 - 2032, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:70.2(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident, a social need for assuring safety of fusion energy has grown gradually in the Japanese (JA) fusion research community. DEMO safety research has been launched as a part of BA DEMO Design Activities (BA-DDA). This paper reports progress in the fusion DEMO safety research conducted under BA-DDA. Safety requirements and evaluation guidelines have been, first of all, established based on those established in the Japanese ITER site invitation activities. The amounts of radioactive source terms and energies that can mobilize such source terms have been assessed for a reference DEMO, in which the blanket technology is based on the Japanese fusion technology R&D programme. Reference event sequences expected in DEMO have been analyzed based on the master logic diagram and functional FMEA techniques. Accident initiators of particular importance in DEMO have been selected based on the event sequence analysis.
Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Gulden, W.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9, p.1405139_1 - 1405139_11, 2014/10
Key aspects of the safety study of a water-cooled fusion DEMO reactor is reported. Safety requirements, dose target, DEMO plant model and confinement strategy of the safety study are briefly introduced. The internal hazard of a water-cooled DEMO, i.e. radioactive inventories, stored energies that can mobilize these inventories and accident initiators and scenarios, are evaluated. It is pointed out that the enthalpy in the first wall/blanket cooling loops, the decay heat and the energy potentially released by the Be-steam chemical reaction are of special concern for the water-cooled DEMO. An ex-vessel loss-of-coolant of the first wall/blanket cooling loop is also quantitatively analyzed. The integrity of the building against the ex-VV LOCA is discussed.
Nagao, Seiya*; Niibori, Yuichi*; Tanaka, Tadao; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Saito, Takumi*; Kirishima, Akira*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Hama, Katsuhiro; Iwatsuki, Teruki; et al.
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 20(1), p.3 - 14, 2013/06
This paper shows a current status of groundwater colloids studies on the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes in Japan, and summaries realistic approach of the colloids studies at a substantial research network for Japanese universities and institutes.
Yanagi, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Takumi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Iikubo, Satoshi*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Kamiya, Toshio*; Hirano, Masahiro*; Hosono, Hideo*
Journal of Applied Physics, 105(9), p.093916_1 - 093916_8, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:83.35(Physics, Applied)Electronic and magnetic properties of a layered compound LaMnPO are examined in relation to a newly discovered iso-structural superconductor LaFeAs(P)O. Neutron diffraction measurements, together with temperature dependent magnetic susceptibility, clarify that LaMnPO is an antiferromagnet at least up to 375 K. The spin moment of a Mn ion is determined to be 2.26 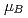 at room temperature, and the spin configuration is antiparallel in the Mn-P plane and parallel to between the Mn-P planes, which is rather different from that of LaFeAsO. Optical absorption spectra, photoemission spectra, and temperature dependent electrical conductivity indicate that LaMnPO is a semiconductor. Furthermore, nominally undoped LaMnPO exhibits
at room temperature, and the spin configuration is antiparallel in the Mn-P plane and parallel to between the Mn-P planes, which is rather different from that of LaFeAsO. Optical absorption spectra, photoemission spectra, and temperature dependent electrical conductivity indicate that LaMnPO is a semiconductor. Furthermore, nominally undoped LaMnPO exhibits  -type conduction while the conduction type is changed by doping of Cu or Ca to the La sites, indicating that LaMnPO is a bipolar conductor. Density functional calculation using the GGA+U approximation supports the above conclusions; the electronic band structure has an open band gap and the antiferromagnetic spin configuration is more stable than the ferromagnetic one.
-type conduction while the conduction type is changed by doping of Cu or Ca to the La sites, indicating that LaMnPO is a bipolar conductor. Density functional calculation using the GGA+U approximation supports the above conclusions; the electronic band structure has an open band gap and the antiferromagnetic spin configuration is more stable than the ferromagnetic one.
Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Hanada, Masaya; Akino, Noboru; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Yamamoto, Takumi*
JAEA-Technology 2008-091, 23 Pages, 2009/03
A plasma generator whose inner dimensions are 25 cm in width, 59 cm in length, and 31 cm in depth for a high power and long pulse ion source in neutral beam injector has been designed and fabricated. The plasma generator has a beam extraction area of 12 cm in width and 46 cm in length. A target of the output beam using the plasma generator is to produce deuterium positive ion beams up to 120 keV, 65 A for longer than 200 s pulses. Arrangement of the permanent magnets and filaments has been designed by using an electron trajectory simulation code to produce uniform and high density plasma with high proton yield. Cooling channels have been also designed to operate the long pulse plasma generation with a 100 kW arc discharge power.
Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nemoto, Takumi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Yagi, Masahiro; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Watanabe, Shukichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-028, 115 Pages, 2006/03
JRR-4, a light-water-moderated and cooled, swimming pool type research reactor using high-enriched uranium plate-type fuels had been operated from 1965 to 1996. In order to convert to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels, modification work had been carried out for 2 years, from 1996 to 1998. After the modification, start-up experiments were carried out to obtain characteristics of the low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel core. The measured excess reactivity, reactor shutdown margin and the maximum reactivity addition rate satisfied the nuclear limitation of the safety report for licensing. It was confirmed that conversion to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels was carried out properly. Besides, the necessary data for reactor operation were obtained, such as nuclear, thermal hydraulic and reactor control characteristics. This report describes the results of start-up experiments and burnup experiments. The first criticality of low-enriched-uranium-silicied core was achieved on 14th July 1998, and the operation for joint-use has been carried out since 6th October 1998.
Umeda, Naotaka; Yamamoto, Takumi; Hanada, Masaya; Grisham, L. R.*; Kawai, Mikito; Oga, Tokumichi; Akino, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.385 - 390, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)In negative ion based neutral beam injector (N-NBI) for JT-60U, some modifications for extent pulse duration from 10 second, which is design value, to 30 second was conducted. Main limit to prevent pulse extension was heat loads onto grounded grid in an ion source and onto beam limiter placed at 22 m from the ion source. To reduce these heat loads, beam extraction area was optimized and the limiter was changed to one which had about twice thermal capacity. As a result of these modifications, the temperature rise of the water which was cooling grounded grid could be suppressed under 40 degree, which can operate in steady state condition. The temperature rise of the limiter could be restricted to 60%. Untill now the beam pulse extended to 17 second of 1.6MW power at 366keV energy, and injection of 30 seconds will be achieved in next experiment.
Inoue, Takashi; Hanada, Masaya; Iga, Takashi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Kawai, Mikito; Morishita, Takatoshi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 66-68, p.597 - 602, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The neutral beam (NB) injection has been one of the most promising methods for plasma heating and current drive in tokamak fusion devices. JAERI has developed high energy electrostatic accelerators for the NB systems in JT-60U and ITER. Recent progress on this R&D are as follows: 1) In the JT-60U NB system, some of the beams has been deflected due to distorted electric field in the accelerator, resulting in an excess heat load on the NB port. By correcting the electric field, a continuous injection of H beam was succeeded for 10 s with the NB power of 2.6 MW at 355 keV. 2) To increase the beam energy, a metal structure called stress ring was designed. The ring reduces electric field concentration at the triple junction point (interface between metal and dielectric insulator inside vacuum). Initial test of the accelerators with the stress rings has shown higher voltage hold off performance in both accelerators for JT-60U and ITER R&D than that without rings.
beam was succeeded for 10 s with the NB power of 2.6 MW at 355 keV. 2) To increase the beam energy, a metal structure called stress ring was designed. The ring reduces electric field concentration at the triple junction point (interface between metal and dielectric insulator inside vacuum). Initial test of the accelerators with the stress rings has shown higher voltage hold off performance in both accelerators for JT-60U and ITER R&D than that without rings.
Kawai, Mikito; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Grisham, L. R.*; Hanada, Masaya; Honda, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi*; Kuriyama, Masaaki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 44(2), p.508 - 512, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)The negative ion source for negative ion based neutral beam injector(N-NBI) of JT-60U aims at generating a negative ion beam with 500 keV and 22A for 10s. The N-NBI system was completed in 1996, followed by starting the efforts to increase beam power and energy. (1)Spatial non-uniformity of the source plasma causes position-dependent divergence of a beamlet due to mis-matching of local beam perveance. A part of the divergent energetic beams is intercepted by the grids and resultantly produce the excessive heat load of the grids and/or induce the high voltage breakdown. So several techniques to take measures against and to correct the non-uniformity in these sources were implemented. (2)Correction of beamlet deflection by adjusting the electric field at the extraction grids. It improved the beam divergence and then decreased an excessive heat load of a beam limiter by more than 50 %. As a result, the maximum injection power 6.2MW and beam pulse duration 10 seconds were obtaind.
Kaneko, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Takumi; Akiba, Masato; Hanada, Masaya; Ikeda, Katsunori*; Inoue, Takashi; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Oka, Yoshihide*; Osakabe, Masaki*; Takeiri, Yasuhiko*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 44(2), p.503 - 507, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)High energy negative-ion-based neutral beam injection (N-NBI) is expected as an efficient and reliable tool of heating and current driving for reactor plasmas such as ITER. A world wide activity on developing technology of negative ion production and beam formation started in 1980's and the great progress has been achieved up to now. In particular, Japan has two large projects that planned adopting N-NBI for real plasma experiments; the JT-60U tokamak and the LHD heliotron, which further motivated the R&D activity. These R&D programs were carried out at JAERI and NIFS separately in Japan, and both were successfully done. The first beam injection experiment was made on the JT-60U in 1996, followed by the LHD in 1998. They were the first experiments on heating plasma by high energy beam in tokamaks and in stellerators, and the obtained results were very promising.
Umeda, Naotaka; Grisham, L. R.*; Yamamoto, Takumi; Kuriyama, Masaaki; Kawai, Mikito; Oga, Tokumichi; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Akino, Noboru; Yamazaki, Haruyuki*; Usui, Katsutomi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.522 - 526, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:74.23(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The Negative-ion based Neutral Beam Injection System (N-NBI) for JT-60U has been operating for plasma heating and non-inductive current drive since 1996. The target is inject of neutral beam into plasma with beam energy 500 keV, injection power 10 MW, for 10 seconds. Until now pulse duration time was restricted up to 5.3 seconds because of larger heat load of port limiter. Recently from the measurement of beam profile at 3.5m downstream from the ion source, it was found that the outermost beamlets in each segment were deflected outward. It was caused by non-uniform electric field by grooves. By improving this, outermost beamlet deflection angle was decreased from 14 mrad to 4 mrad. In this result, 10 seconds injection, which is target parameter, has achieved at 355 keV, 2.6MW, while pulse length was restricted up to 5.3 seconds by larger heat load of port limiter.
Kuriyama, Masaaki; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Grisham, L. R.*; Honda, Atsushi; Ito, Takao; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Ohara, Yoshihiro; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.410 - 423, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:93.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Amemiya, Toru*; Hanada, Masaya; Iga, Takashi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Kuriyama, Masaaki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Okumura, Yoshikazu; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 73(2), p.1090 - 1092, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:65.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Takumi; Konishi, Satoshi; Ohira, Shigeru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Inoue, Masahiko*; Watanabe, Tetsuo*; Hirata, Kazuhiro*; Naruse, Yuji; Okuno, Kenji; Barnes, J. W.*; et al.
JAERI-M 93-094, 54 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English