Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the impact of nuclear data updates from JENDL-4.0 (J4) to JENDL-5 (J5) on the light-water reactor fuel burnup calculations. Burnup calculations were conducted with J4 and J5 for PWR pin-cell and BWR fuel assembly geometries. The calculation results revealed significant burnup-dependent differences in the neutron multiplication factor (k ). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k
). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of
values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H
Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H O notably impacted the k
O notably impacted the k differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k
differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the
differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the  U,
U,  Gd, and
Gd, and  Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H
Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k
O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Aizawa, Naoto*; Chiba, Go*; Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2025) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2025/04
Currently, a major burnup calculation method for the nuclide composition of nuclear fuel conducts neutron transport calculations at each burnup step to account for changes in the neutron spectrum. While this method is highly accurate, the large computational cost of neutron transport calculations can be problematic. Therefore, a fast burnup calculation method based on neutron spectrum reconstruction with the proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) and regression model is investigated. In this method, dimensionality reduction by POD is applied to many neutron fluxes obtained from detailed burnup calculations for various input parameter sets, and regression models are constructed to connect the dimensionality-reduced neutron fluxes and parameters. By substituting arbitrary input parameters to the regression models, the neutron flux is reconstructed and the burnup calculation is performed. This method performs burnup calculations that consider changes in the neutron spectrum based on input conditions without neutron transport calculations. The present method was applied to a PWR UO fuel pin cell model. The results show the nuclide inventory can be calculated with a prediction accuracy within a few percent. In addition, it is found that the calculation error is dominated by the regression models, which implies the further improvement of the regression models leads to improving the accuracy.
fuel pin cell model. The results show the nuclide inventory can be calculated with a prediction accuracy within a few percent. In addition, it is found that the calculation error is dominated by the regression models, which implies the further improvement of the regression models leads to improving the accuracy.
Sugiyama, Hitoshi*; Kato, Kenichi*; Sekine, Naoko*; Sekine, Yurina; Watanabe, Tomoaki*; Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Chemical Physics Letters, 856, p.141655_1 - 141655_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical)To investigate the effects of polymer hydrophilicity on structures of water in hydrogels, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction measurements were performed. The results show that the amount of intermediate water in polyacrylamide (PAA) hydrogel is about 12% smaller than that in poly-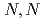 -dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogel. Furthermore, it was found that the bound water in PAA hydrogel primarily exists around the surface of the polymer bundles, whereas that in PDMAA hydrogel acts as a crosslinker factor for dehydration and water absorption in hydrogels.
-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogel. Furthermore, it was found that the bound water in PAA hydrogel primarily exists around the surface of the polymer bundles, whereas that in PDMAA hydrogel acts as a crosslinker factor for dehydration and water absorption in hydrogels.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Suyama, Kenya; Tada, Kenichi; Ferrer, R. M.*; Hykes, J.*; Wemple, C. A.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(11), p.2230 - 2239, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library for the advanced lattice physics code CASMO5 has been prepared based on JENDL-5. In JENDL-5, many essential nuclides for conventional LWR analysis have also been modified based on state-of-the-art evaluations. The new JENDL-5-based CASMO5 library was prepared by replacing as much of the nuclear data of the current CASMO5 ENDF/B-VII.1-based library as possible with JENDL-5. This study verified and validated the new library. Verifications were performed based on the OECD/NEA burnup credit criticality safety benchmark phase III-C, and the calculated k and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
Rochman, D.*; Minato, Futoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; 52 of others*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.9_1 - 9_83, 2024/10
Suyama, Kenya; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Shimada, Kazuya; Fujita, Tatsuya; Ueki, Taro; Nguyen, H.
JAEA-Conf 2024-001, 40 Pages, 2024/07
The 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) was held from October 1 to October 6, 2023, at the Sendai International Center (Aobayama, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi-prefecture 980-0856, Japan), organized by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and co-organized by the Reactor Physics Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) and the Nuclear Energy Agency of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). 224 presentations passed peer review and 273 technical session registrations, bringing the total number of registered participants to 289, including accompanying persons. Technical tours were also conducted to i) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO holdings and Interim Storage Facility Information Center, ii) Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA (STACY Renewable Reactor and FCA), iii) NanoTerasu of Tohoku University (synchrotron radiation facility) and Onagawa Nuclear Power Station of Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc. This report summarizes the conference and compiles the papers that were presented and agreed to be published in the Proceedings.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.958 - 966, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The total fission energy released in a criticality accident involving fissile solution boiling tends to be high because the relatively high fission power continues during boiling. Simulating fission power change correctly during boiling seems essential to estimate the total fission energy. Fission power during boiling changes depending on fissile concentration and volume as the solution evaporates. In this study, we investigated the effect of concentration and volume change on estimated total fission energy for a long time of boiling. We introduced a model calculating the evaporation of fissile solution into the modified quasi-steady-state method to simulate power change during boiling. Three CRAC experiments and the Idaho Chemical Processing Plant (ICPP) criticality accident in 1959 were analyzed. As a result, the calculated energy considering concentration and volume change during boiling reproduced the measured energy well.
Watanabe, Tomoaki
Robutsuri No Kenkyu (Internet), (77), 3 Pages, 2024/06
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Ueki, Taro; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/04
Solomon, a Monte Carlo solver being developed by JAEA, can calculate criticality in multi-material randomized systems for criticality evaluation of fuel debris. This study investigates the applicability of Solomon to critical mass calculations of fuel debris. We performed critical mass calculations of fuel randomization systems using Solomon. The fuel randomization systems, where burned fuels with different burnups and water are randomly distributed, were modeled by the incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF) model or voxel geometry in Solomon. Critical mass calculations of simple homogeneous and heterogeneous systems were also performed, and the critical sizes were compared to fuel randomization systems. The results showed that the fuel randomization causes significant variations in the critical mass. The obtained critical sizes were distributed close to a normal distribution, which made it reasonable to estimate the uncertainty of critical mass as the standard deviation. The critical sizes with uncertainty obtained by Solomon were smaller than those of a simple heterogeneous system. This indicates Solomon would be useful for estimating or evaluating a reasonable safety margin in criticality safety evaluations of fuel debris.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1386 - 1396, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burnup calculations for estimating the nuclide composition of the spent fuel are highly dependent on nuclear data. Many nuclides in the latest version of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 were modified from JENDL-4.0 and the modification affects the burnup calculations. This study confirmed the validity of JENDL-5 in the burnup calculations. The PIE data of Takahama-3 was used for the validation. The effect of modifications of the parameters, e.g., cross sections and fission yields, from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the nuclide compositions was quantitatively investigated. The calculation results showed that JENDL-5 has a similar performance to JENDL-4.0. The calculation results also revealed that the modifications of the cross sections of actinide nuclides, fission yields, and thermal scattering low data of hydrogen in H O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s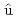 ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, was released in December 2021. In JENDL-5, nuclear reaction cross sections for Gd-155 and Gd-157 were modified in addition to many heavy nuclides such as U-235. Fission yields and decay data, which are essential to characterize burnup fuels, were completely revised. This study investigated the effects of the nuclear data revisions from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the neutronic characteristics of burnup fuels to validate JENDL-5. Burnup calculations of the 9x9 STEP-3 BWR fuel assembly based on the OECD/NEA Phase III-C benchmark were performed using JENDL-4.0 and JENDL-5. As a result, the k for JENDL-5 was smaller than that of JENDL-4.0 throughout the burnup, with a large difference of about 600 pcm at 12 GWd/t, around the peak of the k
for JENDL-5 was smaller than that of JENDL-4.0 throughout the burnup, with a large difference of about 600 pcm at 12 GWd/t, around the peak of the k . Above 20 GWd/t, the difference in k
. Above 20 GWd/t, the difference in k increases with increasing burnup value, reaching nearly 600 pcm at 50 GWd/t. In addition, this study investigates which nuclear data contribute significantly to the difference in k
increases with increasing burnup value, reaching nearly 600 pcm at 50 GWd/t. In addition, this study investigates which nuclear data contribute significantly to the difference in k by performing burnup calculations with replacing nuclear data of individual nuclides from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5.
by performing burnup calculations with replacing nuclear data of individual nuclides from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 20th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM22) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/06
Since the 1990s, the importance of the handbook has changed significantly, as the computational power has improved and continuous energy Monte Carlo codes have become widely used, which enables highly accurate criticality calculations, when necessary, irrespective of the complexity of the system. Because the value of performing a large number of calculations in advance and summarizing the data has decreased, since the second edition was published publicly in 1999, there has been no revision of criticality safety handbooks in Japan for nearly a quarter of a century. In Japan, where the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident occurred in 2011, it became necessary to deal with criticality safety issues in the transport and storage of the fuel debris which contains complex constituent elements, and the summary the criticality safety management for such material is an urgent issue. In the area of burnup credit, the transport and storage of fuel assemblies with low achieved burnups due to the consequences of accidents might be the problem. In addition, nuclear data, which is the input for the continuous energy Monte Carlo code, has been improved several times, now JENDL-5 is available from the end of 2021, and its incorporation becomes a need in the field. This report provides an overview of the latest criticality safety research in Japan and the planned revision of the Criticality Safety Handbook, which could be applied to the transport and storage sectors.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Gunji, Satoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Umeda, Miki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/09
Criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station would be a risk-informed control to mitigate consequences of criticality events, instead of a deterministic control to prevent such events. The Nuclear Regulation Authority of Japan has administrated a research and development program to tackle this challenge since 2014. The Nuclear Safety Research Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, commissioned by the authority, is conducting activities such as computations of criticality characteristics of the fuel debris, development of a criticality analysis code, preparation of criticality experiments, and development of a criticality risk analysis method.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Okubo, Kiyoshi*; Araki, Shohei; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/09
Watanabe, Tamaki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Hanamura, Kotoku*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Kamoshida, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Toshihiko*; Koyama, Ryo*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1105 - 1108, 2019/07
Upgrades for the RIKEN heavy-ion linac (RILAC) involving a new superconducting linac (SRILAC) are currently underway at the RIKEN radioactive isotope beam factory (RIBF). It is crucially important to develop nondestructive beam measurement diagnostics. We have developed a beam energy position monitor (BEPM) system which can measure not only the beam position but also the beam energy simultaneously by measuring the time of flight of the beam. We fabricated 11 BEPMs and completed the position calibration to obtain the sensitivity and offset for each BEPMs. The position accuracy has been achieved to be less than  0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
Watanabe, Takashi*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ozawa, Osamu*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Akahori, Tomoyuki*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 2019 International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW 2019) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/06
Radiation hard image sensors have been developed past decades among the world. Almost papers discussed properties before and after radiation but images during radiation were not described yet. We have developed a new type of rad-hard pixel and integrated to 1.3M-pixel, 18-bit digital CMOS image sensor. Pixel area consists of several types of variation and the sensor has been analyzed during gamma ray radiation higher than 1 kGy/h up to 200 kGy. As the result, one type of pixel showed almost zero dark current increase at whole period.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Watanabe, Takashi*; Tanaka, Shigeo*; Ozawa, Osamu*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Ueno, Shunji*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2017) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2018/11
no abstracts in English