Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
Hata, Kuniki; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Watanabe, Yutaka*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(4), p.126 - 130, 2023/04
Gamma-radiolysis experiments with gas-liquid coexistent samples were carried out to investigate effects of gas-phase radiolysis on corrosive environment for materials in solutions under irradiation. After gamma-ray irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, nitrate ion, nitrite ion were detected in the liquid phase. The production yields of nitrate ion and nitrite ion increased with increasing gas-phase volume and oxygen concentration. This result indicated that chemical reactions including oxygen and nitrogen in the gas phase were required for the production of nitrate ion and nitrite ion. To magnify the effects of gas-phase radiolysis in the gas-liquid coexistent samples, absorption dose rate in the liquid phase was reduced by one-hundredth using lead shield. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the pH in the shielded liquid phase were similar to those in the irradiated pure water, which did not contact with gas phase. This result indicated that the effects of nitrate ion and nitrite ion dissolved in the liquid phase on water radiolysis were not important in the current experimental system, in which the effects of gas-phase radiolysis were increased by 100-times.
Nagata, Shuhei*; Ogawa, Yusuke*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.21 - 22, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
 Cs
CsUchiyama, Yusuke*; Tokunaga, Natsuki*; Azuma, Kohei*; Kamidaira, Yuki; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Yamada, Masatoshi*; Tateda, Yutaka*; Ishimaru, Takashi*; Ito, Yukari*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 816, p.151573_1 - 151573_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.48(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 -decay spectroscopy of
-decay spectroscopy of  Ta
TaMukai, Momo*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Jeong, S. C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Brunet, M.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kondev, F. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(3), p.034331_1 - 034331_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear) Re
ReWatanabe, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Andreyev, A. N.; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Kondev, F. G.*; Lane, G. J.*; Litvinov, Yu. A.*; Liu, J. J.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 814, p.136088_1 - 136088_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:63.10(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Watanabe, Tamaki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Hanamura, Kotoku*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Kamoshida, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Toshihiko*; Koyama, Ryo*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1105 - 1108, 2019/07
Upgrades for the RIKEN heavy-ion linac (RILAC) involving a new superconducting linac (SRILAC) are currently underway at the RIKEN radioactive isotope beam factory (RIBF). It is crucially important to develop nondestructive beam measurement diagnostics. We have developed a beam energy position monitor (BEPM) system which can measure not only the beam position but also the beam energy simultaneously by measuring the time of flight of the beam. We fabricated 11 BEPMs and completed the position calibration to obtain the sensitivity and offset for each BEPMs. The position accuracy has been achieved to be less than  0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
Watanabe, Tamaki*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; Fujimaki, Masaki*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Koyama, Ryo*; Toyama, Takeshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.49 - 54, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
 = 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph
= 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrographIto, Yuta*; Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Arai, Fumiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 120(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:92.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Masses of  Es,
Es,  Fm and the transfermium nuclei
Fm and the transfermium nuclei  Md, and
Md, and  No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed
No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed 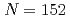 neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of
neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of 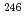 Es and
Es and 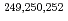 Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of
Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of 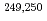 Md as anchor points for
Md as anchor points for  decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to
decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to  Bh and
Bh and  Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter
Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter 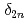 derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed
derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed  neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; MacCormick, M.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 407, p.160 - 165, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)Various isotopes of Ac, Ra, Fr, and Rn were produced by fusion-evaporation reactions using a  Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
 Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrier
B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrierDas, S. K.*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Jeong, S. C.*; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Makoto; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(5), p.055805_1 - 055805_4, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.67(Physics, Nuclear) Li
LiIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Jung, H. S.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 376, p.379 - 381, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)Koshimizu, Masanori*; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Yanagida, Takayuki*; Fujimoto, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Asai, Keisuke*
Journal of Luminescence, 169(Part B), p.678 - 681, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:78.01(Optics)We analyzed the effects of linear energy transfer (LET) on the scintillation properties of a Li glass scintillator, GS20. The scintillation time profiles were measured by using pulsed ion beams having different LETs. The rise in the scintillation time profiles was faster for higher LET, whereas the decay part was not significantly different for largely different LETs. The LET effects in the rise was ascribed to the effects of excited states interaction during the energy transfer process from the host glass to the luminescent centers, Ce ions. Supposing that the light yield decreases with LET, the fast rise at high LET was explained in terms of the competition between the energy transfer and the quenching due to the excited states interaction.
ions. Supposing that the light yield decreases with LET, the fast rise at high LET was explained in terms of the competition between the energy transfer and the quenching due to the excited states interaction.
 Si investigated by decay spectroscopy of
Si investigated by decay spectroscopy of  Al
AlSteiger, K.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Li, Z.*; Gernh user, R.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Chen, R.*; Faestermann, T.*; Hinke, C.*; Kr
user, R.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Chen, R.*; Faestermann, T.*; Hinke, C.*; Kr cken, R.*; Nishimura, Mitsuki*; et al.
cken, R.*; Nishimura, Mitsuki*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 51(9), p.117_1 - 117_9, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.96(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Kukita, Yutaka; Watanabe, Norio
JAEA-Technology 2014-036, 38 Pages, 2014/11
NAIIC emphasized the possibility of seismically-induced reactor coolant leakage and implied its causal connection to the accident, in particular at the Fukushima Daiichi Unit 1. This view of NAIIC has been addressed by the Accident Investigation Committee established by the Cabinet decision, NISA, and the Secretariat of NRA. Based on seismic response analyses, plant records and simulations, their reports uniformly note that seismically-induced leakage is unlikely to be a causal factor for the core damage though the possibility of insignificantly small leakage cannot be ruled out completely. Also refuted are some of the arguments made by NAIIC as grounds for suspecting safety-significant leakage. The present report re-examines the leak detection capability through the review of plant instruments and post-accident simulations, and adds some arguments in order to resolve the issue raised by NAIIC without technical ambiguity as far as possible. As well, the plant design uniqueness of Unit 1, the history of facility changes, the operating procedures and the actual operations are looked into to raise issues for further investigation.
 Li tracer
Li tracerIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(11), p.110303_1 - 110303_4, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.06(Physics, Applied)Yasuda, Mari; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-011, 59 Pages, 2014/08
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data about the radioactivity concentrations which accumulated by the analysis.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Onizawa, Kunio; Watanabe, Tadashi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2014/07
For structural integrity assessment on reactor pressure vessel (RPV) of pressurized water reactor during the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, temperature of coolant water and heat transfer coefficient between coolant water and RPV are dominant factors. These values can be determined on the basis of thermal-hydraulics (TH) analysis simulating PTS events. Using these values, structural integrity assessment of RPV is performed by thermal-structural analysis, e.g. loading that affects the crack initiation and propagation is evaluated. In this study, we performed the TH and thermal-structural analyses using three-dimensional model of cold-leg, downcomer and RPV to assess loading conditions during the PTS more accurate. We obtained the loading histories at the reactor core region of RPV where a crack is postulated in the structural integrity assessment. Through the comparison between analysis results and current evaluation method, conservatism of current method will be discussed.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Wada, Michiharu*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sakamoto, Chika*; Takatsuka, Takaaki*; Furukawa, Takeshi*; Iimura, Hideki; Ito, Yuta*; Kubo, Toshiyuki*; Matsuo, Yukari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 295, p.1 - 10, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English