Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
被引用回数:0TbMn Sn
Sn is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn
is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn Sn
Sn using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb
using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb 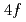 orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn
orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn Sn
Sn , despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
, despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
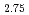 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:78.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the local or itinerant extreme, magnetic excitations can be described by the Heisenberg model which treats electron spins as localized moments, or by the itinerant-electron model where the exchange interaction between electrons leads to unequal numbers of electrons with up and down spins. However, the nature of the magnetic excitations has been elusive when both local moments and itinerant electrons are present in the intermediate range. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we provide direct spectroscopic evidence on the coexistence of and interplay between local moments and itinerant electrons in a van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe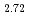 GeTe
GeTe , which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe
, which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe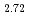 GeTe
GeTe . Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy
. Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy  electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light
electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light  electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dimerized magnets forming alternating Heisenberg chains exhibit quantum coherence and entanglement and thus can find potential applications in quantum information and computation. However, magnetic systems typically undergo thermal decoherence at finite temperatures. Here, we show inelastic neutron scattering results on an alternating antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic chain compound Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline
that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline  -axis. The excitation gap is of
-axis. The excitation gap is of  18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na
18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO , but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
, but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
 TeO
TeO
Bao, S.*; Cai, Z.*; Si, W.*; Wang, W.*; Wang, X.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(21), p.214419_1 - 214419_8, 2020/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:74.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform thermodynamic and inelastic neutron scattering (INS) measurements to study the lattice dynamics (phonons) of a cubic collinear antiferromagnet Cu TeO
TeO which hosts topological spin excitations (magnons). While the specific heat and thermal conductivity results show that the thermal transport is dominated by phonons, the deviation of the thermal conductivity from a pure phononic model indicates that there is a strong coupling between magnons and phonons. In the INS measurements, we find a mode in the excitation spectra at 4.5 K, which exhibits a slight downward dispersion around the Brillouin zone center. This mode disappears above the N
which hosts topological spin excitations (magnons). While the specific heat and thermal conductivity results show that the thermal transport is dominated by phonons, the deviation of the thermal conductivity from a pure phononic model indicates that there is a strong coupling between magnons and phonons. In the INS measurements, we find a mode in the excitation spectra at 4.5 K, which exhibits a slight downward dispersion around the Brillouin zone center. This mode disappears above the N el temperature and thus cannot be a phonon. Furthermore, the dispersion is distinct from that of a magnon. Instead, it can be explained by the magnon-polaron mode, collective excitations resulting from the hybridization between magnons and phonons. We consider the suppression of the thermal conductivity and emergence of the magnon-polaron mode to be evidence for magnon-phonon coupling in Cu
el temperature and thus cannot be a phonon. Furthermore, the dispersion is distinct from that of a magnon. Instead, it can be explained by the magnon-polaron mode, collective excitations resulting from the hybridization between magnons and phonons. We consider the suppression of the thermal conductivity and emergence of the magnon-polaron mode to be evidence for magnon-phonon coupling in Cu TeO
TeO .
.
 Mn
Mn Sb
Sb
Cai, Z.*; Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Wang, J.*; Ran, K.*; Li, S.*; 蒲沢 和也*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(13), p.134408_1 - 134408_10, 2020/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:38.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ディラック物質は量子現象と共にキャリアの役割を探索するのに良い系で、磁気ワイル半金属のSr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb はワイルフェルミオンとマグノンの関係を研究する良い舞台である。本研究では、Sr
はワイルフェルミオンとマグノンの関係を研究する良い舞台である。本研究では、Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb の単結晶の中性子非弾性散乱実験を行い、磁性Mn層の分散は約76meVまで広がり、層間の分散は6meVの狭いバンド幅を持つことを見出した。また、これらの実験結果はハイゼンベルグ・スピンハミルトニアンを用いた線形スピン波理論によって再現可能である。本研究では、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンが共存しているにもかかわらず、Sr
の単結晶の中性子非弾性散乱実験を行い、磁性Mn層の分散は約76meVまで広がり、層間の分散は6meVの狭いバンド幅を持つことを見出した。また、これらの実験結果はハイゼンベルグ・スピンハミルトニアンを用いた線形スピン波理論によって再現可能である。本研究では、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンが共存しているにもかかわらず、Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb 中のワイルフェルミオンが磁気ダイナミクスに影響を与えているという明確な証拠は得られなかった。これは、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンがSb層とMn層に別々に存在し、この擬二次元性による層間結合の弱さに起因するもの考えられる。
中のワイルフェルミオンが磁気ダイナミクスに影響を与えているという明確な証拠は得られなかった。これは、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンがSb層とMn層に別々に存在し、この擬二次元性による層間結合の弱さに起因するもの考えられる。
 Bi
Bi Se
Se
Wang, J.*; Ran, K.*; Li, S.*; Ma, Z.*; Bao, S.*; Cai, Z.*; Zhang, Y.*; 中島 健次; 河村 聖子; 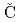 erm
erm k, P.*; et al.
k, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2802_1 - 2802_6, 2019/06
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:80.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Superconductivity mediated by phonons is typically conventional, exhibiting a momentum-independent  -wave pairing function, due to the isotropic interactions between electrons and phonons along different crystalline directions. Here, by performing inelastic neutron scattering measurements on a superconducting single crystal of Sr
-wave pairing function, due to the isotropic interactions between electrons and phonons along different crystalline directions. Here, by performing inelastic neutron scattering measurements on a superconducting single crystal of Sr Bi
Bi Se
Se , a prime candidate for realizing topological superconductivity by doping the topo-logical insulator Bi
, a prime candidate for realizing topological superconductivity by doping the topo-logical insulator Bi Se
Se , we found that there exist singular phonons, with the linewidths of the acoustic phonons increasing substantially at long wavelengths, but only for those along the [001] direction. This observation indicates a large and singular electron-phonon coupling at small momenta, which we propose to give rise to the exotic
, we found that there exist singular phonons, with the linewidths of the acoustic phonons increasing substantially at long wavelengths, but only for those along the [001] direction. This observation indicates a large and singular electron-phonon coupling at small momenta, which we propose to give rise to the exotic  -wave nematic superconducting pairing in the MxBi
-wave nematic superconducting pairing in the MxBi Se
Se (M = Cu, Sr, Nb) superconductor family. Therefore, we show that these superconductors may be the first examples where electron-phonon interaction can induce more exotic superconducting pairing than the
(M = Cu, Sr, Nb) superconductor family. Therefore, we show that these superconductors may be the first examples where electron-phonon interaction can induce more exotic superconducting pairing than the  -wave.
-wave.
 Rb
RbHe, C.*; Shen, S.*; Wen, S.*; Zhu, L.*; Wu, X.*; Li, G.*; Zhao, Y.*; Yan, Y.*; Bai, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(3), p.034320_1 - 034320_10, 2013/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:43.66(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states of  Rb are studied via the fusion-evaporation reactions
Rb are studied via the fusion-evaporation reactions  Cu+
Cu+ F,
F, 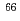 Zn+
Zn+ O, and
O, and  Zn+
Zn+ O with the beam energies of 75 MeV, 76 MeV, and 80 MeV, respectively. Twenty-three states with twenty-eight
O with the beam energies of 75 MeV, 76 MeV, and 80 MeV, respectively. Twenty-three states with twenty-eight  transitions are added to the previously proposed level scheme, where the second negative-parity band is significantly pushed up to spins of 22
transitions are added to the previously proposed level scheme, where the second negative-parity band is significantly pushed up to spins of 22 and 15
and 15 and two sidebands are built on the known first negative-parity band. Two successive band crossings with frequencies 0.51 MeV and 0.61 MeV in the
and two sidebands are built on the known first negative-parity band. Two successive band crossings with frequencies 0.51 MeV and 0.61 MeV in the  = 0 branch as well as another one in the
= 0 branch as well as another one in the  =1 branch of the second negative-parity band are observed. Signature inversions occur in the positive-parity and first negative-parity bands at the spins of 11
=1 branch of the second negative-parity band are observed. Signature inversions occur in the positive-parity and first negative-parity bands at the spins of 11 and 16
and 16 , respectively. The signature splitting is seen obviously in the second negative-parity band, but the signature inversion is not observed. It is also found that the structure of the two negative-parity bands is similar to that of its isotone
, respectively. The signature splitting is seen obviously in the second negative-parity band, but the signature inversion is not observed. It is also found that the structure of the two negative-parity bands is similar to that of its isotone 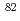 Y. Signature inversion in the positive-parity yrast band with configuration
Y. Signature inversion in the positive-parity yrast band with configuration  g9/2
g9/2 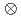
 g9/2 in this nucleus is discussed using the projected shell model.
g9/2 in this nucleus is discussed using the projected shell model.
Chen, L.-M.; 中島 一久; Hong, W.*; Hua, J. F.*; 亀島 敬; 小瀧 秀行; 杉山 精博*; Wen, X.*; Wu, Y.*; Tang, C.*; et al.
Chinese Optics Letters, 5(S1), p.S133 - S135, 2007/05
Experiments for the laser guiding studies has been carried out with the 30 fs, 100 TW laser pulse interaction with the long slab and discharged capillary of underdense plasma. Formation of extremely long plasma channel with its length 10 times above the Rayleigh length is observed when the laser pulse power is much higher than the critical power for relativistic self-focusing. The long self-guiding channel formation is accompanied by the quasi-monoenergetic electron acceleration with a low transverse emittance and high electric current (10 nC/shot). In order to continuously elongate plasma channel, a 4 cm-scale discharged capillary was used. We successfully demonstrated laser-plasma acceleration of high-quality electron beams up to nearly GeV. Our results exactly verified the prediction of laser-wakefield acceleration through a cm-scale plasma channel in the blowout bubble regime.
Chen, L.-M.; 小瀧 秀行; 中島 一久*; Koga, J. K.; Bulanov, S. V.; 田島 俊樹; Gu, Y. Q.*; Peng, H. S.*; Wang, X. X.*; Wen, T. S.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.040703_1 - 040703_4, 2007/04
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:75.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)レーザーの自己導波の調査のため、長いunderdenseのプラズマと100TWレーザーパルスの相互作用実験を行い、レイリー長の約20倍の10mmという非常に長いプラズマチャネルを観測した。レーザーパルスがチャネル中で曲がること、及び電子キャビティ形成が実験的に初めて観測された。
 X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffractionWang, W. H.*; Wen, P.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Pan, M. X.*; 岡田 卓; 内海 渉
Applied Physics Letters, 83(25), p.5202 - 5204, 2003/12
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:61.65(Physics, Applied)8.3GPaまでの高圧下において温度を種々に変化させ、その際のZr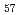 Nb
Nb Cu
Cu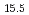 Ni
Ni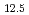 Al
Al バルク金属ガラスの核発生並びに結晶成長プロセスをその場エックス線回折により調べた。結晶化プロセスは熱処理条件によって、さまざまな振る舞いをし、高圧下での昇温は液体の過冷却状態を安定化させる方向に作用することが明らかとなった。実験により明らかになった核発生並びに結晶成長の圧力依存性を核発生理論により議論する。
バルク金属ガラスの核発生並びに結晶成長プロセスをその場エックス線回折により調べた。結晶化プロセスは熱処理条件によって、さまざまな振る舞いをし、高圧下での昇温は液体の過冷却状態を安定化させる方向に作用することが明らかとなった。実験により明らかになった核発生並びに結晶成長の圧力依存性を核発生理論により議論する。
Wang, W. H.*; 岡田 卓; Wen, P.*; Wang, X. L.*; Pan, M. X.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; 内海 渉
Physical Review B, 68(18), p.184105_1 - 184105_6, 2003/11
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:79.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)バルク金属ガラスの代表であるZrTiCuNiBe(vit4)の核発生並びに結晶成長における圧力効果を10GPa領域まで放射光を用いたその場エックス線実験により観測した。その結果、圧力は、過冷却液体状態を安定化させる方向に働くとともに、結晶化温度を上昇させる効果があることが明らかになった。
亀島 敬; 小瀧 秀行; 神門 正城; 大東 出; 川瀬 啓悟; 福田 祐仁; Chen, L. M.*; 本間 隆之; 近藤 修司; Esirkepov, T. Z.; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザープラズマ電子加速は非常に高い電場を持っているが、加速空間が非常に短いという問題点を持っているため、その電子ビームの加速エネルギーは100MeV程度に制限されていた。近年、このレーザープラズマ電子加速が抱える問題点をキャピラリー放電管を用いることで大幅に解決がなされた。プラズマは密度が高いほど屈折率が低くなる特徴を利用して放電管の中でプラズマ密度を中心で薄く、その外周を高く分布させれば光ファイバーと同じ原理でレーザーは放電管内のプラズマ中を集光伝搬しながら相互作用する。ゆえに、加速空間を大幅に拡張することができる。この実験を2006年に中国工程物理研究院とKEK、及び原子力機構で共同実験を行い、キャピラリ放電管を用いて4.4Jのレーザーパルスの集光伝搬及び0.56GeVの電子ビームの生成に成功した。加えて、JAEAにて同様の実験を2007年に行い、1Jのレーザーパルスの集光伝搬及び電子ビームの発生に成功した。
King, G.*; Bartz, M.*; Bossin, L.*; Wen, X.*; 塚本 すみ子*; Herman, F.*; 小形 学; 末岡 茂
no journal, ,
Electron spin resonance dating of quartz minerals offers a significant advantage over luminescence dating because of its later signal saturation. We are seeking to exploit this to build upon earlier studies in the development of a thermochronometry system capable of resolving rock cooling rates throughout the Quaternary. In order to determine a rock cooling history, it is necessary to constrain both signal accumulation and signal thermal loss robustly within the laboratory. We have collated a series of geological samples including rocks from boreholes that have known isothermal histories to investigate the potential of this technique. Our objective is to use the latter rocks to confirm the validity of our laboratory measurements and data-fitting/numerical models. Specifically, we have investigated known-thermal history samples from the MIZ1 borehole (Japan) and the KTB borehole (Germany). Preliminary data reveal that the ESR dose response and thermal decay of different quartz samples is highly variable.
 ne valley incision?
ne valley incision?King, G. E.*; Wen, X.*; Bartz, M.*; Anderson, L.*; Bossin, L.*; 塚本 すみ子*; Li, Y.*; Herman, F.*; 小形 学; 末岡 茂
no journal, ,
To determine a rock cooling history using ESR thermochronometry, signal accumulation and signal thermal loss must be robustly determined within the laboratory. We have collected a series of geological samples including rocks from boreholes that have known isothermal histories to investigate the potential of this technique. Our objective is to use the latter rocks to confirm the validity of our laboratory measurements and data-fitting/numerical models. Specifically, we have investigated known-thermal history samples from the MIZ1 borehole (Japan) and the KTB borehole (Germany) as well as samples from Sion in the Western European Alps. Preliminary data reveal that the ESR dose response and thermal decay of different quartz samples is highly variable. Whereas the Al-centre of some samples exhibits linear dose response to laboratory irradiation up to 15 kGy, the Al-centre of other samples exhibits exponential, or double exponential growth and saturates at doses of 3-4 kGy. The Ti-centre of most samples is well described by a single saturating exponential function, however samples from the MIZ1 borehole exhibit pronounced sub-linearity in the low-dose response region. Furthermore, whereas for some samples the Al-centre is less thermally stable than the Ti-centre, for other samples the inverse is observed. These observations suggest that a uniform measurement protocol and data-fitting approach may not be appropriate for quartz ESR data. Inversion of two KTB samples yielded temperatures within uncertainty of borehole temperature, however results for the MIZ1 borehole are more variable and can only recover temperature at best within c.a. 10%. Investigations into the cause of the poor results for the MIZ1 borehole are ongoing (i.e. measurement protocol, data-fitting/numerical model) and will be discussed. Preliminary data from Sion are promising and reveal consistent cooling rates.
King, G. E.*; Wen, X.*; Bartz, M.*; Bossin, L.*; 塚本 すみ子*; Li, Y.*; Herman, F.*; 小形 学; 末岡 茂
no journal, ,
Whereas the luminescence thermochronometry system is limited to areas experiencing very rapid rock cooling (exhumation) of 10s of mm/yr, our data indicate that ESR thermochronometry can resolve rates of  1 mm/yr over Quaternary timescales. To determine a rock cooling history using ESR thermochronometry, signal accumulation and signal thermal loss must be robustly determined within the laboratory. We have collected a series of borehole samples with known isothermal histories to investigate the potential of this technique. Our objective is to use the latter rocks to confirm the validity of our laboratory measurements and data-fitting/numerical models by using the ESR-thermochronometry method to recover their known in-situ temperatures. Specifically, we have investigated known-thermal history samples from the MIZ1 borehole (Japan) and the KTB borehole (Germany). Preliminary data reveal that the ESR dose response and thermal decay of different quartz samples is highly variable. Whereas the Al-centre of some samples exhibits linear dose response to laboratory irradiation up to 15 kGy, the Al-centre of other samples exhibits exponential, or double-exponential growth and saturates at doses of 3-4 kGy. The Ti-centre of most samples is well described by a single saturating exponential function, however samples from the MIZ1 borehole exhibit pronounced sublinearity in the low-dose response region. Furthermore, whereas for some samples the Al-centre is less thermally stable than the Ti-centre, for other samples the inverse is observed. These observations suggest that a uniform measurement protocol and data-fitting approach may not be appropriate for quartz ESR data.
1 mm/yr over Quaternary timescales. To determine a rock cooling history using ESR thermochronometry, signal accumulation and signal thermal loss must be robustly determined within the laboratory. We have collected a series of borehole samples with known isothermal histories to investigate the potential of this technique. Our objective is to use the latter rocks to confirm the validity of our laboratory measurements and data-fitting/numerical models by using the ESR-thermochronometry method to recover their known in-situ temperatures. Specifically, we have investigated known-thermal history samples from the MIZ1 borehole (Japan) and the KTB borehole (Germany). Preliminary data reveal that the ESR dose response and thermal decay of different quartz samples is highly variable. Whereas the Al-centre of some samples exhibits linear dose response to laboratory irradiation up to 15 kGy, the Al-centre of other samples exhibits exponential, or double-exponential growth and saturates at doses of 3-4 kGy. The Ti-centre of most samples is well described by a single saturating exponential function, however samples from the MIZ1 borehole exhibit pronounced sublinearity in the low-dose response region. Furthermore, whereas for some samples the Al-centre is less thermally stable than the Ti-centre, for other samples the inverse is observed. These observations suggest that a uniform measurement protocol and data-fitting approach may not be appropriate for quartz ESR data.