Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wiesen, S.*; Brezinsek, S.*; J rvinen, A.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Huber, A.*; Parail, V.*; Corrigan, G.*; 林 伸彦; JET-EFDA Contributors*
rvinen, A.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Huber, A.*; Parail, V.*; Corrigan, G.*; 林 伸彦; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 53(12), p.124039_1 - 124039_12, 2011/12
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:67.34(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A type-I ELMy H-mode discharge in JET has been analysed numerically using JINTRAC integrated code in order to obtain a self-consistent description of edge and core plasma. The time-dependent model consists of a self-consistent coupling of 1D core code JETTO/SANCO and 2D multi-fluid scrape-off-layer (SOL) code EDGE2D-EIRENE. The inter- and intra-ELM transport model has been adapted to match the experimental pre- and post ELM plasma profiles measured in JET and at the same time the observed ELM dynamics in terms of ELM frequency, ELM energy loss, ELM wetted area and heat flows towards target plates. It is found that the scaling for the free streaming approximations of ELM filamentary parallel SOL transport for the maximum heat flux, energy density and heat flux factor can be reproduced with the JINTRAC model. Results for the JET all-carbon reference case are then utilised to predict a type-I ELMy H-mode for ITER-like wall (ILW) assuming a full-tungsten divertor and beryllium main-chamber wall in the model. It is found that a moderate amount of seeded neon impurity (or other impurity species) is necessary to match a similar level of radiation when carbon is absent in the system. Finally, results of the ILW setup are used to estimate the total amount of tungsten particles eroded per ELM from the target plates and a rough estimate of the core radiative fraction due to W accumulation is given.
林 伸彦; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; 相羽 信行; 滝塚 知典; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P. T.*; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103030_1 - 103030_8, 2011/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:27.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two integrated core / scrape-off-layer / divertor transport codes TOPICS-IB and JINTRAC with links to MHD stability codes have been coupled with models of pellet injection to clarify effects of pellet on the behavior of edge localized modes (ELMs). Both codes predicted the following two triggering mechanisms. The energy absorption by the pellet and its further displacement due to the 

 drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent
drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent 

 drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
林 伸彦; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; 相羽 信行; 滝塚 知典; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P.*; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Two integrated core / scrape-off-layer (SOL) / divertor transport codes TOPICS-IB and JINTRAC with links to MHD stability codes have been coupled with models of pellet injection to clarify effects of pellet on the behavior of edge localized modes (ELMs). The energy absorption by pellet and its further displacement due to E B drift as well as transport enhancement by the pellet were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes the radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E
B drift as well as transport enhancement by the pellet were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes the radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E B drift. On the other hand, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of an increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
B drift. On the other hand, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of an increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
林 伸彦; 滝塚 知典; 相羽 信行; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095015_1 - 095015_8, 2009/09
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:50.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energy loss due to an edge localized mode (ELM) crash and its cycle have been studied by using an integrated core transport code with a stability code for peeling-ballooning modes and a transport model of scrape-off-layer (SOL) and divertor plasmas. The integrated code reproduces a series of ELMs in which the ELM energy loss increases with decreasing collisionality and the ELM frequency increases linearly with the input power, as seen in experiments of type-I ELMs. A transport model with the neoclassical transport in the pedestal connected to the SOL parallel transport reproduces a lowered inter-ELM transport in the case of low collisionality so that the ELM loss power is enhanced as observed in experiments. The inter-ELM energy confinement time evaluated from simulation results agrees with the JT-60U scaling. The steep pressure gradient in the core just beyond the pedestal top, desirable for improved H-mode plasmas with the 
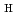 factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient in the core beyond the pedestal top broadens eigenfunction profiles of unstable modes and possibly induces subsequent instabilities. In the subsequent instabilities, when a large energy is transported to the vicinity of the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient in the core beyond the pedestal top broadens eigenfunction profiles of unstable modes and possibly induces subsequent instabilities. In the subsequent instabilities, when a large energy is transported to the vicinity of the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
林 伸彦; 滝塚 知典; 相羽 信行; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The energy loss due to an edge localized mode (ELM) crash and its cycle have been studied by using an integrated transport code with a stability code for peeling-ballooning modes and a transport model of scrape-off-layer (SOL) and divertor plasmas. The integrated code reproduces a series of ELMs with the following characteristics. The ELM energy loss increases with decreasing the collisionality and the ELM frequency increases linearly with the input power, as the same as experiments of type-I ELMs. A transport model with the pedestal neoclassical transport connected to the SOL parallel transport reproduces the inter-ELM transport, which decreases in the low collisionality so that the ELM loss power is enhanced as observed in experiments. The inter-ELM energy confinement time agrees with the scaling based on the JT-60U data. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top, required for improved H-mode plasmas with the 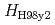 factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top broadens the region of the ELM enhanced transport and induces subsequent instabilities. When the large energy is transported near to the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top broadens the region of the ELM enhanced transport and induces subsequent instabilities. When the large energy is transported near to the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
林 伸彦; 滝塚 知典; 相羽 信行; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
no journal, ,
ピーリング・バルーニングモード安定性解析コードとSOL-ダイバータモデルを統合した輸送コードを用いて、ELMによるエネルギー損失とそのサイクルを調べた。統合コードは、実験で観測されたType-I ELMと同様に、衝突周波数の減少とともにELMエネルギー損失が増大し、加熱パワーに比例してELM周波数が増加する一連のELMを再現した。SOLの磁力線方向輸送と結合したペデスタルの新古典輸送モデルが、実験で観測されたように低衝突周波数で減少しELMによる損失パワーを増大させるELM間輸送を再現した。ELM間のエネルギー閉じ込め時間は、JT-60Uデータに基づいた比例則と一致した。HHファクターが1以上の改善Hモードプラズマに必要なペデスタル内側圧力勾配の急峻化が、ELMエネルギー損失を増大させELM周波数を減少させることを明らかにした。この時、ELM損失パワーは一定である。ペデスタル内側圧力急峻化は、ELMで増倍される輸送の範囲を広くし、2次的な不安定性を誘起するからである。不安定性によりセパラトリックス近くまで大きなエネルギーが輸送された場合、そこで続いて起きる不安定性が損失を増倍させる。
林 伸彦; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; 相羽 信行; 滝塚 知典; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P. T.*; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久
no journal, ,
Two integrated core / scrape-off-layer / divertor transport codes TOPICS-IB and JINTRAC with links to MHD stability codes have been coupled with models of pellet injection to clarify effects of pellet on the behavior of edge localized modes (ELMs). Both codes predicted the following two triggering mechanisms. The energy absorption by the pellet and its further displacement due to the E B drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E
B drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E B drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
B drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.