Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
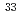 Mg sheds new light on the
Mg sheds new light on the  =20 island of inversion
=20 island of inversionKanungo, R.*; Nociforo, C.*; Prochazka, A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aumann, T.*; Boutin, D.*; Cortina-Gil, D.*; Davids, B.*; Diakaki, M.*; Farinon, F.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 685(4-5), p.253 - 257, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:86.47(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Rf
RfQian, J.*; Heinz, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Peterson, D.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Ahmad, I.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(6), p.064319_1 - 064319_13, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:85.45(Physics, Nuclear) -,
-,  -, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for
-, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for  Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160
Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160  s has been discovered in
s has been discovered in  Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high-
Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high- isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in
isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in 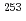 No, the
No, the  -decay daughter of
-decay daughter of  Rf, have been assigned on the basis of
Rf, have been assigned on the basis of  -decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2
-decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2 [620] states in
[620] states in  =151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at
=151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at  =152 increases with the atomic number.
=152 increases with the atomic number.
 O as a new doubly magic nucleus
O as a new doubly magic nucleusKanungo, R.*; Nociforo, C.*; Prochazka, A.*; Aumann, T.*; Boutin, D.*; Cortina-Gil, D.*; Davids, B.*; Diakaki, M.*; Farinon, F.*; Geissel, H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 102(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_4, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:96.80(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
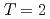 mirrors
mirrors  Ca and
Ca and  S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplines
S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplinesDoornenbal, P.*; Reiter, P.*; Grawe, H.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Al-Khatib, A.*; Banu, A.*; Beck, T.*; Becker, F.*; Bednarczyk, P.*; Benzoni, G.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 647(4), p.237 - 242, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.72(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The first excited state of  Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured
Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured 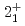 energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus
energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus  S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the
S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the 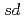 valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the
valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the 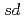 shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
 Sr in environmental samples at the attogram-level by accelerator mass spectrometry
Sr in environmental samples at the attogram-level by accelerator mass spectrometryMartschini, M.*; Honda, Maki; Merchel, S.*; Winkler, S.*; Golser, R.*
no journal, ,
The quantitative analysis of  Sr is cumbersome and time-consuming because it is a pure
Sr is cumbersome and time-consuming because it is a pure  -ray emitter. The detection limit of
-ray emitter. The detection limit of  Sr by conventional accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) methods is comparable to the typical detection limit of 3 mBq for
Sr by conventional accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) methods is comparable to the typical detection limit of 3 mBq for  -ray detection methods, mainly due to the interference of the isobaric
-ray detection methods, mainly due to the interference of the isobaric  Zr. The worldwide unique Ion Laser Interaction Mass Spectrometry (ILIAMS), performed at the University of Vienna, effectively removes
Zr. The worldwide unique Ion Laser Interaction Mass Spectrometry (ILIAMS), performed at the University of Vienna, effectively removes  Zr with a laser and reaction gases. Therefore, the detection limits of
Zr with a laser and reaction gases. Therefore, the detection limits of  Sr is superior (
Sr is superior ( 0.1 mBq) to conventional AMS systems not equipped with such an ion-laser interaction isobaric removal system. In this study,
0.1 mBq) to conventional AMS systems not equipped with such an ion-laser interaction isobaric removal system. In this study,  Sr analysis in coral samples etc., an environmental sample under extreme conditions (e.g. low concentrations of
Sr analysis in coral samples etc., an environmental sample under extreme conditions (e.g. low concentrations of  Bq/g and limited sample volumes of grams), was tried. To lower the detection limit
Bq/g and limited sample volumes of grams), was tried. To lower the detection limit  0.1 mBq, Sr was purified (Sr carrier) from old age coral with almost no
0.1 mBq, Sr was purified (Sr carrier) from old age coral with almost no  Sr contamination from atmospheric nuclear tests, chemical separation of environmental samples were conducted, and
Sr contamination from atmospheric nuclear tests, chemical separation of environmental samples were conducted, and  Sr was measured by AMS. The results showed that the detection limit of
Sr was measured by AMS. The results showed that the detection limit of  Sr achieved in the analysis was
Sr achieved in the analysis was  0.03 mBq (
0.03 mBq ( Sr/Sr
Sr/Sr  5
5 10
10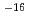 , 1/100 of the
, 1/100 of the  -ray detection methods). The detection limit achieved in this study corresponds to 2 ag of
-ray detection methods). The detection limit achieved in this study corresponds to 2 ag of  Sr in 1 mg of Sr target. The latest results of highly sensitive
Sr in 1 mg of Sr target. The latest results of highly sensitive  Sr analysis in small amounts of general environmental samples (coral, seawater, etc.) are mainly presented.
Sr analysis in small amounts of general environmental samples (coral, seawater, etc.) are mainly presented.