Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Shobu, Takahisa; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)Tsurumi, Miwa*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Ikkatai, Yuko*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; Shinoda, Taro*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Tsuji, Naoki*; Diniz, G.*; Kataoka, Jun*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 50(13), p.e2023GL103612_1 - e2023GL103612_9, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:68.56(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary) ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered van der Waals halides are particularly sensitive to external pressure, suggesting a feasible route to pinpoint their structure with extraordinary behavior. However, a very sensitive pressure response usually lead to a detrimental phase transition and/or lattice distortion, making the approach of materials manipulation in a continuous manner remain challenging. Here, the extremely weak interlayer coupling and high tunability of layered RhI crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:83.88(Mechanics)Yoshida, Shuhei*; Fu, R.*; Gong, W.; Ikeuchi, Takuto*; Bai, Y.*; Feng, Z.*; Wu, G.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Hansen, N.*; Huang, X.*; et al.
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 1249, p.012027_1 - 012027_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:80.61(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.79(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na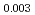 Sn
Sn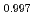 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
Wu, P.*; Zhang, B.*; Peng, K. L.*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kofu, Maiko; Lee, S. H.*; Kumigashira, Hiroshi*; Hu, C. S.*; Qi, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering, we have studied how electronic structures and lattice dynamics evolve with temperature in Na-doped SnSe.
Li, Z.*; He, T.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Miao, S.*; Wu, A.*; Liu, L.*; Wu, G.*; Chen, P.*
ACS Catalysis, 7(10), p.6762 - 6769, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:185 Percentile:96.61(Chemistry, Physical) Rb
RbHe, C.*; Shen, S.*; Wen, S.*; Zhu, L.*; Wu, X.*; Li, G.*; Zhao, Y.*; Yan, Y.*; Bai, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(3), p.034320_1 - 034320_10, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.96(Physics, Nuclear) at molybdenum 3p
at molybdenum 3p , 3p
, 3p , and oxygen 1s edges
, and oxygen 1s edgesWu, G.*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(2), p.406 - 410, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.90(Instruments & Instrumentation)We investigated photon-stimulated ion desorption (PSID) from solid MoO following Mo 3p
following Mo 3p , 3p
, 3p and O 1s inner-shell excitations. The photon-energy dependences of O+ ion desorption yields were measured using quadrupole mass spectrometry. Near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectra were measured by the total electron yield method and were compared with the desorption yield curves. Relatively high desorption yields were observed in O 1s
and O 1s inner-shell excitations. The photon-energy dependences of O+ ion desorption yields were measured using quadrupole mass spectrometry. Near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectra were measured by the total electron yield method and were compared with the desorption yield curves. Relatively high desorption yields were observed in O 1s  e
e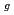 resonance compared with that in O 1s
resonance compared with that in O 1s  t
t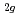 resonance, while no enhanced yields were observed in either the Mo 3p
resonance, while no enhanced yields were observed in either the Mo 3p or Mo 3p
or Mo 3p edge. The enhancement effect in the O 1s
edge. The enhancement effect in the O 1s  e
e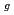 resonance was attributed to fast bond breakage induced by the antibonding nature of the
resonance was attributed to fast bond breakage induced by the antibonding nature of the  -like e
-like e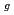 orbital. On the other hand, the non-enhancement following the Mo 3p
orbital. On the other hand, the non-enhancement following the Mo 3p and 3p
and 3p edges was ascribed to the de-excitation of the excited electrons via very fast Coster-Kronig transitions, which can take place only following Mo 3p
edges was ascribed to the de-excitation of the excited electrons via very fast Coster-Kronig transitions, which can take place only following Mo 3p and 3p
and 3p excitations.
excitations.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Wu, G.*; Kitajima, Yoshinori*
Surface Science, 593(1-3), p.310 - 317, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.12(Chemistry, Physical)Using a newly developed rotatable time-of-flight mass spectrometer(R-TOF-MS) and polarized synchrotron radiation, orientation effect on fragmentation and desorption pathways occurring at the top-most layers of molecular solids have been investigated. Reported will be polarization-angle dependencies of TOF mass spectra, high-resolution electron- and ion-NEXAFS in condensed chlorobenzene.
Baba, Yuji; Wu, G.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 19(4), p.1485 - 1489, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.89(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Wu, G.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 114-116, p.841 - 848, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:86.49(Spectroscopy)no abstracts in English
 excitation
excitationWu, G.; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 8(Part.2), p.469 - 471, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Wu, G.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Physical Review B, 62(10), p.R6053 - R6056, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:95.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Takahiro; Dodbiba, G.*; Wu, I.*; Fujita, Toyohisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Xu, P. G.; Morooka, Satoshi; Shibayama, Yuki; Wu, S. C.*; Fang, W.*; Shobu, Takahisa
no journal, ,
Yamashita, Takayuki; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morooka, Satoshi; Wu, G.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Shobu, Takahisa; Wu, S. C.*
no journal, ,
Xu, P. G.; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Morooka, Satoshi; Takamura, Masato*; Wu, S.*; Otake, Yoshie*; Shobu, Takahisa
no journal, ,