Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Xu, Z.*; Dai, G.*; Li, Y.*; Yin, Z.*; Rong, Y.*; Tian, L.*; Liu, P.*; Wang, H.*; Xing, L.*; Wei, Y.*; et al.
npj Quantum Materials (Internet), 5(1), p.11_1 - 11_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:40.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lin, P.*; Xu, C.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Chen, H.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Xing, W.*; Sun, L.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Yamazaki, Hideo*; Kokubu, Yoko; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 678, p.409 - 418, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.32(Environmental Sciences)Nagasaki sediments containing bomb-derived Pu provided a unique opportunity to explore the long term geochemical behavior of Pu. Through a combination of selective extractions and molecular characterization via electrospray ionization Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, we determined that 55  3% of the
3% of the 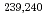 Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these
Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these 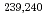 Pu (31
Pu (31  2% on average), and less than 20% of the
2% on average), and less than 20% of the 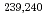 Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
 Pt
PtZhou, X. H.*; Xing, Y. B.*; Liu, M. L.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Guo, Y. X.*; Ma, L.*; Lei, X. G.*; Guo, W. T.*; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; et al.
Physical Review C, 75(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_17, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:73.87(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in  Pt has been studied experimentally by in-beam
Pt has been studied experimentally by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy. The previously known bands based on the
-ray spectroscopy. The previously known bands based on the ![$$nu i_{13/2}, nu 7/2^{-}[503] $$](/search/images/EROG23JANFPXWMJTF2ZH0LBALRXHKIBXF2ZF24ZNPVNTKMBTLUQCI.gif) and
and 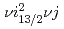 configurations have been extended to high-spin states, and new rotational bands associated with the
configurations have been extended to high-spin states, and new rotational bands associated with the ![$$nu 3/2^{-}[512]$$](/search/images/EROG23JAGMXTEXT1FV4VWNJRGJOSI.gif) and
and ![$$nu 1/2^{-}[521]$$](/search/images/EROG23JAGEXTEXT1FV4VWNJSGFOSI.gif) Nilsson orbits have been identified. The total Routhian surface calculations indicate that the transitional nucleus
Nilsson orbits have been identified. The total Routhian surface calculations indicate that the transitional nucleus  Pt is very soft with respect to
Pt is very soft with respect to  and
and  deformations. The band properties have been compared with the systematics observed in neiboring nuclei and have been interpreted within the framework of the cranked shell model.
deformations. The band properties have been compared with the systematics observed in neiboring nuclei and have been interpreted within the framework of the cranked shell model.
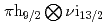 oblate band in
oblate band in  Tl
TlZhou, X. H.*; Ma, L.*; Xing, Y. B.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Guo, Y. X.*; Lei, X. G.*; Xie, C. Y.*; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 28(3), p.271 - 275, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.09(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states in  Tl have been studied experimentally by in-beam
Tl have been studied experimentally by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy. A rotational band built on the
-ray spectroscopy. A rotational band built on the 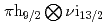 configuration with oblate deformation has been established for
configuration with oblate deformation has been established for  Tl. Based on the structure systematics of the oblate
Tl. Based on the structure systematics of the oblate 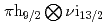 bands in heavier odd-odd Tl nuclei, we have tentatively proposed spin values for the new band in
bands in heavier odd-odd Tl nuclei, we have tentatively proposed spin values for the new band in  Tl. The new oblate band shows low-spin signature inversion, and it can be interpreted qualitatively by the two-quasiparticle plus rotor model including a
Tl. The new oblate band shows low-spin signature inversion, and it can be interpreted qualitatively by the two-quasiparticle plus rotor model including a  -dependent
-dependent  -
- residual interaction.
residual interaction.