Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.04(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe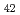 Mn
Mn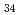 Al
Al Ni
Ni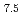 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
徐 平光; Zhang, S.-Y.*; Harjo, S.; Vogel, S. C.*; 友田 陽*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.7_1 - 7_13, 2024/01
Comprehensive information about the  microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.
microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.  isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90
isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90 TD
TD  ND (transverse direction
ND (transverse direction  normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 11 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:0High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
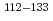 Sb
SbLechner, S.*; 宮城 宇志*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Bissell, M. L.*; Blaum, K.*; Cheal, B.*; Devlin, C. S.*; Garcia Ruiz, R. F.*; Ginges, J. S. M.*; Heylen, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 847, p.138278_1 - 138278_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)不安定核を含むアンチモン同位体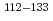 Sbの磁気モーメントと電気的四重極モーメントをレーザー分光を用いて測定した。現象論的な相互作用と有効演算子を用いた殻模型計算によって測定値をよく再現することができた。第一原理に基づいたVS-IMSRG法による殻模型計算では、磁気モーメントは現象論的な有効演算子を用いればよく実験値を再現するものの、電気的四重極モーメントについては有効電荷を用いても現象論的な相互作用を用いた計算ほどには実験値を再現することができなかった。
Sbの磁気モーメントと電気的四重極モーメントをレーザー分光を用いて測定した。現象論的な相互作用と有効演算子を用いた殻模型計算によって測定値をよく再現することができた。第一原理に基づいたVS-IMSRG法による殻模型計算では、磁気モーメントは現象論的な有効演算子を用いればよく実験値を再現するものの、電気的四重極モーメントについては有効電荷を用いても現象論的な相互作用を用いた計算ほどには実験値を再現することができなかった。
Wang, Y. W.*; Wang, H. H.*; Su, Y. H.; 徐 平光; 篠原 武尚
Materials Science & Engineering A, 887, p.145768_1 - 145768_13, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.26(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A unique impact fracture behavior is found in a high-Mn austenitic steel (24Mn-4Cr-0.4C-0.3Cu) in this work. The steel exhibits concurrent twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) effect and the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. By analyzing the load-deflection curves recorded during Charpy impact testing, the resistance to crack initiation and propagation is quantified from the absorbed energy. The high-Mn steel demonstrates good resistance to crack initiation at 273 K and 77 K. However, as the temperature decreases from 273 K to 77 K, there is an accelerated transition from stable crack growth to unstable crack growth during impact, resulting in the deterioration of resistance to crack propagation. The plastic deformation of the impact-tested samples, especially in the region close to the crack-path profile was quantitatively analyzed using neutron Bragg-edge transmission (BET) imaging. The deformation zones, divided by using the width of the 200 Bragg edge, exhibit good agreement with the impact absorbed energy characteristics obtained from dynamic load-deflection curves. Moreover, the unstable growth transition point was roughly determined on the impact-tested sample. Then, the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique is employed to examine the deformation microstructure along the crack-path in the impact-tested samples. The results revealed the dual roles of TRIP effect in impact toughness of the high-Mn steel. On one hand, the TRIP effect plays a positive role in improving resistance to crack initiation and propagation. On the other hand, the excessive accumulation of brittle  /
/ '-martensite caused by the enhanced TRIP effect at 77 K leads to quasi-cleavage fracture, thereby playing a negative role. Finally, we discussed the prominent toughening mechanisms associated with the TWIP and TRIP effects, which greatly impact the impact fracture behavior.
'-martensite caused by the enhanced TRIP effect at 77 K leads to quasi-cleavage fracture, thereby playing a negative role. Finally, we discussed the prominent toughening mechanisms associated with the TWIP and TRIP effects, which greatly impact the impact fracture behavior.
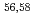 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; 角田 佑介*; 大塚 孝治*; 茶園 亮樹*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)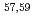 Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、
Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、 Caと
Caと Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。
Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。 Caでは1456(12)keVの
Caでは1456(12)keVの 線遷移が、
線遷移が、 Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に
Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に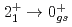 と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、
と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、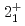 準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である
準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である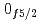 と
と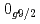 軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは
軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを
Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:85.05(Mechanics)Considering the complex service environments that high-speed railway axles are subjected to, the fatigue crack growth (FCG) behavior of a structurally gradient axle steel with different pre-crack depths both in air and corrosive medium was investigated at a frequency of 5 Hz. The results indicated that in the high 
 region, FCG rate was dramatically accelerated by corrosion, but the gap narrows as
region, FCG rate was dramatically accelerated by corrosion, but the gap narrows as 
 decreased. The accelerated corrosion FCG rate was a comprehensive result of the acceleration effect of the anodic dissolution, hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity and the retardation effect of corrosion-induced crack-tip blunting. Despite the fact that the corrosion resistance gradually decreased as the pre-crack depth increased, the FCG rate in the corrosive medium gradually decreased. This was because fatigue loading played a more important role than corrosion in accelerating the corrosion FCG rate.
decreased. The accelerated corrosion FCG rate was a comprehensive result of the acceleration effect of the anodic dissolution, hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity and the retardation effect of corrosion-induced crack-tip blunting. Despite the fact that the corrosion resistance gradually decreased as the pre-crack depth increased, the FCG rate in the corrosive medium gradually decreased. This was because fatigue loading played a more important role than corrosion in accelerating the corrosion FCG rate.
Zhang, H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Ao, N.*; Zhang, J. W.*; Li, H.*; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.
International Journal of Fatigue, 166, p.107296_1 - 107296_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:61.91(Engineering, Mechanical)Abnormal damages in railway axles can lead to a significant hazard to running safety and reliability. To this end, a surface treatment was selected to effectively inhibit fatigue crack initiation and growth. In this study, a single edge notch bending fatigue test campaign with artificial notches was conducted to elucidate the fatigue crack non-propagation behavior in railway S38C axles subjected to an induction hardening process. The fatigue cracking behavior in the gradient structure was revealed by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, and fractography. The microhardness distribution was measured using a Vickers tester. The obtained results show that the microhardness of the strengthening layer is nearly triple that of the matrix. Owing to the gradient microstructures and hardness, as well as compressive residual stress, the fatigue long crack propagates faster once it passes through the hardened zone (approximately 2.0 mm in the radial depth). Thereafter, local retarding (including deflection, branching, and blunting) of the long crack occurs because of the relatively coarse ferrite and pearlite in the transition region and matrix. Totally, this fatigue cracking resistance is reasonably believed to be due to the gradient microstructure and residual stress. These findings help to tailor a suitable detection strategy for maximum defects or cracks in railway axles.
Liss, K.-D.*; 徐 平光; 城 鮎美*; Zhang, S. Y.*; 行武 栄太郎*; 菖蒲 敬久; 秋田 貢一*
Advanced Engineering Materials, 9 Pages, 2023/00
In polycrystals, grains with certain orientations grow at high temperatures at the expense of grains with other unfavorable orientations. Grain growth involves a variety of situations and mechanisms that make experimental study, modeling, and understanding extremely complex. Normal grain growth occurs in a self-similar manner, with curved grain boundaries serving as the driving force and a parabolic growth law that scales up the grain size by the square root of time. More complex growth forms include boundary pinning of precipitates and other boundaries, topological transitions that alter driving forces, grain coalescence and anomalous grain growth, but these are considered "erratic" and their initiation is an open question in modern research, without a simple experimental approach on how they should be studied. Here, we show that grain rotation upon coalescence is spontaneously activated between one grain and a favorable neighbor, through the necessary diffusive mass transport at further boundaries of the same grain leading to their activation and a competitive "erratic" reorientation in a zigzag way, while other grains in the matrix remain stable. After two grains have eventually coalesced, their surrounding boundaries are still activated leading to further rotation and growth, filling the missing puzzle stone in thermodynamic theory between normal and abnormal growth, the latter stating that abnormal growth only takes place when the size of the growing grain is already large. Prerequisites and postulates of abnormal grain growth are based on advantageous texture, grain boundary mobility, enhanced diffusion kinetics and coalescence, which can be well explained by our observations. Moreover, our observations have been enabled through a novel experimental approach using the white-beam X-ray Laue diffraction method in bulk transmission mode on a polycrystalline.
Liu, X. J.*; 徐 平光; 城 鮎美*; Zhang, S. Y.*; 菖蒲 敬久; 行武 栄太郎*; 秋田 貢一*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:41.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ time/temperature-resolved synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction is applied to study heat-mediated structural changes and phase transformations in rolled sheets of AZ91 and AZ31 magnesium alloys. Azimuthal diffraction intensities along the Debye-Scherrer rings (AT-plots) are used to obtain information on grain recovery and recrystallization temperatures as well as temperature-assisted grain rotations. The azimuthally integrated diffraction intensities, plotted as functions of the scattering vector (QT-plots), provide vital data on the temperature-dependent lattice parameters of the Mg/Al matrix and intermetallic precipitates, as well as on the evolution of the precipitates' volume fraction. It was found that in AZ31, the main precipitates are of the AlMn type, which is rather stable in the investigated temperature range (up to 773 K). In contrast, in AZ91, the major intermetallic precipitates, Al Mg
Mg , undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
, undergo complete dissolution above 600 K. It is caused by the enhanced diffusion of Al into the Mg/Al matrix, which according to the Al-Mg phase diagram, can adopt more Al at elevated temperatures. This diffusion is revealed by the proportional diminishing of the matrix lattice parameter (chemical strain), allowing us to quantify the Al content in the matrix. Fast temperature-dependent manipulation with intermetallic content in the Mg/Al alloy can, in principle, be used for controlling its mechanical properties.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; 西尾 勝久; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; 牧井 宏之; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; 廣瀬 健太郎; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The long-lived  Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction
Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe on
Fe on  Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of
Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of  Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1
Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1  -ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the
-ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5
Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5 3.5 mb at
3.5 mb at 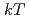 = 30 keV and 13.4
= 30 keV and 13.4 1.7 mb at
1.7 mb at 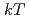 = 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of
= 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of  Fe from the
Fe from the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe rate are at most 25
Fe rate are at most 25 . We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of
. We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of  Fe.
Fe.

Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; 中島 健次; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:61.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report thermodynamic and neutron diffraction measurements on the magnetic ordering properties of the honeycomb lattice magnet YbCl . We find YbCl
. We find YbCl exhibits a N
exhibits a N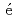 el type long-range magnetic order at the wavevector (0, 0, 0) below T
el type long-range magnetic order at the wavevector (0, 0, 0) below T = 600 mK. This magnetic order is associated with a small sharp peak in heat capacity and most magnetic entropy release occurs above the magnetic ordering temperature. The magnetic moment lies in-plane, parallel to the monoclinic a-axis, whose magnitude m
= 600 mK. This magnetic order is associated with a small sharp peak in heat capacity and most magnetic entropy release occurs above the magnetic ordering temperature. The magnetic moment lies in-plane, parallel to the monoclinic a-axis, whose magnitude m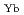 = 0.86(3)
= 0.86(3) 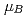 is considerably smaller than the expected fully ordered moment of 2.24
is considerably smaller than the expected fully ordered moment of 2.24 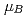 for the doublet crystal-field ground state. The magnetic ordering moment gradually increases with increasing magnetic field perpendicular to the ab-plane, reaching a maximum value of 1.6(2)
for the doublet crystal-field ground state. The magnetic ordering moment gradually increases with increasing magnetic field perpendicular to the ab-plane, reaching a maximum value of 1.6(2) 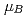 at 4 T, before it is completely suppressed above
at 4 T, before it is completely suppressed above  9 T. These results indicate the presence of strong quantum fluctuations in YbCl
9 T. These results indicate the presence of strong quantum fluctuations in YbCl .
.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; 久保田 悠樹*; Corsi, A.*; 吉田 数貴; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; 木村 真明*; Michel, N.*; 緒方 一介*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)ボロミアン核であり中性子ハロー構造が期待される Bに対する(
Bに対する( ,
,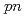 )反応実験を行った。断面積の運動量分布を分析することで、
)反応実験を行った。断面積の運動量分布を分析することで、 と
と 軌道の分光学的因子を決定した。驚くべきことに、
軌道の分光学的因子を決定した。驚くべきことに、 の分光学的因子は9(2)%と小さいことが明らかになった。この結果は、連続状態を含むdeformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov理論によってよく説明された。本研究の結果によると、現在知られているハロー構造を持つとされる原子核の中で
の分光学的因子は9(2)%と小さいことが明らかになった。この結果は、連続状態を含むdeformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov理論によってよく説明された。本研究の結果によると、現在知られているハロー構造を持つとされる原子核の中で Bは
Bは および
および 軌道の成分が最も小さく、
軌道の成分が最も小さく、 または
または 軌道成分が支配的であることが必ずしもハロー構造の前提条件ではない可能性を示唆している。
軌道成分が支配的であることが必ずしもハロー構造の前提条件ではない可能性を示唆している。
 Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:69.78(Physics, Nuclear)中性子過剰核である Coに対する(
Coに対する( )ノックアウト反応が理化学研究所RIBFで測定された。
)ノックアウト反応が理化学研究所RIBFで測定された。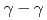 coincidenceの方法で準位構造が決定され、測定された包括的断面積および排他的断面積から暫定的ではあるがスピン・パリティが決定された。殻模型計算との比較により、
coincidenceの方法で準位構造が決定され、測定された包括的断面積および排他的断面積から暫定的ではあるがスピン・パリティが決定された。殻模型計算との比較により、 Coの低励起状態には球形核と変形核が共存することが示唆された。
Coの低励起状態には球形核と変形核が共存することが示唆された。
Xu, Z.*; Dai, G.*; Li, Y.*; Yin, Z.*; Rong, Y.*; Tian, L.*; Liu, P.*; Wang, H.*; Xing, L.*; Wei, Y.*; et al.
npj Quantum Materials (Internet), 5(1), p.11_1 - 11_7, 2020/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:40.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We use neutron scattering to study Vanadium (hole)-doped LiFe V
V As. In the undoped state, LiFeAs exhibits superconductivity at
As. In the undoped state, LiFeAs exhibits superconductivity at 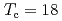 K and transverse incommensurate spin excitations similar to electron overdoped iron pnictides. Upon Vanadium doping to form LiFe
K and transverse incommensurate spin excitations similar to electron overdoped iron pnictides. Upon Vanadium doping to form LiFe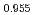 V
V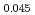 , the transverse incommensurate spin excitations in LiFeAs transform into longitudinally elongated ones in a similar fashion to that of potassium (hole)-doped Ba
, the transverse incommensurate spin excitations in LiFeAs transform into longitudinally elongated ones in a similar fashion to that of potassium (hole)-doped Ba K
K Fe
Fe As
As but with dramatically enhanced magnetic scattering and elimination of superconductivity. This is different from the suppression of the overall magnetic excitations in hole-doped BaFe
but with dramatically enhanced magnetic scattering and elimination of superconductivity. This is different from the suppression of the overall magnetic excitations in hole-doped BaFe As
As and the enhancement of superconductivity near optimal hole doping. These results are consistent with density function theory plus dynamic mean field theory calculations, suggesting that Vanadium doping in LiFeAs may induce an enlarged effective magnetic moment
and the enhancement of superconductivity near optimal hole doping. These results are consistent with density function theory plus dynamic mean field theory calculations, suggesting that Vanadium doping in LiFeAs may induce an enlarged effective magnetic moment 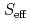 with a spin crossover ground state arising from the inter-orbital scattering of itinerant electrons.
with a spin crossover ground state arising from the inter-orbital scattering of itinerant electrons.
河野 俊彦*; Cho, Y. S.*; Dimitriou, P.*; Filipescu, D.*; 岩本 信之; Plujko, V.*; Tao, X.*; 宇都宮 弘章*; Varlamov, V.*; Xu, R.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 163, p.109 - 162, 2020/01
被引用回数:80 パーセンタイル:99.62(Physics, Nuclear)We report our coordinated efforts to address these data needs such as radiation shielding design and radiation transport analyses, and present the results of the new evaluations of more than 200 nuclides included in the new updated IAEA Photonuclear Data Library, where the photon energy goes up to 200 MeV. We discuss the new assessment method and make recommendations to the user community in cases where the experimental data are discrepant and the assessments disagree. In addition, in the absence of experimental data, we present model predictions for photon-induced reaction cross section on nuclides of potential interest to medical radioisotope production.
 decay of
decay of 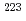 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Fine structure in the  decay of
decay of 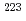 U was observed in the fusion-evaporation reaction
U was observed in the fusion-evaporation reaction  Re(
Re( Ar,p3n) by using fast digital pulse processing technique. Two
Ar,p3n) by using fast digital pulse processing technique. Two  -decay branches of
-decay branches of 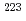 U feeding the ground state and 244 keV excited state of
U feeding the ground state and 244 keV excited state of 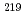 Th were identified by establishing the decay chain
Th were identified by establishing the decay chain 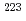 U
U
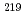 Th
Th
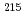 Ra
Ra
 Rn. The
Rn. The  -particle energy for the ground-state to ground-state transition of
-particle energy for the ground-state to ground-state transition of 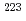 U was determined to be 8993(17) keV, 213 keV higher than the previous value, the half-life was updated to be 62
U was determined to be 8993(17) keV, 213 keV higher than the previous value, the half-life was updated to be 62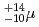 s. Evolution of nuclear structure for
s. Evolution of nuclear structure for  =131 even-
=131 even- isotones from Po to U was discussed in the frameworks of nuclear mass and reduced
isotones from Po to U was discussed in the frameworks of nuclear mass and reduced  -decay width, a weakening octupole deformation in the ground state of
-decay width, a weakening octupole deformation in the ground state of  U relative to its lighter isotones
U relative to its lighter isotones  Ra and
Ra and  Th was suggested.
Th was suggested.
 Pd
Pd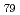 and
and  Pd
Pd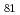 ; Competing proton and neutron excitations in neutron-rich palladium nuclides towards the
; Competing proton and neutron excitations in neutron-rich palladium nuclides towards the 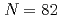 shell closure
shell closure渡邉 寛*; Wang, H. K.*; Lorusso, G.*; 西村 俊二*; Xu, Z. Y.*; 炭竃 聡之*; Orlandi, R.; 他47名*
Physics Letters B, 792, p.263 - 268, 2019/05
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:53.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The isotopes  Pd and
Pd and  Pd, respectively with 79 and 81 neutrons, are key isotopes to understand the evolution of the N=82 shell closure below
Pd, respectively with 79 and 81 neutrons, are key isotopes to understand the evolution of the N=82 shell closure below  Pd. These nuclei were studied at RIBF (RIKEN). New isomeric states with half-lives of 144(4) ns and 39(6)
Pd. These nuclei were studied at RIBF (RIKEN). New isomeric states with half-lives of 144(4) ns and 39(6)  s were assigned spins and parities of (23/2
s were assigned spins and parities of (23/2 ) and (19/2
) and (19/2 ) in
) in  Pd and
Pd and  Pd, respectively. The assignment was carried out based on the results of the
Pd, respectively. The assignment was carried out based on the results of the  -ray intensity balance analysis and the measured transition strengths with the aid of a shell-model calculation. The isomoer in
-ray intensity balance analysis and the measured transition strengths with the aid of a shell-model calculation. The isomoer in  Pd was ascribed predominantly to three neutron-hole excitations in the N=50-82 shell. The 19/2
Pd was ascribed predominantly to three neutron-hole excitations in the N=50-82 shell. The 19/2 state in
state in  Pd is expected to involve the coupling of proton and neutron configurations. The new data will provide important benchmarks for a better understanding of
Pd is expected to involve the coupling of proton and neutron configurations. The new data will provide important benchmarks for a better understanding of  -process nucleosynthesis.
-process nucleosynthesis.
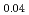 (Sb
(Sb Bi
Bi )
)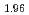 Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Xu, T.*; Li, G.*; Qiao, S.*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 角田 一樹*; 石田 行章*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(14), p.144413_1 - 144413_7, 2019/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:56.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the microscopic origin of ferromagnetism coupled with topological insulators in V-doped (Sb,Bi) Te
Te employing X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and angle-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopies, combined with first-principles calculations. We found an magnetic moment at the Te site anti-parallel to that of the V and Sb sites, which plays a key role in the ferromagnetic order. We ascribe it to the hybridization between Te 5
employing X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and angle-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopies, combined with first-principles calculations. We found an magnetic moment at the Te site anti-parallel to that of the V and Sb sites, which plays a key role in the ferromagnetic order. We ascribe it to the hybridization between Te 5 and V 3
and V 3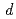 majority spin states at the Fermi energy, consistent with the Zener-type
majority spin states at the Fermi energy, consistent with the Zener-type  -
-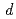 exchange interaction scenario. The substitution of Bi for Sb suppresses the bulk ferromagnetism by introducing extra electron carriers in the majority spin channel of the Te
exchange interaction scenario. The substitution of Bi for Sb suppresses the bulk ferromagnetism by introducing extra electron carriers in the majority spin channel of the Te  states that compensates the antiparallel magnetic moment on the Te site. Our findings reveal important clues to designing magnetic topological insulators with higher Curie temperature that work under ambient conditions.
states that compensates the antiparallel magnetic moment on the Te site. Our findings reveal important clues to designing magnetic topological insulators with higher Curie temperature that work under ambient conditions.
 Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,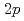 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
, 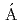 *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)( ,
,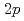 )反応による
)反応による Niの核構造の探索実験を行った。Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, Sieja相互作用を用いた殻模型計算では実験結果を説明しうる陽子空孔状態が得られており、理論的な断面積計算は実験値とよい一致を与えた。実験で得られたすべての状態を理論的に一意に決定することはできなかったが、過去の実験結果と同様にNi同位体でのZ = 28の大きなshell gapを示す結果が得られた。
Niの核構造の探索実験を行った。Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, Sieja相互作用を用いた殻模型計算では実験結果を説明しうる陽子空孔状態が得られており、理論的な断面積計算は実験値とよい一致を与えた。実験で得られたすべての状態を理論的に一意に決定することはできなかったが、過去の実験結果と同様にNi同位体でのZ = 28の大きなshell gapを示す結果が得られた。